Single-photon emission computed tomography is a nuclear medicine tomographic imaging technique using gamma rays. It is very similar to conventional nuclear medicine planar imaging using a gamma camera, but is able to provide true 3D information. This information is typically presented as cross-sectional slices through the patient, but can be freely reformatted or manipulated as required.

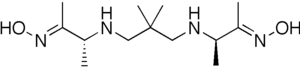
In organic chemistry, an oxime is a organic compound belonging to the imines, with the general formula RR’C=N−OH, where R is an organic side-chain and R’ may be hydrogen, forming an aldoxime, or another organic group, forming a ketoxime. O-substituted oximes form a closely related family of compounds. Amidoximes are oximes of amides with general structure R1C(=NOH)NR2R3.

Technetium (99mTc) sestamibi (INN) is a pharmaceutical agent used in nuclear medicine imaging. The drug is a coordination complex consisting of the radioisotope technetium-99m bound to six (sesta=6) methoxyisobutylisonitrile (MIBI) ligands. The anion is not defined. The generic drug became available late September 2008. A scan of a patient using MIBI is commonly known as a "MIBI scan".

Scintigraphy, also known as a gamma scan, is a diagnostic test in nuclear medicine, where radioisotopes attached to drugs that travel to a specific organ or tissue (radiopharmaceuticals) are taken internally and the emitted gamma radiation is captured by external detectors to form two-dimensional images in a similar process to the capture of x-ray images. In contrast, SPECT and positron emission tomography (PET) form 3-dimensional images and are therefore classified as separate techniques from scintigraphy, although they also use gamma cameras to detect internal radiation. Scintigraphy is unlike a diagnostic X-ray where external radiation is passed through the body to form an image.
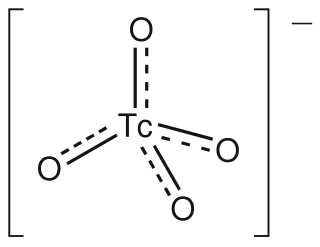
The pertechnetate ion is an oxyanion with the chemical formula TcO−
4. It is often used as a convenient water-soluble source of isotopes of the radioactive element technetium (Tc). In particular it is used to carry the 99mTc isotope which is commonly used in nuclear medicine in several nuclear scanning procedures.

A bone scan or bone scintigraphy is a nuclear medicine imaging technique of the bone. It can help diagnose a number of bone conditions, including cancer of the bone or metastasis, location of bone inflammation and fractures, and bone infection (osteomyelitis).

Sodium pertechnetate is the inorganic compound with the formula NaTcO4. This colourless salt contains the pertechnetate anion, TcO−
4. The radioactive 99m
Tc
O−
4 anion is an important radiopharmaceutical for diagnostic use. The advantages to 99m
Tc
include its short half-life of 6 hours and the low radiation exposure to the patient, which allow a patient to be injected with activities of more than 30 millicuries. Na[99m
Tc
O
4] is a precursor to a variety of derivatives that are used to image different parts of the body.
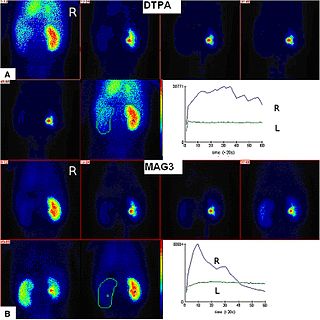
Radioisotope renography is a form of medical imaging of the kidneys that uses radiolabelling. A renogram, which may also be known as a MAG3 scan, allows a nuclear medicine physician or a radiologist to visualize the kidneys and learn more about how they are functioning. MAG3 is an acronym for mercapto acetyl tri glycine, a compound that is chelated with a radioactive element – technetium-99m.

A ventilation/perfusion lung scan, also called a V/Q lung scan, or ventilation/perfusion scintigraphy, is a type of medical imaging using scintigraphy and medical isotopes to evaluate the circulation of air and blood within a patient's lungs, in order to determine the ventilation/perfusion ratio. The ventilation part of the test looks at the ability of air to reach all parts of the lungs, while the perfusion part evaluates how well blood circulates within the lungs. As Q in physiology is the letter used to describe bloodflow the term V/Q scan emerged.
Technetium (99mTc) fanolesomab is a mouse monoclonal antibody formerly used to aid in the diagnosis of appendicitis. It is labeled with a radioisotope, technetium-99m (99mTc).
Technetium (99mTc) sulesomab is a radio-pharmaceutical composed of anti-human mouse monoclonal antibody that targets the granulocyte associated NCA-90 cell antigen and a conjugated technetium-99m radionuclide. After intravenous administration, Leukoscan enables sensitive and specific whole body measurement of granulocyte infiltration and activation by gamma camera imaging of 99mTc-antibody bound cells. Total clearance of LeukoScan from blood samples after administration and imaging has been reported at 48 hour time points indicating limited retention of the agent in circulation

Technetium-99m (99mTc) is a metastable nuclear isomer of technetium-99, symbolized as 99mTc, that is used in tens of millions of medical diagnostic procedures annually, making it the most commonly used medical radioisotope in the world.

Myocardial perfusion imaging or scanning is a nuclear medicine procedure that illustrates the function of the heart muscle (myocardium).
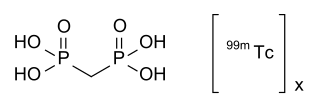
Technetium (99mTc) medronic acid is a pharmaceutical product used in nuclear medicine to localize bone metastases as well as other diseases that can alter the natural turn-over in the bone by bone scintigraphy.
Technetium 99mTc albumin aggregated (99mTc-MAA) is an injectable radiopharmaceutical used in nuclear medicine. It consists of a sterile aqueous suspension of Technetium-99m (99mTc) labeled to human albumin aggregate particles. It is commonly used for lung perfusion scanning. It is also less commonly used to visualise a peritoneovenous shunt and for isotope venography.

Cholescintigraphy or hepatobiliary scintigraphy is scintigraphy of the hepatobiliary tract, including the gallbladder and bile ducts. The image produced by this type of medical imaging, called a cholescintigram, is also known by other names depending on which radiotracer is used, such as HIDA scan, PIPIDA scan, DISIDA scan, or BrIDA scan. Cholescintigraphic scanning is a nuclear medicine procedure to evaluate the health and function of the gallbladder and biliary system. A radioactive tracer is injected through any accessible vein and then allowed to circulate to the liver, where it is excreted into the bile ducts and stored by the gallbladder until released into the duodenum.
Perfusion is the passage of fluid through the lymphatic system or blood vessels to an organ or a tissue. The practice of perfusion scanning is the process by which this perfusion can be observed, recorded and quantified. The term perfusion scanning encompasses a wide range of medical imaging modalities.

Technetium (99mTc) tetrofosmin is a drug used in nuclear medicine cardiac imaging. It is sold under the brand name Myoview. The radioisotope, technetium-99m, is chelated by two 1,2-bis[di-(2-ethoxyethyl)phosphino]ethane ligands which belong to the group of diphosphines and which are referred to as tetrofosmin.

Iofetamine, brand names Perfusamine, SPECTamine), or N-isopropyl-(123I)-p-iodoamphetamine (IMP), is a lipid-soluble amine and radiopharmaceutical drug used in cerebral blood perfusion imaging with single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT). Labeled with the radioactive isotope iodine-123, it is approved for use in the United States as a diagnostic aid in determining the localization of and in the evaluation of non-lacunar stroke and complex partial seizures, as well as in the early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease.
Organotechnetium chemistry is the science of describing the physical properties, synthesis, and reactions of organotechnetium compounds, which are organometallic compounds containing carbon-to-technetium chemical bonds. The most common organotechnetium compounds are coordination complexes used as radiopharmaceutical imaging agents.