
Germanium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It is lustrous, hard-brittle, grayish-white and similar in appearance to silicon. It is a metalloid in the carbon group that is chemically similar to its group neighbors silicon and tin. Like silicon, germanium naturally reacts and forms complexes with oxygen in nature.
A metalloid is a type of chemical element which has a preponderance of properties in between, or that are a mixture of, those of metals and nonmetals. There is no standard definition of a metalloid and no complete agreement on which elements are metalloids. Despite the lack of specificity, the term remains in use in the literature of chemistry.
Sodium oxide is a chemical compound with the formula Na2O. It is used in ceramics and glasses. It is a white solid but the compound is rarely encountered. Instead "sodium oxide" is used to describe components of various materials such as glasses and fertilizers which contain oxides that include sodium and other elements.

The correct name of the chemical element with the symbol 'Ge' is GermanIUM, not 'Germane'. Thus, while the compound GeH4 may be called 'Germane', the "synthesis" of the element, involved the isolation ("synthesis") of GermanIUM {the 'IUM' being capitlaized for emphais, not to indicate actual speling}. Similarly, the 'Ocurrence', 'Reactions', 'Uses in semi-conductor industry', and 'Safety' all ought refer to the element using the correct spelling.

Bismuth germanium oxide or bismuth germanate is an inorganic chemical compound of bismuth, germanium and oxygen. Most commonly the term refers to the compound with chemical formula Bi4Ge3O12 (BGO), with the cubic evlitine crystal structure, used as a scintillator. (The term may also refer to a different compound with formula Bi12GeO20, an electro-optical material with sillenite structure, and Bi2Ge3O9.)
Germanium dioxide, also called germanium(IV) oxide, germania, and salt of germanium, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula GeO2. It is the main commercial source of germanium. It also forms as a passivation layer on pure germanium in contact with atmospheric oxygen.
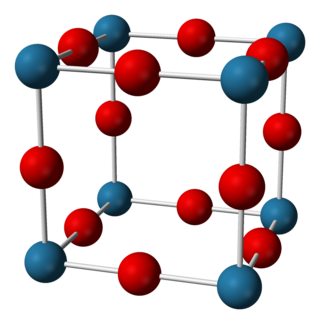
Sodium nitride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula Na3N. In contrast to lithium nitride and some other nitrides, sodium nitride is an extremely unstable alkali metal nitride. It can be generated by combining atomic beams of sodium and nitrogen deposited onto a low-temperature sapphire substrate. It readily decomposes into its elements:

Germanium disulfide or Germanium(IV) sulfide is the inorganic compound with the formula GeS2. It is a white high-melting crystalline solid. The compound is a 3-dimensional polymer, in contrast to silicon disulfide, which is a one-dimensional polymer. The Ge-S distance is 2.19 Å.

Germanium dichloride is a chemical compound of germanium and chlorine with the formula GeCl2. It is a yellow solid. Germanium dichloride is an example of a compound featuring germanium in the +2 oxidation state.

In chemistry, germanate is a compound containing an oxyanion of germanium. In the naming of inorganic compounds it is a suffix that indicates a polyatomic anion with a central germanium atom, for example potassium hexafluorogermanate, K2GeF6.

Germanium tetrafluoride (GeF4) is a chemical compound of germanium and fluorine. It is a colorless gas.
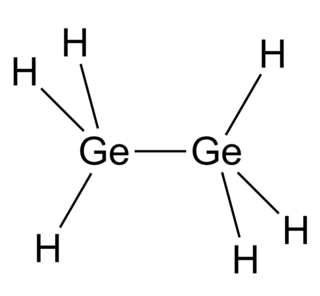
Digermane is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ge2H6. One of the few hydrides of germanium, it is a colourless liquid. Its molecular geometry is similar to ethane.
Germanium(II) hydroxide, normally written as Ge(OH)2, is a poorly characterised compound, sometimes called hydrous germanium(II) oxide or germanous hydroxide. It was first reported by Winkler in 1886.

NASICON is an acronym for sodium (Na) super ionic conductor, which usually refers to a family of solids with the chemical formula Na1+xZr2SixP3−xO12, 0 < x < 3. In a broader sense, it is also used for similar compounds where Na, Zr and/or Si are replaced by isovalent elements. NASICON compounds have high ionic conductivities, on the order of 10−3 S/cm, which rival those of liquid electrolytes. They are caused by hopping of Na ions among interstitial sites of the NASICON crystal lattice.
The nitridogermanates are chemical compounds containing germanium atoms bound to nitrogen. The simplest anion is GeN48−, but these are often condensed, with the elimination of nitrogen.
Germyl, trihydridogermanate(1-), trihydrogermanide, trihydridogermyl or according to IUPAC Red Book: germanide is an anion containing germanium bounded with three hydrogens, with formula GeH−3. Germyl is the IUPAC term for the –GeH3 group. For less electropositive elements the bond can be considered covalent rather than ionic as "germanide" indicates. Germanide is the base for germane when it loses a proton.
Sulfidogermanates or thiogermanates are chemical compounds containing anions with sulfur atoms bound to germanium. They are in the class of chalcogenidotetrelates. Related compounds include thiosilicates, thiostannates, selenidogermanates, telluridogermanates and selenidostannates.

Niobium(V) oxalate is the hydrogen oxalate salt of niobium(V). The neutral salt has not been prepared.
Germanium compounds are chemical compounds formed by the element germanium (Ge). Germanium is insoluble in dilute acids and alkalis but dissolves slowly in hot concentrated sulfuric and nitric acids and reacts violently with molten alkalis to produce germanates ([GeO
3]2−
). Germanium occurs mostly in the oxidation state +4 although many +2 compounds are known. Other oxidation states are rare: +3 is found in compounds such as Ge2Cl6, and +3 and +1 are found on the surface of oxides, or negative oxidation states in germanides, such as −4 in Mg
2Ge. Germanium cluster anions (Zintl ions) such as Ge42−, Ge94−, Ge92−, [(Ge9)2]6− have been prepared by the extraction from alloys containing alkali metals and germanium in liquid ammonia in the presence of ethylenediamine or a cryptand. The oxidation states of the element in these ions are not integers—similar to the ozonides O3−.
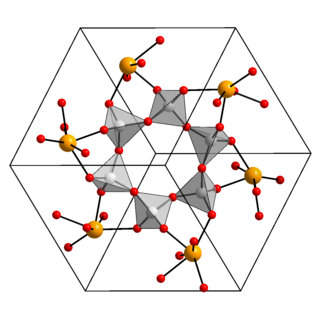
Lead metagermante is one of the germanates of lead with the chemical formula of PbGeO3. Other germanates include Pb5Ge3O11.













