Related Research Articles
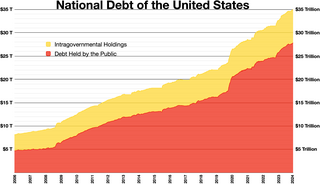
The national debt of the United States is the total national debt owed by the federal government of the United States to Treasury security holders. The national debt at any point in time is the face value of the then-outstanding Treasury securities that have been issued by the Treasury and other federal agencies. The terms "national deficit" and "national surplus" usually refer to the federal government budget balance from year to year, not the cumulative amount of debt. In a deficit year the national debt increases as the government needs to borrow funds to finance the deficit, while in a surplus year the debt decreases as more money is received than spent, enabling the government to reduce the debt by buying back some Treasury securities. In general, government debt increases as a result of government spending and decreases from tax or other receipts, both of which fluctuate during the course of a fiscal year. There are two components of gross national debt:

Fiscal policy is any changes the government makes to the national budget to influence a nation's economy. "An essential purpose of this Financial Report is to help American citizens understand the current fiscal policy and the importance and magnitude of policy reforms essential to make it sustainable. A sustainable fiscal policy is explained as the debt held by the public to Gross Domestic Product which is either stable or declining over the long term". The approach to economic policy in the United States was rather laissez-faire until the Great Depression. The government tried to stay away from economic matters as much as possible and hoped that a balanced budget would be maintained. Prior to the Great Depression, the economy did have economic downturns and some were quite severe. However, the economy tended to self-correct so the laissez faire approach to the economy tended to work.

The United States budget comprises the spending and revenues of the U.S. federal government. The budget is the financial representation of the priorities of the government, reflecting historical debates and competing economic philosophies. The government primarily spends on healthcare, retirement, and defense programs. The non-partisan Congressional Budget Office provides extensive analysis of the budget and its economic effects. It has reported that large budget deficits over the next 30 years are projected to drive federal debt held by the public to unprecedented levels—from 98 percent of gross domestic product (GDP) in 2020 to 195 percent by 2050.
The 2006 United States Federal Budget began as a proposal by President George W. Bush to fund government operations for October 1, 2005 – September 30, 2006. The requested budget was submitted to the 109th Congress on February 7, 2005.
The budget of the United States government for fiscal year 2007 was produced through a budget process involving both the legislative and executive branches of the federal government. While the Congress has the constitutional "power of the purse", the President and his appointees play a major role in budget deliberations. Since 1976, the federal fiscal year has started on October 1 of each year.
The 2008 United States Federal Budget began as a proposal by President George W. Bush to fund government operations for October 1, 2007 – September 30, 2008. The requested budget was submitted to the 110th Congress on February 5, 2007.
The United States federal budget for fiscal year 2009 began as a spending request submitted by President George W. Bush to the 110th Congress. The final resolution written and submitted by the 110th Congress to be forwarded to the President was approved by the House on June 5, 2008.

The United States Federal Budget for Fiscal Year 2010, titled A New Era of Responsibility: Renewing America's Promise, is a spending request by President Barack Obama to fund government operations for October 2009–September 2010. Figures shown in the spending request do not reflect the actual appropriations for Fiscal Year 2010, which must be authorized by Congress.
The United States Federal Budget for Fiscal Year 1997, was a spending request by President Bill Clinton to fund government operations for October 1996-September 1997. Figures shown in the spending request do not reflect the actual appropriations for Fiscal Year 1997, which must be authorized by Congress. The requested budget was submitted to Congress on February 5, 1996.
The 2011 United States federal budget was the United States federal budget to fund government operations for the fiscal year 2011. The budget was the subject of a spending request by President Barack Obama. The actual appropriations for Fiscal Year 2011 had to be authorized by the full Congress before it could take effect, according to the U.S. budget process.
The Budget of the United States Government Fiscal Year 1999
The 2004 United States Federal Budget began as a proposal by President George W. Bush to fund government operations for October 1, 2003 – September 30, 2004. The requested budget was submitted to the 108th Congress on February 3, 2003.
The United States Federal Budget for Fiscal Year 1998, was a spending request by President Bill Clinton to fund government operations for October 1997 – September 1998. Figures shown in the spending request do not reflect the actual appropriations for Fiscal Year 1998, which must be authorized by Congress.
The United States Federal Budget for Fiscal Year 2000, was a spending request by President Bill Clinton to fund government operations for October 1999-September 2000. Figures shown in the spending request do not reflect the actual appropriations for Fiscal Year 2000, which must be authorized by Congress.
The United States Federal Budget for Fiscal Year 2001, was a spending request by President Bill Clinton to fund government operations for October 2000-September 2001. Figures shown in the spending request do not reflect the actual appropriations for Fiscal Year 2001, which must be authorized by Congress.
The United States Federal Budget for Fiscal Year 2002, was a spending request by President George W. Bush to fund government operations for October 2001-September 2002. Figures shown in the spending request do not reflect the actual appropriations for Fiscal Year 2002, which must be authorized by Congress.
The 2003 United States Federal Budget began as a proposal by President George W. Bush to fund government operations for October 1, 2002 – September 30, 2003. The requested budget was submitted to the 107th Congress on February 4, 2002.
The 1995 United States federal budget is the United States federal budget to fund government operations for the fiscal year 1995, which was October 1994 – September 1995. This budget was the last to be submitted before the Republican Revolution in the 1994 midterm elections.
The 1994 United States federal budget is the United States federal budget to fund government operations for the fiscal year 1994, which was October 1993 – September 1994. This budget was the first federal budget submitted by Bill Clinton.
The 1993 United States federal budget is the United States federal budget to fund government operations for the fiscal year 1993, which was October 1992 – September 1993. This budget was the final federal budget submitted by George H. W. Bush before he was defeated by Bill Clinton in the 1992 United States presidential election.
References
- 1 2 3 4 "Budget FY 2022 - Table 1.1 - Summary of Receipts, Outlays, and Surpluses or Deficits (–): 1789–2026" (XLSX). Office of Management and Budget. Historical Tables, Budget of the United States Government, Fiscal Year 2022. Government Publishing Office. May 28, 2021. Retrieved October 31, 2021.
- 1 2 3 4 "Budget FY 2022 - Table 1.2 - Summary of Receipts, Outlays, and Surpluses or Deficits (–) as Percentages of GDP: 1930–2026" (XLSX). Office of Management and Budget. Historical Tables, Budget of the United States Government, Fiscal Year 2022. Government Publishing Office. May 28, 2021. Retrieved October 31, 2021.
- ↑ "Budget FY 2022 - Table 2.1 - Receipts by Source: 1934–2026" (XLSX). Office of Management and Budget. Historical Tables, Budget of the United States Government, Fiscal Year 2022. Government Publishing Office. May 28, 2021. Retrieved October 31, 2021.
- ↑ "Budget FY 2022 - Table 2.5 - Composition of "Other Receipts": 1940–2026" (XLSX). Office of Management and Budget. Historical Tables, Budget of the United States Government, Fiscal Year 2022. Government Publishing Office. May 28, 2021. Retrieved October 31, 2021.