Related Research Articles
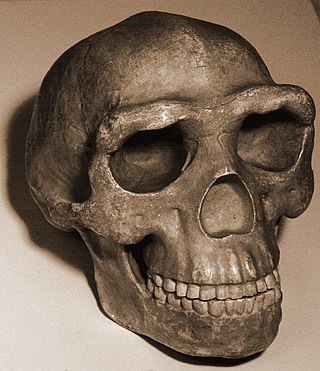
Peking Man is a subspecies of H. erectus which inhabited what is now northern China during the Middle Pleistocene. Its fossils have been found in a cave some 50 km (31 mi) southwest of Beijing, known as the Zhoukoudian Peking Man Site. The first fossil, a tooth, was discovered in 1921, and Zhoukoudian has since become the most productive H. erectus site in the world. Peking Man was instrumental in the foundation of Chinese anthropology, and fostered an important dialogue between Western and Eastern science. Peking Man became the centre of anthropological discussion, and was classified as a direct human ancestor, propping up the Out of Asia theory that humans evolved in Asia.
Below are notable events in archaeology that occurred in 1926.

Below are notable events in archaeology that occurred in 1877.

Zhoukoudian Peking Man Site (周口店北京人遗址), also romanized as Choukoutien, is a cave system in suburban Fangshan District, Beijing. It has yielded many archaeological discoveries, including one of the first specimens of Homo erectus, dubbed Peking Man, and a fine assemblage of bones of the giant short-faced hyena Pachycrocuta brevirostris.

Johan Gunnar Andersson was a Swedish archaeologist, geomorphologist, and paleontologist who was closely associated with the beginnings of Chinese archaeology in the 1920s.
Below are notable events in archaeology that occurred in 1922.
Below are notable events in archaeology that occurred in 1923.
The year 1959 in archaeology involved some significant events.
Below are notable events in archaeology that occurred in 1949.
The year 1979 in archaeology involved some significant events.
Below are notable events in archaeology that occurred in 1928.
Below are notable events in archaeology that occurred in 1929.

The Snape Anglo-Saxon Cemetery is a place of burial dated to the 6th century AD located on Snape Common, near to the town of Aldeburgh in Suffolk, Eastern England. Dating to the early part of the Anglo-Saxon Era of English history, it contains a variety of different forms of burial, with inhumation and cremation burials being found in roughly equal proportions. The site is also known for the inclusion of a high status ship burial. A number of these burials were included within burial mounds.
Below are notable events in archaeology that occurred in 1950.

Pei Wenzhong, or W. C. Pei, was a Chinese paleontologist, archaeologist and anthropologist born in Fengnan. He is considered a founding figure of Chinese anthropology.
The Cenozoic Research Laboratory of the Geological Survey of China was established within the Peking Union Medical College in 1928 by Canadian paleoanthropologist Davidson Black and Chinese geologists Ding Wenjing and Weng Wenhao for the research and appraisal of Peking Man fossils unearthed at Zhoukoudian.

The Sutton Hoo purse-lid is one of the major objects excavated from the Anglo-Saxon royal burial-ground at Sutton Hoo in Suffolk, England. The site contains a collection of burial mounds, of which much the most significant is the undisturbed ship burial in Mound 1 containing very rich grave goods including the purse-lid. The person buried in Mound 1 is usually thought to have been Rædwald, King of East Anglia, who died around 624. The purse-lid is considered to be "one of the most remarkable creations of the early medieval period." About seven and a half inches long, it is decorated with beautiful ornament in gold and garnet cloisonné enamel, and was undoubtedly a symbol of great wealth and status. In 2017 the purse-lid was on display at the British Museum.
Helena Francisca Hamerow, is an American archaeologist, best known for her work on the archeology of early medieval communities in Northwestern Europe. She is Professor of Early Medieval archaeology and former Head of the School of Archaeology, University of Oxford.

Edward Thurlow Leeds was an English archaeologist and museum curator. He was Keeper of the Ashmolean Museum from 1928 to 1945.
Catherine Mary Hills is a British archaeologist and academic, who is a leading expert in Anglo-Saxon material culture. She is a senior research fellow at the McDonald Institute for Archaeological Research, University of Cambridge.
References
- ↑ "The scientific work". Archaeological Museum of Thebes . Retrieved 2017-11-23.
- ↑ Leeds, E. T. (1923). "A Saxon Village near Sutton Courtenay, Berks". Archaeologia . LXXII. London: 147–92. doi:10.1017/S0261340900010328.
- ↑ "The Anglo-Saxon Settlement at Sutton Courtenay". Oxford: Ashmolean Museum. Archived from the original on 2013-09-21. Retrieved 2012-06-18.
- ↑ Hills, Catherine (2011-07-30). "Philip Rahtz". The Guardian . London. p. 37.
- ↑ "Oscar Montelius - Swedish archaeologist". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 17 May 2017.