
Sodium cyanide is a poisonous compound with the formula NaCN. It is a white, water-soluble solid. Cyanide has a high affinity for metals, which leads to the high toxicity of this salt. Its main application, in gold mining, also exploits its high reactivity toward metals. It is a moderately strong base.

In chemistry, pyrophosphates are phosphorus oxyanions that contain two phosphorus atoms in a P–O–P linkage. A number of pyrophosphate salts exist, such as disodium pyrophosphate (Na2H2P2O7) and tetrasodium pyrophosphate (Na4P2O7), among others. Often pyrophosphates are called diphosphates. The parent pyrophosphates are derived from partial or complete neutralization of pyrophosphoric acid. The pyrophosphate bond is also sometimes referred to as a phosphoanhydride bond, a naming convention which emphasizes the loss of water that occurs when two phosphates form a new P–O–P bond, and which mirrors the nomenclature for anhydrides of carboxylic acids. Pyrophosphates are found in ATP and other nucleotide triphosphates, which are important in biochemistry. The term pyrophosphate is also the name of esters formed by the condensation of a phosphorylated biological compound with inorganic phosphate, as for dimethylallyl pyrophosphate. This bond is also referred to as a high-energy phosphate bond.

Phosphoric acid is a colorless, odorless phosphorus-containing solid, and inorganic compound with the chemical formula H3PO4. It is commonly encountered as an 85% aqueous solution, which is a colourless, odourless, and non-volatile syrupy liquid. It is a major industrial chemical, being a component of many fertilizers.

Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula KOH, and is commonly called caustic potash.
Hydrobromic acid is a strong acid formed by dissolving the diatomic molecule hydrogen bromide (HBr) in water. "Constant boiling" hydrobromic acid is an aqueous solution that distills at 124.3 °C (255.7 °F) and contains 47.6% HBr by mass, which is 8.77 mol/L. Hydrobromic acid has a pKa of −9, making it a stronger acid than hydrochloric acid, but not as strong as hydroiodic acid. Hydrobromic acid is one of the strongest mineral acids known.

Sodium hexametaphosphate (SHMP) is a salt of composition Na6[(PO3)6]. Sodium hexametaphosphate of commerce is typically a mixture of metaphosphates (empirical formula: NaPO3), of which the hexamer is one, and is usually the compound referred to by this name. Such a mixture is more correctly termed sodium polymetaphosphate. They are white solids that dissolve in water.

Sodium triphosphate (STP), also sodium tripolyphosphate (STPP), or tripolyphosphate (TPP),) is an inorganic compound with formula Na5P3O10. It is the sodium salt of the polyphosphate penta-anion, which is the conjugate base of triphosphoric acid. It is produced on a large scale as a component of many domestic and industrial products, especially detergents. Environmental problems associated with eutrophication are attributed to its widespread use.

Sodium fluoride (NaF) is an inorganic compound with the formula NaF. It is a colorless or white solid that is readily soluble in water. It is used in trace amounts in the fluoridation of drinking water to prevent tooth decay, and in toothpastes and topical pharmaceuticals for the same purpose. In 2020, it was the 265th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 1 million prescriptions. It is also used in metallurgy and in medical imaging.
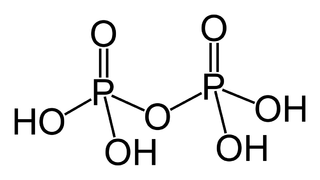
Pyrophosphoric acid, also known as diphosphoric acid, is the inorganic compound with the formula H4P2O7 or, more descriptively, [(HO)2P(O)]2O. Colorless and odorless, it is soluble in water, diethyl ether, and ethyl alcohol. The anhydrous acid crystallizes in two polymorphs, which melt at 54.3 and 71.5 °C. The compound is a component of polyphosphoric acid, an important source of phosphoric acid. Anions, salts, and esters of pyrophosphoric acid are called pyrophosphates.
Vanadium(V) oxide (vanadia) is the inorganic compound with the formula V2O5. Commonly known as vanadium pentoxide, it is a brown/yellow solid, although when freshly precipitated from aqueous solution, its colour is deep orange. Because of its high oxidation state, it is both an amphoteric oxide and an oxidizing agent. From the industrial perspective, it is the most important compound of vanadium, being the principal precursor to alloys of vanadium and is a widely used industrial catalyst.

Monocalcium phosphate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca(H2PO4)2 ("AMCP" or "CMP-A" for anhydrous monocalcium phosphate). It is commonly found as the monohydrate ("MCP" or "MCP-M"), Ca(H2PO4)2·H2O. Both salts are colourless solids. They are used mainly as superphosphate fertilizers and are also popular leavening agents.

Phosphoryl chloride is a colourless liquid with the formula POCl3. It hydrolyses in moist air releasing phosphoric acid and fumes of hydrogen chloride. It is manufactured industrially on a large scale from phosphorus trichloride and oxygen or phosphorus pentoxide. It is mainly used to make phosphate esters such as tricresyl phosphate.

Sodium monofluorophosphate, commonly abbreviated SMFP, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Na2PO3F. Typical for a salt, MFP is odourless, colourless, and water-soluble. This salt is an ingredient in some toothpastes.
Dicalcium phosphate is the calcium phosphate with the formula CaHPO4 and its dihydrate. The "di" prefix in the common name arises because the formation of the HPO42– anion involves the removal of two protons from phosphoric acid, H3PO4. It is also known as dibasic calcium phosphate or calcium monohydrogen phosphate. Dicalcium phosphate is used as a food additive, it is found in some toothpastes as a polishing agent and is a biomaterial.

Hexafluorosilicic acid is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula H
2SiF
6. Aqueous solutions of hexafluorosilicic acid consist of salts of the cation and hexafluorosilicate anion. These salts and their aqueous solutions are colorless.
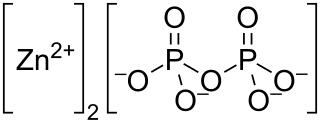
Zinc pyrophosphate (Zn2P2O7) is an ionic inorganic chemical compound composed of Zn2+ cations and pyrophosphate anions.

Disodium pyrophosphate or sodium acid pyrophosphate (SAPP) is an inorganic compound consisting of sodium cations and pyrophosphate anion. It is a white, water-soluble solid that serves as a buffering and chelating agent, with many applications in the food industry. When crystallized from water, it forms a hexahydrate, but it dehydrates above room temperature. Pyrophosphate is a polyvalent anion with a high affinity for polyvalent cations, e.g. Ca2+.

Disodium phosphate (DSP), or disodium hydrogen phosphate, or sodium phosphate dibasic, is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2HPO4. It is one of several sodium phosphates. The salt is known in anhydrous form as well as forms with 2, 7, 8, and 12 hydrates. All are water-soluble white powders; the anhydrous salt being hygroscopic.

Monosodium phosphate (MSP), also known as monobasic sodium phosphate and sodium dihydrogen phosphate, is an inorganic compound of sodium with a dihydrogen phosphate (H2PO4−) anion. One of many sodium phosphates, it is a common industrial chemical. The salt exists in an anhydrous form, as well as mono- and dihydrates.

Copper(II) phosphate are inorganic compounds with the formula Cu3(PO4)2. They can be regarded as the cupric salts of phosphoric acid. Anhydrous copper(II) phosphate and a trihydrate are blue solids.





















