| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1973 List of years in Libya | ||||
The following lists events that happened in 1973 in Libya .
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1973 List of years in Libya | ||||
The following lists events that happened in 1973 in Libya .

Muammar Muhammad Abu Minyar al-Gaddafi was a Libyan revolutionary, politician and political theorist who ruled Libya from 1969 until his assassination by rebel forces in 2011. He came to power through a military coup, first becoming Revolutionary Chairman of the Libyan Arab Republic from 1969 to 1977 and then the 'Brotherly Leader' of the Great Socialist People's Libyan Arab Jamahiriya from 1977 to 2011. Initially ideologically committed to Arab nationalism and Nasserism, Gaddafi later ruled according to his own Third International Theory.

Benghazi is the second-most-populous city in Libya as well as the largest city in Cyrenaica, with an estimated population of 1,207,250 in 2020. Located on the Gulf of Sidra in the Mediterranean, Benghazi is also a major seaport.

In the first Gulf of Sidra incident, 19 August 1981, two Libyan Su-22 Fitters fired upon two U.S. F-14 Tomcats and were subsequently shot down off the Libyan coast. Libya had claimed that the entire Gulf was their territory, at 32° 30′ N, with an exclusive 62-nautical-mile fishing zone, which Libyan leader Muammar Gaddafi asserted as "The Line of Death" in 1973. Two further incidents occurred in the area in 1986 and in 1989.

Musa Sadr al-Din al-Sadr was an Iranian-Lebanese Shia Muslim cleric and politician. In Lebanon, he founded and revived many Lebanese Shia organizations, including schools, charities, and the Amal Movement.

Muammar Gaddafi became the de facto leader of Libya on 1 September 1969 after leading a group of young Libyan Army officers against King Idris I in a bloodless coup d'état. After the king had fled the country, the Revolutionary Command Council (RCC) headed by Gaddafi abolished the monarchy and the old constitution and established the Libyan Arab Republic, with the motto "freedom, socialism and unity". The name of Libya was changed several times during Gaddafi's tenure as leader. From 1969 to 1977, the name was the Libyan Arab Republic. In 1977, the name was changed to Socialist People's Libyan Arab Jamahiriya. Jamahiriya was a term coined by Gaddafi, usually translated as "state of the masses". The country was renamed again in 1986 as the Great Socialist People's Libyan Arab Jamahiriya, after the United States bombing that year.

Abdul Ati al-Obeidi was a Libyan politician and diplomat. He held various top posts in Libya under Muammar Gaddafi; he was Prime Minister from 1977 to 1979 and General Secretary of General People's Congress from 1979 to 1981. He was one of three main negotiators in Libya's decision to denounce and drop their nuclear weapons program.

The Revolutionary Command Council was a twelve-member governing body that ruled the Libyan Arab Republic after the 1969 Libyan coup d'état by the Free Officers Movement, which overthrew the Senussi monarchy of King Idris I. The council's chairman was Muammar Gaddafi, who had the most influence and served as Libya's de facto head of state as Revolutionary Chairman of the Libyan Arab Republic and commander-in-chief of the armed forces. It was ideologically Arab nationalist, republican, anti-imperialist and pan-Arabist.

The Sirte Basin is a late Mesozoic and Cenozoic triple junction continental rift along northern Africa that was initiated during the late Jurassic Period. It borders a relatively stable Paleozoic craton and cratonic sag basins along its southern margins. The province extends offshore into the Mediterranean Sea, with the northern boundary drawn at the 2,000 meter (m) bathymetric contour. It borders in the north on the Gulf of Sidra and extends south into northern Chad.

Moussa Muhammad El-Haj Nemr Koussa is a Libyan political figure and diplomat, who held several high-profile positions in the Libyan government, lastly as Minister of Foreign Affairs from March 2009, into the Libyan Civil War, when he resigned his position on 30 March 2011.

The Tripoli protests and clashes were a series of confrontations between Libyan anti-government demonstrators and forces loyal to Libyan leader Muammar Gaddafi in the capital city of Tripoli that took place in February 2011, at the beginning of the Libyan civil war. During the early days of the uprising, there was significant unrest in the city, but the city remained under the control of the government.
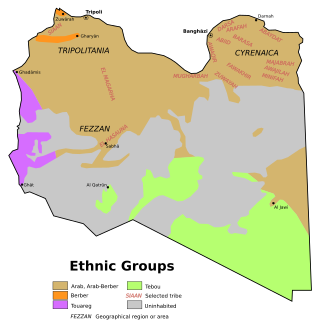
The Magarha is one of the major Arab tribes of Libya. They originate from Fezzan province of Libya and have been an influential supporters and beneficiaries of Muammar Gaddafi during his long rule and then Libya's 2011 civil war. Some Magarha have relocated to Sirte and elsewhere along the coast.
Iman al-Obeidi is a former Libyan postgraduate law student who received worldwide media attention during the Libyan Civil War. This was because she burst into the restaurant of the Rixos Hotel in Tripoli and told the international press corps there that Libyan troops had beaten and gang-raped her. Her public statement challenged both the Gaddafi government and the taboo against discussing sex crimes in Libya.
The 2011 Libyan rape allegations were controversial allegations that Gaddafi's forces in Libya were committing mass rape during the 2011 Libyan civil war. Prosecutor of the International Criminal Court Luis Moreno Ocampo said "we have information that there was a policy to rape in Libya those who were against the government." Libyan psychologist Seham Sergiwa said she distributed questionnaires in opposition-held areas and along the Libya–Tunisia border, and 259 women responded that they were raped. Sergiwa told Amnesty International's specialist on Libya that she had lost contact with the 140 victims she interviewed and was unable to provide documentary evidence. In March 2011, Iman al-Obeidi said she was gang-raped before Libyan security services dragged her away.

The killing of Muammar Gaddafi took place on 20 October 2011 after the Battle of Sirte. Muammar Gaddafi, the deposed leader of Libya, was captured by NTC forces and executed shortly afterwards.
Ali Attalah Obeidi was an Air Marshall Brigadier in the army of former Libyan leader Muammar Gaddafi until the 2011 Libyan civil war when he defected to the opposition in April. The anti-Gaddafi forces showed a video of him, to prove this defection. The video showed him saying that he had quit because Gaddafi had given orders to kill civilians and he did not want the blood of his own people on his hands. It is claimed the former general walked for fifteen days from Tripoli to the besieged city of Misrata. Obeidi claimed he had escaped from Mitaga air base to join the National Transitional Council.

Kosovo's declaration of independence from Serbia was enacted on Sunday, 17 February 2008 by a unanimous vote of the Assembly of Kosovo without popular referendum. All 11 representatives of the Serb minority boycotted the proceedings. International reaction was mixed, and the world community continues to be divided on the issue of the international recognition of Kosovo. Libya extended official diplomatic recognition to Kosovo on 25 September 2013. Serbian president Aleksandar Vučić announced in 2023 that Libya has withdrawn recognition of Kosovo.
The Cultural Revolution in Libya was a nearly four-year period of political and social change in Libya. It started with Muammar Gaddafi's declaration of a cultural revolution during a speech in Zuwara on 15 April 1973. This came after increasing tensions between Gaddafi and his colleagues in the Revolutionary Command Council (RCC) had led him to agree to step down. Gaddafi had told the RCC that he would announce his resignation to the people during his Zuwara speech, but he instead surprised them with his declaration of the Cultural Revolution. By the end of the Cultural Revolution period, Gaddafi was the uncontested leader of Libya.
The following lists events that happened in 1979 in Libya.
The following lists events that happened in 1977 in Libya.

Libya–Qatar relations are the bilateral relations between Libya and State of Qatar. The two countries are members of the Arab League and the United Nations.