
The politics of Italy are conducted through a parliamentary republic with a multi-party system. Italy has been a democratic republic since 2 June 1946, when the monarchy was abolished by popular referendum and a constituent assembly, formed by the representatives of all the anti-fascist forces that contributed to the defeat of Nazi and Fascist forces during the liberation of Italy, was elected to draft a constitution, which was promulgated on 1 January 1948.

Christian Democracy was a Christian democratic political party in Italy. The DC was founded on 15 December 1943 in the Italian Social Republic as the nominal successor of the Italian People's Party, which had the same symbol, a crusader shield. As a Catholic-inspired, centrist, catch-all party comprising both centre-right and centre-left political factions, the DC played a dominant role in the politics of Italy for fifty years, and had been part of the government from soon after its inception until its final demise on 16 January 1994 amid the Tangentopoli scandals. Christian Democrats led the Italian government continuously from 1946 until 1981. The party was nicknamed the "White Whale" due to its huge organisation and official colour. During its time in government, the Italian Communist Party was the largest opposition party.

Enrico Berlinguer was an Italian politician and statesman. Considered the most popular leader of the Italian Communist Party (PCI), he led the PCI as the national secretary from 1972 until his death during a tense period in Italy's history, which was marked by the Years of Lead and social conflicts, such as the Hot Autumn of 1969–1970. Berlinguer was born into a middle-class family; his father was a socialist who became a deputy and later senator. After leading the party's youth wing in his hometown, he led the PCI's youth wing, the Italian Communist Youth Federation (FGCI), at the national level from 1949 to 1956. In 1968, he was elected to the country's Chamber of Deputies, and he became the leader of the PCI in 1972; he remained a deputy until his death in 1984. Under his leadership, the number of votes for the PCI peaked. The PCI's results in 1976 remain the highest for any Italian left-wing or centre-left party both in terms of votes and vote share, and the party's results in 1984, just after his death, remain the best result for an Italian left-wing party in European elections, and were toppled, in terms of vote share in a lower-turnout election, in the 2014 European Parliament election in Italy.

The Italian Communist Party was a communist and democratic socialist political party in Italy. It was founded in Livorno as the Communist Party of Italy on 21 January 1921, when it seceded from the Italian Socialist Party (PSI), under the leadership of Amadeo Bordiga, Antonio Gramsci, and Nicola Bombacci. Outlawed during the Italian fascist regime, the party continued to operate underground and played a major role in the Italian resistance movement. The party's peaceful and national road to socialism, or the Italian road to socialism, the realisation of the communist project through democracy, repudiating the use of violence and applying the Constitution of Italy in all its parts, a strategy inaugurated under Palmiro Togliatti but that some date back to Gramsci, would become the leitmotif of the party's history.

The Olive Tree was a denomination used for several successive centre-left political and electoral alliances of Italian political parties from 1995 to 2007.

The Left Democratic Front (LDF) is an alliance of left-wing political parties led by Communist Party of India (Marxist) in the Indian state of Kerala. It is the current ruling political alliance of Kerala, since 2016. It is one of the two major political alliances in Kerala, the other being Indian National Congress-led United Democratic Front, each of which has been in power alternately for the last four decades. LDF has won the elections to the State Legislature of Kerala in the years 1980, 1987, 1996, 2006, 2016 and had a historic re-election in 2021 where an incumbent government was re-elected for first time in 40 years. LDF has won 6 out of 10 elections since the formation of the alliance in 1980. The alliance consists of CPI(M), CPI and various smaller parties.

The Historic Compromise, also known as the Third Phase or the Democratic Alternative, was a historical political accommodation between Christian Democracy (DC) and the Italian Communist Party (PCI) in the 1970s.

The Party of Italian Communists was a communist party in Italy established in October 1998 by splinters from the Communist Refoundation Party (PRC). The split was led by Armando Cossutta, founder and early leader of the PRC, who opposed Fausto Bertinotti's leadership and, especially, his decision to withdraw support from Romano Prodi's first cabinet. In December 2014, the party was transformed into the Communist Party of Italy (PCd'I), which would later evolve into the new version of the Italian Communist Party (PCI).

The Italian Socialist Party was a social democratic and democratic socialist political party in Italy, whose history stretched for longer than a century, making it one of the longest-living parties of the country. Founded in Genoa in 1892, the PSI was from the beginning a big tent of Italy's political left and socialism, ranging from the revolutionary socialism of Andrea Costa to the Marxist-inspired reformist socialism of Filippo Turati and the anarchism of Anna Kuliscioff. Under Turati's leadership, the party was a frequent ally of the Italian Republican Party and the Italian Radical Party at the parliamentary level, while lately entering in dialogue with the remnants of the Historical Left and the Liberal Union during Giovanni Giolitti's governments to ensure representation for the labour movement and the working class. In the 1900s and 1910s, the PSI achieved significant electoral success, becoming Italy's first party in 1919 and during the country's Biennio Rosso in 1921, when it was victim of violent paramilitary activities from the far right, and was not able to move the country in the revolutionary direction it wanted.

The 1979 Italian general election was held in Italy on 3 June 1979. This election was called just a week before the European elections.

The 1980 Piedmontese regional election took place on 8 June 1980.

The Ligurian regional election of 1980 took place on 8 June 1980.
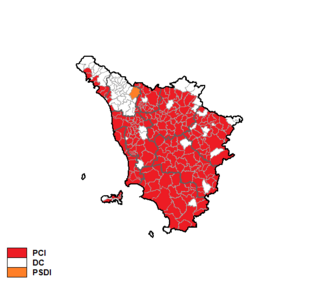
The Tuscan regional election of 1975 took place on 15 June 1975.
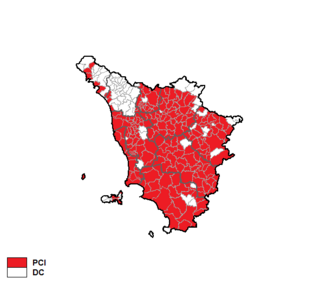
The Tuscan regional election of 1980 took place on 8 June 1980.

The Umbrian regional election of 1980 took place on 8 June 1980.

The Sardinian regional election of 1979 took place on 17 June 1979.

The Italian regional elections of 1980 were held on 8 and 9 June. The fifteen ordinary regions, created in 1970, elected their third assemblies.

Proletarian Democracy was a far-left political party in Italy.

The Communist Refoundation Party is a communist political party in Italy that emerged from a split of the Italian Communist Party (PCI) in 1991. The party's secretary is Maurizio Acerbo, who replaced Paolo Ferrero in 2017. Armando Cossutta was the party's founder, while Fausto Bertinotti its longest-serving leader (1994–2008). The latter transformed the PRC from a traditional communist party into a collection of radical social movements.





















