The 7th Infantry Division is an active duty infantry division of the United States Army based at Joint Base Lewis-McChord charged with sustaining the combat readiness of two Stryker brigade combat teams (BCT), a combat aviation brigade, and a Division Artillery Unit, as well as participating in several yearly partnered exercises and operations in support of U.S. Army Pacific and the Indo-Pacific region. The 7th Infantry Division is the only active-duty multi-component division headquarters in the Army. The 7th Infantry Division is also home to two of the Army's newest enabling battlefield capabilities, the Multi Domain Task Force and the Intelligence, Information, Cyber, Electronic Warfare and Space Capabilities, or I2CEWS battalion.

The 77th Sustainment Brigade is a unit of the United States Army that inherited the lineage of the 77th Infantry Division, which served in World War I and World War II. Its headquarters has been at Fort Dix, New Jersey, since its predecessor command, the 77th Regional Readiness Command, was disestablished in 2008 from Fort Totten in Bayside, Queens, New York. Soldiers from the 77th have served in most major conflicts and contingency operations involving the US since World War II.

The 90th Infantry Division was a unit of the United States Army that served in World War I and World War II. Its lineage is carried on by the 90th Sustainment Brigade.

The 42nd Infantry Division (42ID) ("Rainbow") is a division of the United States Army National Guard. It was nicknamed the Rainbow Division because, during rapid mobilization for service in WW1, it was formed from 27 National Guard units from across the US. The division was engaged in four major operations between July 1918 and the armistice in November 1918, and demobilized in 1919. Since World War I, the 42nd Infantry Division has served in World War II and the Global War on Terrorism (GWOT).

The 30th Infantry Division was a United States Army unit of the National Guard that served in World War I and World War II. It was nicknamed the "Old Hickory" division, in honor of President Andrew Jackson. The Germans nicknamed this division "Roosevelt's SS". The 30th Infantry Division, involved in 282 days of intense combat over a period from June 1944 through April 1945, was regarded by a team of historians led by S.L.A. Marshall as the American infantry division that had "performed the most efficient and consistent battle services" in the European Theater of Operations (ETO). In the present day, the division's lineage continues as 30th Armored Brigade Combat Team, part of the North Carolina National Guard. The unit's most recent combat deployment was in 2019.

The 27th Infantry Division was a unit of the Army National Guard in World War I and World War II. The division traces its history from the New York Division, formed originally in 1908. The 6th Division designation was changed to the 27th Division in July 1917.

The Battle of Saipan was an amphibious assault launched by the United States against the Empire of Japan during the Pacific campaign of World War II between 15 June and 9 July 1944. The initial invasion triggered the Battle of the Philippine Sea, which effectively destroyed Japanese carrier-based airpower, and the battle resulted in the American capture of the island. Its occupation put the major cities of the Japanese home islands within the range of B-29 bombers, making them vulnerable to strategic bombing by the United States Army Air Forces. It also precipitated the resignation of Hideki Tōjō, the prime minister of Japan.

The 69th Infantry Regiment is an infantry regiment of the United States Army. It is from New York City, part of the New York Army National Guard. It is known as the "Fighting Sixty-Ninth", a name said to have been given by Robert E. Lee during the Civil War. An Irish-American heritage is attributed to the regiment, which is also nicknamed the "Fighting Irish" – a tradition mentioned in Joyce Kilmer's poem "When the 69th Comes Back". Between 1917 and 1992 it was also designated the 165th Infantry Regiment. It is headquartered at the 69th Regiment Armory in Manhattan.

The 6th Marine Regiment is an infantry regiment of the United States Marine Corps based at Marine Corps Base Camp Lejeune, North Carolina. The regiment falls under the command of the 2nd Marine Division of the II Marine Expeditionary Force. Its combat history dates back to World War I when they were part of the American Expeditionary Force. They fought in the Pacific Theater in World War II, most notably at the battles of Guadalcanal, Tarawa, Saipan, Tinian and Okinawa. More recently, the regiment has seen combat during the Gulf War and in support of Operation Iraqi Freedom.

On 15 June 1944, United States Marine forces landed on the southwest coast of the island of Saipan in the central Marianas chain; these were followed a day later by US Army forces. This invasion was part of Operation Forager, an effort to recapture the entire Marianas chain from the Empire of Japan.

The New York Army National Guard is a component of the New York National Guard and the Army National Guard. Nationwide, the Army National Guard comprises approximately one half of the United States Army's available combat forces and approximately one third of its support organization. National coordination of various state National Guard units are maintained through the National Guard Bureau.

Benjamin Lewis Salomon was a United States Army dentist during World War II, assigned as a front-line surgeon. During the Battle of Saipan, when the Japanese started overrunning his hospital, he stood a rear-guard action in which he had no hope of personal survival, allowing the safe evacuation of the wounded, killing as many as 98 enemy troops before being killed himself. In 2002, Salomon posthumously received the Medal of Honor. He is one of only three dental officers to have received the medal, the others being Alexander Gordon Lyle and Weedon Osborne, and is one of three Jewish American soldiers who received the medal for World War II.

The 53rd Troop Command is an administrative headquarters of the New York Army National Guard that provides direction for units not under another brigade or other formation headquarters (HQ). It also provides administrative support to units from other formations in the New York area that are stationed a long way from their higher HQ.

William Joseph O'Brien was a United States Army officer and a recipient of the United States military's highest decoration—the Medal of Honor—for his actions in World War II during the Battle of Saipan.

The 27th Infantry Brigade Combat Team ("Empire") is an infantry brigade combat team of the New York Army National Guard, one of the brigades that make up the 42nd Infantry Division.
The 258th Field Artillery Regiment or "Washington Greys" is a field artillery unit of the New York Army National Guard that traces its lineage from 1789 to present. Circa 1957–1966 it consisted of four battalions.

The 108th Infantry Regiment is a regiment of the New York Army National Guard. It was first formed in 1898 and has been in continuous existence since 1907. As National Guardsmen, Soldiers of the 108th Infantry can be called upon to serve the state and federal governments. The 108th has served in the Spanish–American War, the Mexican Border War, World War I, World War II, Iraq, and Afghanistan.
The 307th Infantry Regiment was a National Army unit first organized for service in World War I as part of the 77th Division in France. It later served in the Pacific Theater during World War II. Since then it has served as a training Regiment. In 1999, it was withdrawn from the Combat Arms Regimental System and redesignated as a non-branch regiment. The regiment's 1st Battalion is assigned to the 174th Infantry Brigade at Joint Base McGuire–Dix–Lakehurst, New Jersey, with the 2nd Battalion is assigned to the 157th Infantry Brigade at Camp Atterbury, Indiana.

The 106th Infantry Regiment is an infantry regiment of the New York Army National Guard that traces its history to the 10th New York National Guard. During World War II, the 106th served in the Pacific Theater and acted both independently and as parts of larger divisions.
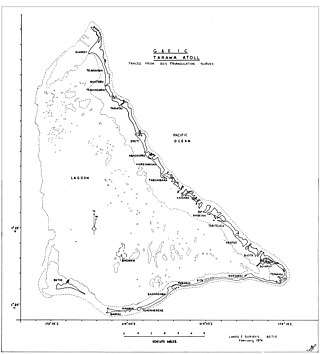
On 10 November 1943, men of the United States Marine Corps invaded the island of Betio, located at the southwest corner of Tarawa Atoll in the Gilbert Islands chain in the Central Pacific. This invasion, known as Operation Galvanic, was a phase of the Pacific Theatre of World War II.

















