Deficit
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (July 2010) |
| Submitted | February 5, 1996 [1] |
|---|---|
| Submitted by | Bill Clinton |
| Submitted to | 104th Congress |
| Total revenue | $1.5 trillion (requested) [2] $1.58 trillion (actual) [3] 18.6% of GDP (actual) [4] |
| Total expenditures | $1.64 trillion (requested) [5] $1.60 trillion (actual) [6] 18.9% of GDP (actual) [4] |
| Deficit | $21.9 billion (actual) [6] 0.3% of GDP (actual) [4] |
| Debt | $5.369 trillion (at fiscal end) 63.3% of GDP [7] |
| GDP | $8.483 trillion [4] |
| Website | Government Publishing Office |
‹ 1996 1998› | |
The United States Federal Budget for Fiscal Year 1997, [8] was a spending request by President Bill Clinton to fund government operations for October 1996-September 1997. Figures shown in the spending request do not reflect the actual appropriations for Fiscal Year 1997, which must be authorized by Congress. The requested budget was submitted to Congress on February 5, 1996.
The stated objectives for President Clinton's FY1997 budget are to: (1) Balance the federal budget within seven years by making cuts in entitlements and discretionary spending while enacting modest tax cuts and (2) Maintaining growth while protecting senior citizens, middle-class families and children. The Clinton Administration projected a US$40 billion surplus by 2002. [8]
A key aspect of the FY1997 budget is what was known as the "trigger". The trigger program essentially ensured that tax cuts after 2000 would end if the deficit was not at least US$20 billion below the Congressional Budget Office's estimate. Conversely, if the deficit was at least US$20 billion below CBO estimates then the tax cuts would continue and the money exceeding the US$20 estimate is used to reduce discretionary spending. [8]
1997 Actual Receipts by Source
(in billions of dollars)
| Source | Requested [2] | Actual [3] |
|---|---|---|
| Individual income tax | 645 | 737 |
| Corporate income tax | 185 | 182 |
| Social Security and other payroll tax | 536 | 539 |
| Excise tax | 57 | 58 |
| Estate and gift taxes | 17 | 20 |
| Customs duties | 20 | 18 |
| Other miscellaneous receipts | 32 | 25 |
| Total | 1,495 | 1,579 |
The President's budget for FY1997 totals $1.635 trillion. Percentages in parentheses indicate estimated percentage change compared to 1996. This budget request is broken down by the following expenditures:
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (July 2010) |
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (July 2010) |
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (July 2010) |
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (July 2010) |
PAYGO is the practice of financing expenditures with funds that are currently available rather than borrowed.

The United States budget comprises the spending and revenues of the U.S. federal government. The budget is the financial representation of the priorities of the government, reflecting historical debates and competing economic philosophies. The government primarily spends on healthcare, retirement, and defense programs. The non-partisan Congressional Budget Office provides extensive analysis of the budget and its economic effects. CBO estimated in February 2024 that Federal debt held by the public is projected to rise from 99 percent of GDP in 2024 to 116 percent in 2034 and would continue to grow if current laws generally remained unchanged. Over that period, the growth of interest costs and mandatory spending outpaces the growth of revenues and the economy, driving up debt. Those factors persist beyond 2034, pushing federal debt higher still, to 172 percent of GDP in 2054.
The 2006 United States Federal Budget began as a proposal by President George W. Bush to fund government operations for October 1, 2005 – September 30, 2006. The requested budget was submitted to the 109th Congress on February 7, 2005.
The budget of the United States government for fiscal year 2007 was produced through a budget process involving both the legislative and executive branches of the federal government. While the Congress has the constitutional "power of the purse", the President and his appointees play a major role in budget deliberations. Since 1976, the federal fiscal year has started on October 1 of each year.
The 2008 United States Federal Budget began as a proposal by President George W. Bush to fund government operations for October 1, 2007 – September 30, 2008. The requested budget was submitted to the 110th Congress on February 5, 2007.
The United States federal budget for fiscal year 2009 began as a spending request submitted by President George W. Bush to the 110th Congress. The final resolution written and submitted by the 110th Congress to be forwarded to the President was approved by the House on June 5, 2008.

The United States Federal Budget for Fiscal Year 2010, titled A New Era of Responsibility: Renewing America's Promise, is a spending request by President Barack Obama to fund government operations for October 2009–September 2010. Figures shown in the spending request do not reflect the actual appropriations for Fiscal Year 2010, which must be authorized by Congress.
The 2011 United States federal budget was the budget to fund government operations for the fiscal year 2011. The budget was the subject of a spending request by President Barack Obama. The actual appropriations for Fiscal Year 2011 had to be authorized by the Congress before they could take effect, according to the U.S. budget process.
The 2012 United States federal budget was the budget to fund government operations for the fiscal year 2012, which lasted from October 1, 2011, through September 30, 2012. The original spending request was issued by President Barack Obama in February 2011. That April, the Republican-held House of Representatives announced a competing plan, The Path to Prosperity, emboldened by a major victory in the 2010 Congressional elections associated with the Tea Party movement. The budget plans were both intended to focus on deficit reduction, but differed in their changes to taxation, entitlement programs, defense spending, and research funding.
The Budget of the United States Government Fiscal Year 1999
The 1996 United States federal budget is the United States federal budget to fund government operations for the fiscal year 1996, which was October 1995 – September 1996. This budget was the first to be submitted after the Republican Revolution in the 1994 midterm elections. Disagreements between Democratic President Bill Clinton and Republicans led by Speaker of the House Newt Gingrich resulted in the United States federal government shutdown of 1995 and 1996.
The United States Federal Budget for Fiscal Year 1998, was a spending request by President Bill Clinton to fund government operations for October 1997 – September 1998. Figures shown in the spending request do not reflect the actual appropriations for Fiscal Year 1998, which must be authorized by Congress.
The United States Federal Budget for Fiscal Year 2000, was a spending request by President Bill Clinton to fund government operations for October 1999-September 2000. Figures shown in the spending request do not reflect the actual appropriations for Fiscal Year 2000, which must be authorized by Congress.
The United States Federal Budget for Fiscal Year 2002, was a spending request by President George W. Bush to fund government operations for October 2001-September 2002. Figures shown in the spending request do not reflect the actual appropriations for Fiscal Year 2002, which must be authorized by Congress.
The 2005 United States Federal Budget began as a proposal by President George W. Bush to fund government operations for October 1, 2004 – September 30, 2005. The requested budget was submitted to the 108th Congress on February 2, 2004.
The 2013 United States federal budget is the budget to fund government operations for the fiscal year 2013, which began on October 1, 2012, and ended on September 30, 2013. The original spending request was issued by President Barack Obama in February 2012.
The 1995 United States federal budget is the United States federal budget to fund government operations for the fiscal year 1995, which was October 1994 – September 1995. This budget was the last to be submitted before the Republican Revolution in the 1994 midterm elections.
The 1994 United States federal budget is the United States federal budget to fund government operations for the fiscal year 1994, which was October 1993 – September 1994. This budget was the first federal budget submitted by Bill Clinton.
The 1993 United States federal budget is the United States federal budget to fund government operations for the fiscal year 1993, which was October 1992 – September 1993. This budget was the final federal budget submitted by George H. W. Bush before he was defeated by Bill Clinton in the 1992 United States presidential election.
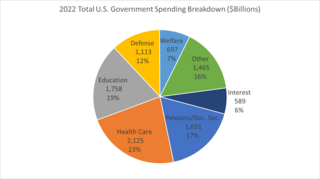
Government spending in the United States is the spending of the federal government of the United States and the spending of its state and local governments.