The 1938 Grand Prix season was the sixth AIACR European Championship season. The championship was won by Rudolf Caracciola, driving for the Mercedes-Benz team. Caracciola won one of the four events that counted towards the championship.
The 1938 Grand Prix season was the sixth AIACR European Championship season. The championship was won by Rudolf Caracciola, driving for the Mercedes-Benz team. Caracciola won one of the four events that counted towards the championship.
| Rd | Date | Name | Circuit | Winning drivers | Winning constructor | Report |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 July | | Reims-Gueux | | Mercedes-Benz | Report |
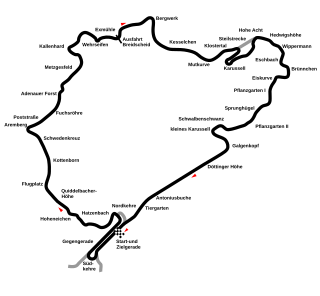
| 2 | 24 July | | Nürburgring | | Mercedes-Benz | Report |
| 3 | 21 August | | Bremgarten | | Mercedes-Benz | Report |
| 4 | 11 September | | Monza | | Auto Union | Report |
Grandes Épreuves are denoted by a yellow background.
| Date | Name | Circuit | Winning driver | Winning constructor | Report |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 April | | Pau | | Delahaye | Report |
| 18 April | | Brooklands | | ERA | Report |
| 23 April | | Carrigrohane | | Delahaye | Report |
| 15 May | | Mellaha | | Mercedes-Benz | Report |
| 29 May | | Gávea | | Alfa Romeo | Report |
| 5 June | | Chimay | | Bugatti | Report |
| 12 June | | Gávea | | Alfa Romeo | Report |
| 7 August | | Montenero | | Mercedes-Benz | Report |
| 15 August | | Pescara | | Mercedes-Benz | Report |
| 27 August | | Brooklands | | ERA | Report |
| 15 October | | Brooklands | | ERA | Report |
| 22 October | | Donington Park | | Auto Union | Report |
|
|

Otto Wilhelm Rudolf Caracciola was a German racing driver. He won the European Drivers' Championship, the pre-1950 equivalent of the modern Formula One World Championship, an unsurpassed three times. He also won the European Hillclimbing Championship three times – twice in sports cars, and once in Grand Prix cars. Caracciola raced for Mercedes-Benz during their original dominating Silver Arrows period, named after the silver colour of the cars, and set speed records for the firm. He was affectionately dubbed Caratsch by the German public, and was known by the title of Regenmeister, or "Rainmaster", for his prowess in wet conditions.

Louis Alexandre Chiron was a Monégasque racing driver who competed in rallies, sports car races, and Grands Prix.

Luigi Cristiano Fagioli was an Italian racing driver, who competed in Grand Prix motor racing from 1928 to 1949, and Formula One from 1950 to 1951. Nicknamed "The Abruzzi Robber", Fagioli won the 1951 French Grand Prix with Alfa Romeo aged 53, and remains the oldest driver to win a Formula One Grand Prix. Fagioli was runner-up in the European Drivers' Championship in 1935 with Mercedes.
The 1926 German Grand Prix was an auto race held at the AVUS track on 11 July 1926. It was the first ever German Grand Prix. The race was held in heavy rain, and was won by Germany's native son, Rudolf Caracciola.
The European Drivers' Championship was an annual competition in auto racing that existed prior to the establishment of the Formula One world championship in 1950. It was established in 1931 and ran until the end of 1939 with a hiatus from 1933–34, and awarded points to drivers based on the results of selected Grand Prix races, the so-called Grandes Épreuves. The championship was discontinued because of the outbreak of World War II in 1939, and no champion was officially declared for the last season.
The 1937 Grand Prix season was the fifth AIACR European Championship season. The championship was won by Rudolf Caracciola, driving for the Mercedes-Benz team. Caracciola won three of the five events that counted towards the championship.

The 1935 Grand Prix season was the second year of the new 750 kg Formula. The success of the previous year encouraged the AIACR to reinitiate the European Championship. It was composed of the seven national Grands Prix and was won by Rudolf Caracciola, driving for the Mercedes-Benz team. The team dominated the season winning five of those Grand Épreuves, as well as four of the other major races of the season. However, in one of the great motor-races in sporting history, Tazio Nuvolari in a Scuderia Ferrari Alfa Romeo beat the combined numbers of the German teams in their home Grand Prix. The season also saw the arrival on the international stage of the bright young talent Bernd Rosemeyer in the Auto Union team.
The World Manufacturers' Championship, also known as Automobile World Championship, was a competition organised by the AIACR between 1925 and 1930. It was the first World Championship in a motorsport.
The 1939 Grand Prix season was the seventh AIACR European Championship season. The championship winner was never officially announced by the AIACR due to the outbreak of World War II less than two weeks after the final event in Switzerland. The Italian GP initially had been a fifth event, but it became clear well before the war that it would be cancelled due to construction work. At that time, it was also undecided which scoring system would be used, the old minimum points system that basically counted positions, or the French maximum points system similar to the modern one. Although Hermann Paul Müller would have won the championship on points according to the old system, the president of Nazi Germany's highest motorsports organisation declared Hermann Lang the champion. Lang was clearly the dominating driver in that season, which was acknowledged by the international press. In the first two of the four championship events, both Lang and Müller won once while the other failed to complete 75% of the distance. The German round saw Lang retiring early, and Müller finishing 2nd behind Caracciola. This left Müller in the lead in both scoring systems, as published in magazines, with the Swiss round deciding the outcome. Müller finished 4th behind three Mercedes, which gave him the lead in the old point system, while in front, Lang had beaten Caracciola for the lead in the maximum points system.
Grands Prix between 1940 and 1945 occurred during World War II and so were limited to a very small number of events. There was no organised championship in these years. The majority of Grand Prix races during this period were run in the Americas. The first post-war races were run in Paris on 9 September 1945, one week after the end of the war.
The 1931 German Grand Prix was a Grand Prix motor race held at the Nürburgring on 19 July 1931. There were two races held simultaneously, Class I for Grand Prix cars over 1100cc over 22 laps, and Class II for cars and cyclecars with capacity 500–1100cc over 18 laps. The race distances were chosen to make both races take approximately the same amount of time, but there were no prizes for outright positions, only for class results.
The 1946 Grand Prix season was the first post-war year for Grand Prix motor racing. It was notable for including the first ever race run to Formula One criteria, the 1946 Turin Grand Prix. There was no organised championship in 1946, although Raymond Sommer proved to be the most successful driver, winning five Grands Prix. Maserati's cars proved difficult to beat, winning 9 of the season's 20 Grand Prix races.
The 1947 Grand Prix season was the second post-war year for Grand Prix racing. It constituted the first full season of the FIA's Formula One motor racing, though some Grands Prix still used other formulas. There was no organised championship in 1947, although several of the more prestigious races were recognised as Grandes Épreuves by the FIA. Luigi Villoresi proved to be the most successful driver, winning six Grands Prix. Alfa Romeo's cars proved difficult to beat, winning 13 of the season's 32 Grands Prix.
The 1948 Grand Prix season was the third post-war year for Grand Prix racing. It was the second season of the FIA's Formula One motor racing, though some of that season's Grand Prix still used other formulas. There was no organised championship in 1948, although several of the more prestigious races were recognised as Grandes Épreuves by the FIA. Luigi Villoresi proved to be the most successful driver, for the second consecutive year, winning six Grands Prix. Maserati's cars proved difficult to beat, winning 13 of the season's 23 Grands Prix.
The 1949 Grand Prix season was the fourth post-war year for Grand Prix racing and the final year before the beginning of the Formula One World Championship. It was the third season of FIA Formula One motor racing, though some of that season's Grands Prix still used other formulas. Races which were run to Formula One criteria restricted engines to 1.5 litres supercharged or 4.5 litres naturally aspirated. There was no organised championship in 1949, although several of the more prestigious races were recognised as Grandes Épreuves by the FIA. Alberto Ascari and Juan Manuel Fangio proved to be the most successful drivers, each winning five Grands Prix. Maserati's cars were the most successful brand, winning 10 of the season's 27 Grand Prix races.

The Mercedes-Benz W154 was a Grand Prix racing car designed by Rudolf Uhlenhaut. The W154 competed in the 1938 and 1939 Grand Prix seasons and was used by Rudolf Caracciola to win the 1938 European Championship.
This is a list of motorsport races held before 1906, which is regarded as the first Grand Prix racing season.

The 1927 Italian Grand Prix was a Grand Prix motor race held at Monza on 4 September 1927.
The Algerian Grand Prix or Grand Prix d'Alger was a motor race held in the 1920s and 1930s at several coastal road courses in the department of French Algeria.

Charles Pierre Elie Montier was a French racing driver and automotive engineer whose race entries included the inaugural 24 Hours of Le Mans.