| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
The following lists events that happened during 1975 in the Kingdom of Morocco .
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
The following lists events that happened during 1975 in the Kingdom of Morocco .

Western Sahara is a disputed territory in North-western Africa. It has a surface area of 272,000 square kilometres (105,000 sq mi). Approximately 30% of the territory is controlled by the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (SADR); the remaining 70% is occupied and administered by neighboring Morocco. It is the most sparsely populated country in Africa and the second most sparsely populated country in the world, mainly consisting of desert flatlands. The population is estimated at 618,600. Nearly 40% of that population lives in Morocco-controlled Laayoune, the largest city of Western Sahara.
The history of Western Sahara can be traced back to the times of Carthaginian explorer Hanno the Navigator in the 5th century BC. Though few historical records are left from that period, Western Sahara's modern history has its roots linked to some nomadic groups such as the Sanhaja group, and the introduction of Islam and the Arabic language at the end of the 8th century AD.

The Polisario Front, Frente Polisario, Frelisario or simply Polisario, is a Sahrawi nationalist liberation movement seeking to establish a Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic for the Sahrawi people through the means of self-determination and armed resistance in the disputed territory of Western Sahara.
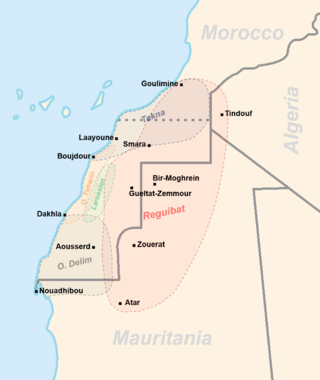
The Sahrawis, or Sahrawi people, are an ethnic group native to the western part of the Sahara desert, which includes the Western Sahara, southern Morocco, much of Mauritania, and along the southwestern border of Algeria. They are of mixed Hassani Arab and Sanhaji Berber descent, as well as West African and other indigenous populations.

Spanish Sahara, officially the Spanish Possessions in the Sahara from 1884 to 1958, then Province of the Sahara between 1958 and 1976, was the name used for the modern territory of Western Sahara when it was occupied and ruled by Spain between 1884 and 1976. It had been one of the most recent acquisitions as well as one of the last remaining holdings of the Spanish Empire, which had once extended from the Americas to the Spanish East Indies.

The Green March was a strategic mass demonstration in November 1975, coordinated by the Moroccan government and military, to force Spain to hand over the disputed, autonomous semi-metropolitan province of Spanish Sahara to Morocco. The Spanish government was preparing to abandon the territory as part of the decolonization of Africa, just as it had granted independence to Equatorial Guinea in 1968. The native inhabitants, the Sahrawi people, aspired to form an independent state. The demonstration of some 350,000 Moroccans advanced several kilometers into the Western Sahara territory. Morocco later gained control of most of the former Spanish Sahara, which it continues to hold.

The Madrid Accords, formally the Declaration of Principles on Western Sahara, was a treaty between Spain, Morocco, and Mauritania setting out six principles which would end the Spanish presence in the territory of Spanish Sahara and arrange a temporary administration in the area pending a referendum.

The International Court of Justice Advisory Opinion on Western Sahara was a 1975 advisory, non-binding opinion by the International Court of Justice (ICJ) of two questions presented to it by the UN General Assembly under Resolution 3292 regarding the disputed territory of Western Sahara. Morocco had approached the UN to adjudicate its and Mauritania's claims over the territory.
The Houston Agreement was the result of negotiations between the Polisario Front and Morocco on the organization of a referendum, which would constitute an expression of self-determination for the people of Western Sahara, possibly leading to full independence or integration within Morocco. The talks were conducted during 1997 in Houston, United States, under the auspices of United Nations representative James Baker, using the framework of the 1991 Settlement Plan. The agreement was supposed to lead to a referendum in 1998, after it had been prevented from taking place in 1992 as originally envisioned.

The Settlement Plan was an agreement between the ethnically Saharawi Polisario Front and Morocco on the organization of a referendum, which would constitute an expression of self-determination for the people of Western Sahara, leading either to full independence, or integration with the Kingdom of Morocco. It resulted in a cease-fire which remains effective until 2020, and the establishment of the MINURSO peace force to oversee it and to organize the referendum. The referendum never occurred.

To assist in the decolonization process of the Spanish Sahara, a colony in North Africa, the United Nations General Assembly in 1975 dispatched a visiting mission to the territory and the surrounding countries, in accordance with its resolution 3292.

Khalihenna Ould Errachid is a Moroccan Sahrawi politician. He is the president of the Royal Advisory Council for Saharan Affairs (CORCAS), a government body behind Morocco's proposed autonomy plan for Western Sahara.

The Western Sahara Autonomy Proposal is an initiative proposed by Morocco in 2006 as a possible solution to the Western Sahara conflict. In 2006, the Moroccan Royal Advisory Council for Saharan Affairs (CORCAS) proposed a plan for the autonomy of Western Sahara and made visits to a number of countries to explain the proposal. The Spanish approach to regional autonomy has been named as a possible model for Western Saharan autonomy, mentioning specifically the cases of the Canary Islands, the Basque Country, Andalusia, or Catalonia. The plan was presented to the UN Security Council in April 2007 and received the backing of the United States and France. This initiative constituted the main ground for the Moroccan proposal at the Manhasset negotiations.

Greater Mauritania is a term for the Mauritanian irredentist claim that generally includes the Western Sahara and other Sahrawi-populated areas of the western Sahara Desert. The term was initially used by Mauritania's first President, Mokhtar Ould Daddah, as he began claiming the territory then known as Spanish Sahara even before Mauritanian independence in 1960.

The Western Sahara War was an armed struggle between the Sahrawi indigenous Polisario Front and Morocco from 1975 to 1991, being the most significant phase of the Western Sahara conflict. The conflict erupted after the withdrawal of Spain from the Spanish Sahara in accordance with the Madrid Accords, by which it transferred administrative control of the territory to Morocco and Mauritania, but not sovereignty. In late 1975, the Moroccan government organized the Green March of some 350,000 Moroccan citizens, escorted by around 20,000 troops, who entered Western Sahara, trying to establish a Moroccan presence. While at first met with just minor resistance by the Polisario Front, Morocco later engaged a long period of guerrilla warfare with the Sahrawi nationalists. During the late 1970s, the Polisario Front, desiring to establish an independent state in the territory, attempted to fight both Mauritania and Morocco. In 1979, Mauritania withdrew from the conflict after signing a peace treaty with the Polisario Front. The war continued in low intensity throughout the 1980s, though Morocco made several attempts to take the upper hand in 1989–1991. A cease-fire agreement was finally reached between the Polisario Front and Morocco in September 1991. Some sources put the final death toll between 10,000 and 20,000 people.

In the 1970s in Morocco, after two coup attempts in 1971 and 1972, the patriotism engendered by Morocco's participation in the Middle East conflict and by the events in Western Sahara contributed to Hassan's popularity and strengthened his hand politically despite serious domestic turmoil. The king had dispatched Moroccan troops to the Sinai front after the outbreak of Arab-Israeli War in October 1973. Although they arrived too late to engage in hostilities, the action won Morocco goodwill among other Arab states. Shortly thereafter, the attention of the government turned to the annexation of then Spanish Sahara from Spain, an issue on which all major domestic parties agreed.
The Battle of Guelta Zemmur occurred on 7 October 1989, when POLISARIO guerrillas commanded by Lahbib Ayub attacked the village of Guelta Zemmur on the Moroccan side of the Moroccan Western Sahara Wall. The attack was the first major military engagement in the war since 1988, as the Polisario Front had ended negotiations with Morocco in that year. The King of Morocco, Hassan II, responded to the offensive by rejecting a second meeting with POLISARIO leaders. According to the Spanish newspaper El País, at least a hundred soldiers from both sides were killed in the clashes.
The following lists events that happened during 1975 in Spanish Sahara.

Sahrawi nationalism is a political ideology that seeks self-determination of the Sahrawi people, the indigenous population of Western Sahara. It has historically been represented by the Polisario Front. It came as a reaction against Spanish colonialist policies imposed from 1958 on, and subsequently in reaction to the Mauritanian and Moroccan invasions of 1975.

The annexation of Western Sahara occurred in two stages: 1976 and 1979. Shortly after Spain gave up control over Spanish Sahara in 1975, both Mauritania and Morocco occupied the territory. On 14 April 1976, the two countries annexed it between themselves via the Western Sahara partition agreement. However, on 14 August 1979, Mauritania renounced all territorial claims to Western Sahara and withdrew its troops, prompting Morocco to extend its annexation to formerly Mauritanian-controlled areas.