
Dubbo is a city in the Orana Region of New South Wales, Australia. It is the largest population centre in the Orana region, with a population of 43,516 at June 2021.
The 1989 Newcastle earthquake was an intraplate earthquake that occurred in Newcastle, New South Wales on Thursday 28 December. The shock measured 5.6 on the Richter scale and was one of Australia's most serious natural disasters, killing 13 people and injuring more than 160. The damage bill has been estimated at A$4 billion, including an insured loss of about $1 billion.

Dalton is a small inland country town in the Southern Tablelands of New South Wales, Australia, in Upper Lachlan Shire. The population was 230 in the 2021 census.

The 1886 Charleston earthquake in South Carolina occurred about 9:50 p.m. local time August 31. It caused 60 deaths and $5–6 million in damage to 2,000 buildings in the Southeastern United States. It is one of the most powerful and damaging earthquakes to hit the East Coast of the United States.

John Whitton, an Anglo–Australian railway engineer, was the Engineer-in-Charge for the New South Wales Government Railways, serving between 1856 and 1890, considered the Father of New South Wales Railways. Under his supervision, it is estimated that 2,171 miles (3,494 km) of railway around New South Wales and Victoria were completed. Whitton was responsible for the construction of parts of the Main Western railway line, in particular the section over the Blue Mountains and the Lithgow Zig Zag, and much of the Main Southern railway line.
The Main Western Railway is a major railway in New South Wales, Australia. It runs through the Blue Mountains, and Central West regions. It is 825 kilometres (513 mi) long, of which 484 kilometres (301 mi) is currently operational.
The 1952 Kern County earthquake occurred on July 21 in the southern San Joaquin Valley and measured 7.3 on the moment magnitude scale. The main shock occurred at 4:52 am Pacific Daylight Time, killed 12 people, injured hundreds more and caused an estimated $60 million in property damage. A small sector of damage near Bealville corresponded to a maximum Mercalli intensity of XI (Extreme), though this intensity rating was not representative of the majority of damage. The earthquake occurred on the White Wolf Fault near the community of Wheeler Ridge and was the strongest to occur in California since the 1906 San Francisco earthquake.

The 1999 Sydney hailstorm was the costliest natural disaster in Australian insurance history, causing extensive damage along the east coast of New South Wales. The storm developed south of Sydney on the afternoon of Wednesday, 14 April 1999, and struck the city's eastern suburbs, including the central business district, later that evening.

The 2008 Chino Hills earthquake occurred at 11:42:15 am PDT on July 29 in Southern California. The epicenter of the magnitude 5.4 earthquake was in Chino Hills, c. 28 miles (45 km) east-southeast of downtown Los Angeles. Movement on an oblique-slip fault resulted in a maximum Mercalli intensity of VI (Strong). Though there were no deaths, eight people were injured, and it caused considerable damage in numerous structures throughout the area and caused some amusement park facilities to shut down their rides. The earthquake led to increased discussion regarding the possibility of a stronger earthquake in the future.

The 1968 Illinois earthquake was the largest recorded earthquake in the U.S. Midwestern state of Illinois. Striking at 11:02 a.m. on November 9, it measured 5.3 on the Richter scale. Although no fatalities occurred, the event caused considerable structural damage to buildings, including the toppling of chimneys and shaking in Chicago, the region's largest city. The earthquake was one of the most widely felt in U.S. history, largely affecting 23 states over an area of 580,000 sq mi (1,500,000 km2). In studying its cause, scientists discovered the Cottage Grove Fault in the Southern Illinois Basin.
Earthquakes have occurred in Western Australia (WA) on a regular basis throughout its geological history.

The 1916 Irondale earthquake struck in the north-central region of the U.S. state of Alabama on October 18. The strongest earthquake in state history, it registered an estimated Richter scale magnitude of 5.1 and resulted in minor damage. Damage was limited to Shelby and Jefferson counties and reached its maximum severity near the epicenter in the city of Irondale, including cracked windows, fallen chimneys, and dried-up wells. While there were no fatalities, the earthquake spawned widespread panic, prompting alarmed workers to evacuate tall buildings.
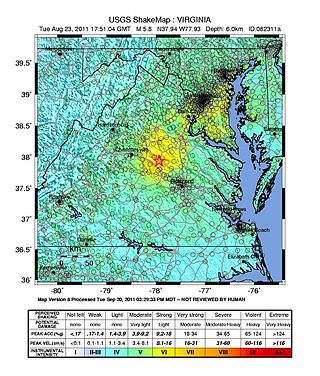
On August 23, 2011, a magnitude 5.8 earthquake hit the Piedmont region of the U.S. state of Virginia at 1:51:04 p.m. EDT. The epicenter, in Louisa County, was 38 mi (61 km) northwest of Richmond and 5 mi (8 km) south-southwest of the town of Mineral. It was an intraplate earthquake with a maximum perceived intensity of VIII (Severe) on the Mercalli intensity scale. Several aftershocks, ranging up to 4.5 in magnitude, occurred after the main tremor.
A magnitude 5.2 earthquake struck Gippsland near Moe at 8.55 pm on 19 June 2012, at a shallow depth of 10.0 km. It was the strongest recorded in Victoria in at least three decades, with some sources suggesting it was the strongest in over a century. It was felt across much of Victoria and parts of New South Wales, with strong shaking reported across the state capital, Melbourne. Some minor building damage was reported in the Latrobe Valley close to the epicentre, and in the eastern suburbs of Melbourne. Around 30 requests for help were made to the SES, mainly due to cracked walls and ceilings, and a number of local businesses lost some stock. Power outages occurred in some homes, but no significant reports of gas leaks were reported. Approximately 60 aftershocks were recorded the following day, but most of these were not felt.

At 02:10 PM local time (UTC-5) on 28 January 2020, an earthquake with a magnitude of 7.7 struck the north side of the Cayman Trough, north of Jamaica and west of the southern tip of Cuba, with the epicenter being 80 miles (130 km) east-southeast of Cayman Brac, Cayman Islands, and 83 miles (134 km) north of Montego Bay, Jamaica. Schools in Jamaica, as well as corporate and public buildings in Miami, were evacuated after shaking was experienced in parts of the U.S. state of Florida, a region not typically thought of in-relation to seismic activity. Light shaking was also reported on the Yucatán Peninsula in Mexico. The quake was the largest seismic event in the Caribbean since 1946. A tsunami warning for the Caribbean Sea was initially issued by the Pacific Tsunami Warning Center, later being withdrawn.
The 1992 St. George earthquake was a 5.8 earthquake that occurred on September 2, 1992 at approximately 4:26 AM MDT along the Washington Fault zone near the larger Hurricane Fault about 5 miles (8.0 km) southeast of St. George in Utah, United States. The quake triggered a landslide that destroyed three houses and caused approximately US$1 million in structural and cosmetic damage to houses, roads, natural formations, and utilities. No people were killed by the quake.
The 2020 Sparta earthquake struck North Carolina on August 9 at 08:07 EDT. The epicenter of this moment magnitude (Mw ) 5.1 earthquake was near the small town of Sparta, Alleghany County. It was the strongest earthquake recorded in North Carolina in 104 years, the second-strongest in the state's history, and the largest to strike the East Coast since the 2011 Virginia earthquake. It caused damage to homes and businesses in Sparta and injured at least one person. The shaking was also felt in other states along the East Coast and Midwest. A state of emergency was declared in Sparta, and North Carolina granted US$24 million in relief fund for repair works.
An earthquake struck approximately 53 kilometres SSE of the town of Mansfield, in the Victorian Alps of Australia on 22 September 2021, at 09:15 local time. The earthquake measured 5.9 on the moment magnitude scale. The earthquake caused minor structural damage in parts of Melbourne and left one person injured. The earthquake was also felt in New South Wales, Australian Capital Territory, South Australia and Tasmania. The earthquake was substantially stronger than the 1989 Newcastle earthquake that measured 5.6 and killed 13 people.
On December 20, 2022, a magnitude 6.4 earthquake struck Ferndale, California in Humboldt County, United States at 10:34:25 UTC, or 2:34 a.m. PST.










