| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1998 List of years in Libya | ||||
The following lists events that happened during 1998 in Libya .
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1998 List of years in Libya | ||||
The following lists events that happened during 1998 in Libya .
The earliest known human settlements in what is now the Democratic Republic of the Congo have been dated back to the Middle Stone Age, approximately 90,000 years ago. The first real states, such as the Kongo, the Lunda, the Luba and Kuba, appeared south of the equatorial forest on the savannah from the 14th century onwards.

Politics of the Democratic Republic of Congo take place in the framework of a republic in transition from a civil war to a semi-presidential republic.

The Democratic Republic of the Congo, also known as the DR Congo, the DRC, or Congo-Kinshasa, is a country in Central Africa. By land area the Congo is the second-largest country in Africa and the 11th-largest in the world. With a population of around 109 million, the Democratic Republic of the Congo is the most populous Francophone country in the world. The national capital and largest city is Kinshasa, which is also the economic center. The country is bordered by the Republic of the Congo, Central African Republic, South Sudan, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Tanzania, Zambia, Angola, the Cabinda exclave of Angola, and the South Atlantic Ocean.

The Air Force of Zimbabwe (AFZ) is the air force of the Zimbabwe Defence Forces. It was known as the Rhodesian Air Force until 1980. The Air Force of Zimbabwe saw service in the Mozambican Civil War in 1985 and the Second Congo War of 1998–2001.

Joseph Kabila Kabange is a Congolese politician who served as President of the Democratic Republic of the Congo between January 2001 and January 2019. He took office ten days after the assassination of his father, President Laurent-Désiré Kabila in the context of the Second Congo War. He was allowed to remain in power after the 2003 Pretoria Accord ended the war as the president of the country's new transitional government. He was elected as president in 2006 and re-elected in 2011 for a second term. Since stepping down after the 2018 election, Kabila, as a former president, serves as a senator for life.

The Second Congo War, also known as Africa's World War or the Great War of Africa, was a major conflict that began on 2 August 1998 in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), just over a year after the First Congo War. The war initially erupted when Congolese president Laurent-Désiré Kabila turned against his former allies from Rwanda and Uganda, who had helped him seize power. Eventually, the conflict expanded, drawing in nine African nations and approximately 25 armed groups, making it one of the largest wars in African history.
Congolese history in the 2000s has primarily revolved around the Second Congo War (1998–2003) and the empowerment of a transitional government.
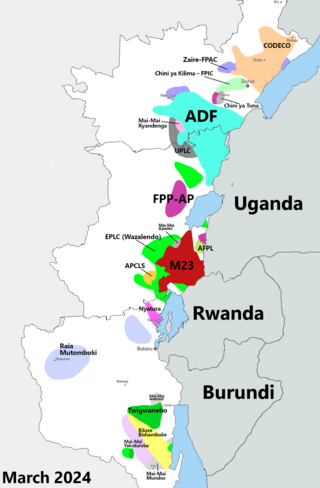
The Kivu conflict is an umbrella term for a series of protracted armed conflicts in the North Kivu and South Kivu provinces in the eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo which have occurred since the end of the Second Congo War. Including neighboring Ituri province, there are more than 120 different armed groups active in the eastern Democratic Republic of Congo. Currently, some of the most active rebel groups include the Allied Democratic Forces, the Cooperative for the Development of the Congo, the March 23 Movement, and many local Mai Mai militias. In addition to rebel groups and the governmental FARDC troops, a number of national and international organizations have intervened militarily in the conflict, including the United Nations force known as MONUSCO, and an East African Community regional force.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1952, adopted unanimously on November 29, 2010, after recalling previous resolutions on the situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, including resolutions 1807 (2008), 1857 (2008) and 1896 (2009), the Council renewed an arms embargo and related targeted sanctions for a further period until November 30, 2011.
The international reactions to the Libyan Civil War were the responses to the series of protests and military confrontations occurring in Libya against the government of Libya and its de facto head of state Muammar Gaddafi.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1970 was a measure adopted unanimously by the UN Security Council on 26 February 2011. It condemned the use of lethal force by the government of Muammar Gaddafi against protesters participating in the Libyan Civil War, and imposed a series of international sanctions in response.
The international reactions to the 2011 military intervention in Libya were the responses to the military intervention in Libya by NATO and allied forces to impose a no-fly zone. The intervention was authorized by United Nations Security Council Resolution 1973, approved in New York on 17 March, in response to the Libyan Civil War, though some governments allege participants in the operation exceeded their mandate.
The international reactions to the killing of Muammar Gaddafi concern the responses of foreign governments and supranational organisations to the killing of former Libyan leader Muammar Gaddafi at the Battle of Sirte, the last major engagement of the 2011 Libyan civil war, on 20 October 2011.
The Congolese Rally for Democracy–Goma was a faction of the Congolese Rally for Democracy, a rebel movement based in Goma, Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) during the Second Congo War (1998–2003). After the war, some members of the group continued sporadic fighting in North Kivu. The movement also entered mainstream politics, participating in democratic elections with little success.
The following lists events that happened during 2012 in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
The following lists events that happened during 1998 in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
The following lists events that happened during 1998 in Sudan.

General elections were held in the Democratic Republic of the Congo on 30 December 2018, to determine a successor to President Joseph Kabila, as well as for the 500 seats of the National Assembly and the 715 elected seats of the 26 provincial assemblies. Félix Tshisekedi (UDPS) won the presidency with 38.6% of the vote, defeating Martin Fayulu and Emmanuel Ramazani Shadary (PPRD). Fayulu alleged that the vote was rigged against him by Tshisekedi and Kabila, challenging the result in the Constitutional Court. Election observers, including the Catholic Church, also cast doubt on the official result. Nonetheless, on 20 January the Court declared Tshisekedi the winner. Parties supporting Kabila won the majority of seats in the National Assembly. Tshisekedi was sworn in as the 5th President of the Democratic Republic of the Congo on 24 January 2019, the first peaceful transition of power in the country since its independence from Belgium in 1960.

On 20 December 2016 the Democratic Republic of the Congo's president, Joseph Kabila, announced that he would not leave office despite the end of his constitutional term. Protests subsequently broke out across the country, which had never had a peaceful transfer of power since it gained independence in 1960. The protests were met with the government's blocking of social media, and violence from security forces which left dozens dead. Foreign governments condemned the attacks against protesters.
Capital punishment in the Democratic Republic of the Congo is a legal penalty; however, the nation has not carried out any executions since 2003, meaning that the country experienced a de facto moratorium on the death penalty from their latest executions in 2003 until March 2024.