
Francesco Maurizio Cossiga was an Italian politician. A member of Christian Democracy, he was prime minister of Italy from 1979 to 1980 and the president of Italy from 1985 to 1992. Cossiga is widely considered one of the most prominent and influential politicians of the First Italian Republic.

Benedetto "Bettino" Craxi was an Italian politician, leader of the Italian Socialist Party (PSI) from 1976 to 1993, and the 45th prime minister of Italy from 1983 to 1987. He was the first PSI member to become prime minister and the second from a socialist party to hold the office. He led the third-longest government in the Italian Republic and he is considered one of the most powerful and prominent politicians of the First Italian Republic.

Alessandro "Sandro" Pertini was an Italian socialist politician who served as the president of Italy from 1978 to 1985.

Arnaldo Forlani was an Italian politician who served as the prime minister of Italy from 1980 to 1981. He also held the office of deputy prime minister, minister of foreign affairs, and minister of defence.

Amintore Fanfani was an Italian politician and statesman, who served as 32nd prime minister of Italy for five separate terms. He was one of the best-known Italian politicians after the Second World War and a historical figure of the left-wing faction of Christian Democracy. He is also considered one of the founders of the modern Italian centre-left.

Giovanni Leone was an Italian politician, jurist and university professor. A founding member of the Christian Democracy (DC), Leone served as the president of Italy from December 1971 until June 1978. He also briefly served as Prime Minister of Italy from June to December 1963 and again from June to December 1968. He was also the president of the Chamber of Deputies from May 1955 until June 1963.

The 2006 Italian presidential election was held on 8–10 May 2006. The result was the election of Giorgio Napolitano, the first time a former member of the Italian Communist Party had been elected to the presidency of the Italian Republic.

Francesco de Martino was an Italian jurist, politician, lifetime senator (1991–2002) and former Vice President of the Council of Ministers. He was considered by many to be the conscience of the Italian Socialist Party.
The term Constitutional arch was used in the post-war Italian political discourse to describe the parties that had taken part in the drafting and approval of the Italian Constitution, and which persisted as a loose coalition on certain policymaking issues.

The Legislature IV of Italy was the 4th legislature of the Italian Republic, and lasted from 16 May 1963 until 4 June 1968. Its composition was the one resulting from the general election of 28 April 1963.

The Legislature V of Italy was the 5th legislature of the Italian Republic, and lasted from 5 June 1968 until 24 May 1972. Its composition was the one resulting from the general election of 19 May 1968.
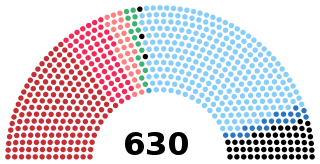
The Legislature VI of Italy was the 6th legislature of the Italian Republic, and lasted from 25 May 1972 until 4 July 1976. Its composition was the one resulting from the general election of 7 May 1972.

The Legislature VII of Italy was the 7th legislature of the Italian Republic, and lasted from 5 July 1976 until 19 June 1979. Its composition was the one resulting from the general election of 20 June 1976.

The 1992 Italian presidential election was held in Italy on 13–25 May 1992, following the resignation of President Francesco Cossiga on 28 April 1992.

The 1985 Italian presidential election was held on 24 June 1985.

The 1971 Italian presidential election was held in Italy on 9–24 December 1971.

The 1964 Italian presidential election was held in Italy from 16 to 28 December 1964, following the resignation of President Antonio Segni on 6 December 1964 due to health problems.

The 1962 Italian presidential election was held in Italy on 2–6 May 1962.

The 1948 Italian presidential election was held in Italy on 10–11 May 1948. Luigi Einaudi, governor of the Bank of Italy and member of the Liberal Party, was elected as the new President of Italy.


















