
The Ryukyu Trench, also called Nansei-Shotō Trench, is a 1398 km (868 mi) long oceanic trench located along the southeastern edge of Japan's Ryukyu Islands in the Philippine Sea in the Pacific Ocean, between northeastern Taiwan and southern Japan. The trench has a maximum depth of 7460 m (24,476 ft). The trench is the result of oceanic crust of the Philippine Plate obliquely subducting beneath the continental crust of the Eurasian plate at a rate of approximately 52 mm/yr. In conjunction with the adjacent Nankai Trough to the northeast, subduction of the Philippine plate has produced 34 volcanoes. The largest earthquake to have been recorded along the Ryukyu Trench, the 1968 Hyūga-nada earthquake, was magnitude 7.5 and occurred along the northernmost part of the trench on 1 April 1968. This earthquake also produced a tsunami.
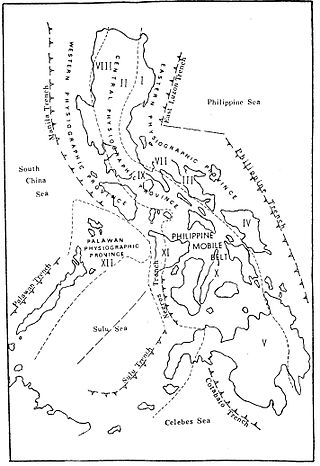
The Manila Trench is an oceanic trench in the Pacific Ocean, located west of the islands of Luzon and Mindoro in the Philippines. The trench reaches a depth of about 5,400 metres (17,700 ft), in contrast with the average depth of the South China Sea of about 1,500 metres (4,900 ft). It is created by subduction, in which the Sunda Plate is subducting under the Philippine Mobile Belt, producing this almost N-S trending trench. The convergent boundary is terminated to the north by the Taiwan collision zone, and to the south by the Mindoro terrane. It is an area pervaded by negative gravity anomalies.

The 2006 Hengchun earthquakes occurred on December 26 at 20:26 and 20:34 local time off the southwest coast of Taiwan in the Luzon Strait, which connects the South China Sea with the Philippine Sea. The International Seismological Centre measured the shocks at 7.0 and 6.9 on the moment magnitude scale. The earthquakes not only caused casualties and building damage, but several submarine communications cables were cut, disrupting telecommunication services in various parts of Asia.

The 1703 Genroku earthquake occurred at 02:00 local time on December 31. The epicenter was near Edo, the forerunner of present-day Tokyo, in the southern part of the Kantō region, Japan. An estimated 2,300 people were killed by the destruction and subsequent fires. The earthquake triggered a major tsunami which caused many additional casualties, giving a total death toll of at least 5,233, possibly up to 200,000. Genroku is a Japanese era spanning from 1688 through 1704.

The 1946 Nankai earthquake was a great earthquake in Nankaidō, Japan. It occurred on December 21, 1946, at 04:19 JST. The earthquake measured between 8.1 and 8.4 on the moment magnitude scale, and was felt from Northern Honshū to Kyūshū. It occurred almost two years after the 1944 Tōnankai earthquake, which ruptured the adjacent part of the Nankai megathrust.

The 1855 Edo earthquake, was the third Ansei Great Earthquake, which occurred during the late-Edo period. It occurred after the 1854 Nankai earthquake, which took place about a year prior. The earthquake occurred at 22:00 local time on 11 November. It had an epicenter close to Edo, causing considerable damage in the Kantō region from the shaking and subsequent fires, with a death toll of 7,000–10,000 people and destroyed around 14,000 buildings. The earthquake had a magnitude of 7.0 on the surface wave magnitude scale and reached a maximum intensity of XI (Extreme) on the Mercalli intensity scale. The earthquake triggered a minor tsunami.
The 1994 Taiwan Strait earthquake occurred on 16 September 1994, at 14:20 local time in the southern Taiwan Strait. The magnitude of this earthquake was given as 6.8 by the USGS and 7.3 by Fujian Seismological Bureau. The epicenter was located about 150 to 180 km from the coast of the border of Guangdong and Fujian, and about 150 km southwest of Taiwan.

The 1771 Great Yaeyama Tsunami was caused by the Yaeyama Great Earthquake at about 8 A.M. on April 24, 1771, south-southeast of Ishigaki Island, part of the former Ryūkyū Kingdom and now part of present-day Okinawa, Japan. According to records, 8,439 people were killed on Ishigaki Island and 2,548 on Miyako Island.

The island of Taiwan was formed approximately 4 to 5 million years ago at a convergent boundary between the Philippine Sea Plate and the Eurasian Plate. In a boundary running the length of the island and continuing southwards, the Eurasian Plate is sliding under the Philippine Sea Plate. In the northeast of the island, the Philippine Sea Plate slides under the Eurasian Plate. Most of the island comprises a huge fault block tilted to the west.
The 1968 Hyūga-nada earthquake occurred on April 1 at . The earthquake had a magnitude of 7.5, and the epicenter was located in Hyūga-nada Sea, off the islands of Kyushu and Shikoku, Japan. The magnitude of this earthquake was also given as 7.5. A tsunami was observed. One person was killed, and 22 people were reported injured. The intensity reached shindo 5 in Miyazaki and Kōchi.

At 23:50 (UTC+8) on 6 February 2018, an earthquake of magnitude 6.4 on the moment magnitude scale hit Taiwan. The epicenter was on the coastline near Hualien, which was the most severely affected area, with a maximum felt intensity of VIII (Severe) on the Mercalli intensity scale. At least 17 deaths were reported, with 285 injured. The maximum foreshock was recorded on 4 February 2018, at 21:56:40. The epicenter was located at Hualien County, Taiwan, reaching a scale of ML 5.8.
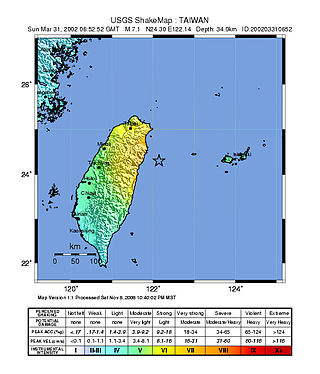
At 14:52 local time on 31 March 2002, an earthquake of magnitude 7.1 on the moment magnitude scale hit Taiwan. The epicenter was offshore from Hualien, which was the most severely affected area with a maximum felt intensity of VII on the Mercalli intensity scale. At least 5 deaths have been reported, with a further 213 injured.

The 1982 Urakawa earthquake was a 6.9 earthquake that struck off the coast of Urakawa, Japan, on 11:32 (JST), March 21, 1982. The epicenter was 42.1°N 142.6°E. The earthquake was the largest earthquake in the history of the region. The earthquake caused 167 injuries and damage in Tomakomai and Sapporo.
The 1604 Quanzhou earthquake was an extremely large seismic event that occurred in the Taiwan Strait, off the coast of Fujian Province, near Quanzhou during the Ming dynasty. According to modern-day calculations, the earthquake had a moment magnitude of 8.1 . It is unknown how many casualties resulted from the quake, but major damage was reported.

The 1867 Keelung earthquake occurred off the northern coast of Taiwan on the morning of December 18 with a magnitude of 7.0. It produced strong shaking that seriously damaged the cities of Keelung and Taipei. A tsunami, thought to be the only confirmed destructive of its kind in Taiwan, drowned hundreds and had a run-up exceeding 15 m (49 ft). The total death toll was estimated to be 580 while more than 100 were injured. It was followed by aftershocks that were felt on average ten times a day.

The Shōnai offshore earthquake occurred at around 14:00 on December 7, 1833. It struck with an epicenter in the Sea of Japan, off the coast of Yamagata Prefecture, Japan. A tsunami was triggered by the estimated MJMA 7.5–7.7 earthquake. One hundred and fifty people were killed and there was severe damage in the prefecture.
On June 5, 1920, a shallow magnitude 8.2 earthquake struck offshore Hualien County, Empire of Japan. It is currently the largest earthquake in Taiwan's modern history.

The eastern margin of the Sea of Japan is a zone of concentrated geological strain which extends several hundred kilometers and north–south along the eastern margin of the Sea of Japan. The margin has undergone convergence tectonics since the end of the Pliocene. It is believed to be an incipient subduction zone which defines the tectonic boundary between the Amurian and Okhotsk plates. This geological zone is seismically active and has been the source of destructive tsunamis. The feature runs off the west coast of Honshu, passes west of the Shakotan Peninsula on Hokkaido and through the Strait of Tartary, between Sakhalin and mainland Russia.

On 3 April 2024, at 07:58:11 NST, a 7.4 earthquake struck 15 km (9.3 mi) south of Hualien City, Hualien County, Taiwan. At least 18 people were killed and over 1,100 were injured in the earthquake. It is the strongest earthquake in Taiwan since the 1999 Jiji earthquake, with three aftershocks above Mw 6.0.















