
In organic chemistry, a dicarbonyl is a molecule containing two carbonyl groups. Although this term could refer to any organic compound containing two carbonyl groups, it is used more specifically to describe molecules in which both carbonyls are in close enough proximity that their reactivity is changed, such as 1,2-, 1,3-, and 1,4-dicarbonyls. Their properties often differ from those of monocarbonyls, and so they are usually considered functional groups of their own. These compounds can have symmetrical or unsymmetrical substituents on each carbonyl, and may also be functionally symmetrical or unsymmetrical.

Terpyridine is a heterocyclic compound derived from pyridine. It is a white solid that is soluble in most organic solvents. The compound is mainly used as a ligand in coordination chemistry.

1,10-Phenanthroline (phen) is a heterocyclic organic compound. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. The 1,10 refer to the location of the nitrogen atoms that replace CH's in the hydrocarbon called phenanthrene.

Dithiolene metal complexes are complexes containing 1,2-dithiolene ligands. 1,2-Dithiolene ligands, a particular case of 1,2-dichalcogenolene species along with 1,2-diselenolene derivatives, are unsaturated bidentate ligand wherein the two donor atoms are sulfur. 1,2-Dithiolene metal complexes are often referred to as "metal dithiolenes", "metallodithiolenes" or "dithiolene complexes". Most molybdenum- and tungsten-containing proteins have dithiolene-like moieties at their active sites, which feature the so-called molybdopterin cofactor bound to the Mo or W.
1,5-Cyclooctadiene is a cyclic hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C8H12, specifically [−(CH2)2−CH=CH−]2.

Organozinc chemistry is the study of the physical properties, synthesis, and reactions of organozinc compounds, which are organometallic compounds that contain carbon (C) to zinc (Zn) chemical bonds.

Group 2 organometallic chemistry refers to the organic derivativess of any group 2 element. It is a subtheme to main group organometallic chemistry. By far the most common group 2 organometallic compounds are the magnesium-containing Grignard reagents which are widely used in organic chemistry. Other organometallic group 2 compounds are typically limited to academic interests.
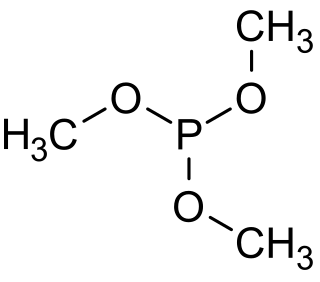
Trimethyl phosphite is an organophosphorus compound with the formula P(OCH3)3, often abbreviated P(OMe)3. It is a colorless liquid with a highly pungent odor. It is the simplest phosphite ester and finds used as a ligand in organometallic chemistry and as a reagent in organic synthesis. The molecule features a pyramidal phosphorus(III) center bound to three methoxy groups.

Salcomine is a coordination complex derived from the salen ligand and cobalt. The complex, which is planar, and a variety of its derivatives are carriers for O2 as well as oxidation catalysts.
Organoiron chemistry is the chemistry of iron compounds containing a carbon-to-iron chemical bond. Organoiron compounds are relevant in organic synthesis as reagents such as iron pentacarbonyl, diiron nonacarbonyl and disodium tetracarbonylferrate. Although iron is generally less active in many catalytic applications, it is less expensive and "greener" than other metals. Organoiron compounds feature a wide range of ligands that support the Fe-C bond; as with other organometals, these supporting ligands prominently include phosphines, carbon monoxide, and cyclopentadienyl, but hard ligands such as amines are employed as well.

Organoruthenium chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to ruthenium chemical bond. Several organoruthenium catalysts are of commercial interest and organoruthenium compounds have been considered for cancer therapy. The chemistry has some stoichiometric similarities with organoiron chemistry, as iron is directly above ruthenium in group 8 of the periodic table. The most important reagents for the introduction of ruthenium are ruthenium(III) chloride and triruthenium dodecacarbonyl.

Oxazoline is a five-membered heterocyclic organic compound with the formula C3H5NO. It is the parent of a family of compounds called oxazolines, which contain non-hydrogenic substituents on carbon and/or nitrogen. Oxazolines are the unsaturated analogues of oxazolidines, and they are isomeric with isoxazolines, where the N and O are directly bonded. Two isomers of oxazoline are known, depending on the location of the double bond.
Hydroacylation is a type of organic reaction in which an electron-rich unsaturated hydrocarbon inserts into a formyl C-H bond. With alkenes, the product is a ketone:
Organoplatinum chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to platinum chemical bond, and the study of platinum as a catalyst in organic reactions. Organoplatinum compounds exist in oxidation state 0 to IV, with oxidation state II most abundant. The general order in bond strength is Pt-C (sp) > Pt-O > Pt-N > Pt-C (sp3). Organoplatinum and organopalladium chemistry are similar, but organoplatinum compounds are more stable and therefore less useful as catalysts.

Nickel(II) bis(acetylacetonate) is a coordination complex with the formula [Ni(acac)2]3, where acac is the anion C5H7O2− derived from deprotonation of acetylacetone. It is a dark green paramagnetic solid that is soluble in organic solvents such as toluene. It reacts with water to give the blue-green diaquo complex Ni(acac)2(H2O)2.
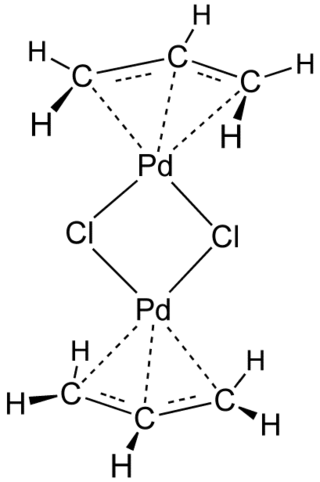
Transition-metal allyl complexes are coordination complexes with allyl and its derivatives as ligands. Allyl is the radical with the connectivity CH2CHCH2, although as a ligand it is usually viewed as an allyl anion CH2=CH−CH2−, which is usually described as two equivalent resonance structures.

1,5-Diaza-3,7-diphosphacyclooctanes are organophosphorus compounds with the formula [R'NCH2P(R)CH2]2, often abbreviated PR2NR'2. They are air-sensitive white solids that are soluble in organic solvents. The ligands exist as meso and d,l-diastereomers, but only the meso forms function as bidentate ligands.
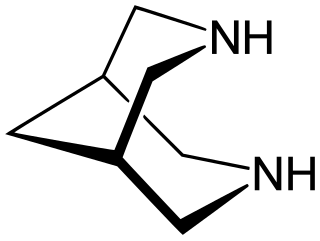
Bispidine (3,7-diazabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane) is an organic compound that is classified as a bicyclic diamine. Although synthetic, it is related structurally to natural alkaloid sparteine. It is a white crystalline solid. It has been widely investigated as a chelating agent. Many derivatives are known.

Transition metal complexes of aldehydes and ketones describes coordination complexes with aldehyde (RCHO) and ketone (R2CO) ligands. Because aldehydes and ketones are common, the area is of fundamental interest. Some reactions that are useful in organic chemistry involve such complexes.
Transition metal complexes of 2,2'-bipyridine are coordination complexes containing one or more 2,2'-bipyridine ligands. Complexes have been described for all of the transition metals. Although few have any practical value, these complexes have been influential. 2,2'-Bipyridine is classified as a diimine ligand. Unlike the structures of pyridine complexes, the two rings in bipy are coplanar, which facilitates electron delocalization. As a consequence of this delocalization, bipy complexes often exhibit distinctive optical and redox properties.















