
Mount Everest, known locally as Sagarmatha or Qomolangma, is Earth's highest mountain above sea level, located in the Mahalangur Himal sub-range of the Himalayas. The China–Nepal border runs across its summit point. Its elevation of 8,848.86 m was most recently established in 2020 by the Chinese and Nepali authorities.

The Sherpa people are one of the Tibetan ethnic groups native to the most mountainous regions of Nepal and Tibetan Autonomous Region of China.

Pumori is a mountain on the Nepal–China border in the Mahalangur section of the Himalayas. Pumori lies just eight kilometres west of Mount Everest. Pumori, meaning "the Mountain Daughter" in Sherpa language, was named by George Mallory. "Pumo" means young girl or daughter and "Ri" means mountain in Sherpa language. Climbers sometimes refer to Pumori as "Everest's Daughter". Mallory also called it Clare Peak, after his daughter.

The Khumbu Icefall is located at the head of the Khumbu Glacier and the foot of the Western Cwm. It lies at an elevation of 5,486 meters on the Nepali slopes of Mount Everest, not far above Base Camp and southwest of the summit. The icefall is regarded as one of the most dangerous sections of the South Col route to Everest's summit.

A serac is a block or column of glacial ice, often formed by intersecting crevasses on a glacier. Commonly house-sized or larger, they are dangerous to mountaineers, since they may topple with little warning. Even when stabilized by persistent cold weather, they can be an impediment to glacier travel.

Apa, nicknamed "Super Sherpa", is a Nepalese Sherpa mountaineer who, until 2017, jointly with Phurba Tashi held the record for reaching the summit of Mount Everest more times than any other climber. As part of The Eco Everest Expedition 2011, Apa made his 21st Mount Everest summit in May 2011 then retired after a promise to his wife to stop climbing after 21 ascents. He first summited Everest in 1990 and his last time to the summit was in 2011.
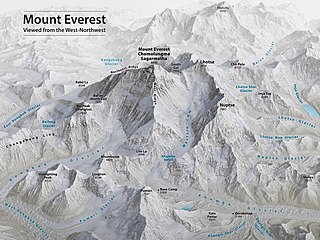
Mount Everest is the world's highest mountain, with a peak at 8,849 metres (29,031.7 ft) above sea level. It is situated in the Himalayan range of Solukhumbu district, Nepal.

The 1996 Mount Everest disaster occurred on 10–11 May 1996 when eight climbers caught in a blizzard died on Mount Everest while attempting to descend from the summit. Over the entire season, 12 people died trying to reach the summit, making it the deadliest season on Mount Everest at the time and the third deadliest after the 23 fatalities resulting from avalanches caused by the April 2015 Nepal earthquake and the 16 fatalities of the 2014 Mount Everest avalanche. The 1996 disaster received widespread publicity and raised questions about the commercialization of Everest.

The Hornbein Couloir is a narrow and steep couloir high to the west on the north face of Mount Everest in Tibet, that extends from about 8,000 to 8,500 m elevation, 350 metres below the summit.
On 9 September 1974, the West Ridge Direct on Mount Everest was attempted by a French expedition. It resulted in the deaths of six climbers in an avalanche on the way to the summit. These deaths took the total number of fatalities on the mountain to 36.

Ang Dorje (Chhuldim) Sherpa is a Nepalese sherpa mountaineering guide, climber, and porter from Pangboche, Nepal, who has reached the summit of Mount Everest 23 times. He was the climbing Sirdar for Rob Hall's Adventure Consultants expedition to Everest in spring 1996, when a freak storm led to the deaths of eight climbers from several expeditions, considered one of the worst disasters in the history of Everest mountaineering.

On 18 April 2014, seracs on the western spur of Mount Everest failed, resulting in an ice avalanche that killed sixteen climbing Sherpas in the Khumbu Icefall. This was the same icefall where the 1970 Mount Everest disaster had taken place. Thirteen bodies were recovered within two days, while the remaining three were never recovered due to the great danger in attempting such an expedition. Many Sherpas were angered by what they saw as the Nepalese government's meager offer of compensation to victims' families, and threatened a protest or strike. On 22 April, the Sherpas announced they would not work on Everest for the remainder of 2014 as a mark of respect for the victims.

The 1975 British Mount Everest Southwest Face expedition was the first to successfully climb Mount Everest by ascending one of its faces. In the post-monsoon season Chris Bonington led the expedition that used rock climbing techniques to put fixed ropes up the face from the Western Cwm to just below the South Summit. A key aspect of the success of the climb was the scaling of the cliffs of the Rock Band at about 8,200 metres (27,000 ft) by Nick Estcourt and Tut Braithwaite.

In the afternoon of 25 April 2015, a MW 7.8 earthquake struck Nepal and surrounding countries. Tremors from the quake triggered an avalanche from Pumori into Base Camp on Mount Everest. At least twenty-two people were killed, surpassing the toll of an avalanche that occurred in 2014 as the deadliest disaster on the mountain.

Asian Trekking is a Nepal-based adventure company, specializing in mountaineering expeditions and trekking in the Himalayas. Started in 1982 by UIAA Honorary Member Ang Tshering Sherpa, it is Nepal's oldest mountaineering and trekking company still in operation. In 2008, Tshering's son Dawa Steven Sherpa, an environmentalist and mountaineer, took leadership of the company.

Sherpa is a 2015 documentary film by Australian filmmaker Jennifer Peedom. It was filmed during the 2014 Mount Everest ice avalanche.

The Mount Everest climbing season of 2013 included 658 summits and 8 deaths. Due to avalanches in 2014 and 2015, this was the last big summiting year until 2016.
















