
William Ernest McKibben is an American environmentalist, author, and journalist who has written extensively on the impact of global warming. He is the Schumann Distinguished Scholar at Middlebury College and leader of the climate campaign group 350.org. He has authored a dozen books about the environment, including his first, The End of Nature (1989), about climate change, and Falter: Has the Human Game Begun to Play Itself Out? (2019), about the state of the environmental challenges facing humanity and future prospects.

Michael Herman Michaud is an American businessman and politician from Maine. Michaud served as the U.S. representative for Maine's 2nd congressional district from 2003 to 2015. He is a member of the Democratic Party. The primarily rural district comprises nearly 80% of the state by area and includes the cities of Lewiston, Auburn, Bangor, Presque Isle, and Ellsworth. It is the largest Congressional district by area east of the Mississippi River.

Carol Martha Browner is an American lawyer, environmentalist, and businesswoman, who served as director of the White House Office of Energy and Climate Change Policy in the Obama administration from 2009 to 2011. Browner previously served as Administrator of the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) during the Clinton administration from 1993 to 2001. She currently works as a Senior Counselor at Albright Stonebridge Group, a global business strategy firm.

Kenneth Lee Salazar is an American lawyer, politician, and diplomat who is the United States ambassador to Mexico. He previously served as the 50th United States Secretary of the Interior in the administration of President Barack Obama from 2009 to 2013. A member of the Democratic Party, he previously was a United States Senator from Colorado from 2005 to 2009. He and Mel Martínez (R-Florida) were the first Hispanic U.S. Senators since 1977; they were joined by Bob Menendez in 2006. Prior to his election to the U.S. Senate, he served as Attorney General of Colorado from 1999 to 2005.

Power Shift is an annual youth summit which has been held in New Zealand, Australia, Canada, the United Kingdom and the United States. Other Power Shift Conferences are also being organised by members of the International Youth Climate Movement including Africa, Japan and India. The focus of the events is on climate change policy.

The energy policy of the United States is determined by federal, state, and local entities. It addresses issues of energy production, distribution, consumption, and modes of use, such as building codes, mileage standards, and commuting policies. Energy policy may be addressed via legislation, regulation, court decisions, public participation, and other techniques.

The Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007, originally named the Clean Energy Act of 2007, is an Act of Congress concerning the energy policy of the United States. As part of the Democratic Party's 100-Hour Plan during the 110th Congress, it was introduced in the United States House of Representatives by Representative Nick Rahall of West Virginia, along with 198 cosponsors. Even though Rahall was 1 of only 4 Democrats to oppose the final bill, it passed in the House without amendment in January 2007. When the Act was introduced in the Senate in June 2007, it was combined with Senate Bill S. 1419: Renewable Fuels, Consumer Protection, and Energy Efficiency Act of 2007. This amended version passed the Senate on June 21, 2007. After further amendments and negotiation between the House and Senate, a revised bill passed both houses on December 18, 2007 and President Bush, a Republican, signed it into law on December 19, 2007, in response to his "Twenty in Ten" challenge to reduce gasoline consumption by 20% in 10 years.
The Chesapeake Climate Action Network (CCAN) is a grassroots nonprofit organization dedicated to fighting global warming in Maryland, Virginia, and the District of Columbia. The organization's mission is to foster a rapid societal switch to clean energy and energy-efficient products, joining similar efforts worldwide to address global warming.

The Global Warming Pollution Reduction Act of 2007 (S. 309) was a bill proposed to amend the 1963 Clean Air Act, a bill that aimed to reduce emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2). A U.S. Senator, Bernie Sanders (I-VT), introduced the resolution in the 110th United States Congress on January 16, 2007. The bill was referred to the Senate Committee on Environment and Public Works but was not enacted into law.
The environmental policy of the United States is a federal governmental action to regulate activities that have an environmental impact in the United States. The goal of environmental policy is to protect the environment for future generations while interfering as little as possible with the efficiency of commerce or the liberty of the people and to limit inequity in who is burdened with environmental costs. As his first official act bringing in the 1970s, President Richard Nixon signed the U.S. National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) into law on New Years Day, 1970. Also in the same year, America began celebrating Earth Day, which has been called "the big bang of U.S. environmental politics, launching the country on a sweeping social learning curve about ecological management never before experienced or attempted in any other nation." NEPA established a comprehensive US national environmental policy and created the requirement to prepare an environmental impact statement for “major federal actions significantly affecting the quality of the environment.” Author and consultant Charles H. Eccleston has called NEPA, the world's “environmental Magna Carta”.
New Energy for America was a plan led by Barack Obama and Joe Biden beginning in 2008 to invest in renewable energy sources, reduce reliance on foreign oil, address global warming issues, and create jobs for Americans. The main objective of the New Energy for America plan was to implement clean energy sources in the United States to switch from nonrenewable resources to renewable resources. The plan led by the Obama Administration aimed to implement short-term solutions to provide immediate relief from pain at the pump, and mid- to- long-term solutions to provide a New Energy for America plan. The goals of the clean energy plan hoped to: invest in renewable technologies that will boost domestic manufacturing and increase homegrown energy, invest in training for workers of clean technologies, strengthen the middle class, and help the economy.

Climate change in Massachusetts affects both urban and rural environments, including forestry, fisheries, agriculture, and coastal development. The Northeast is projected to warm faster than global average temperatures; by 2035, the Northeast is "projected to be more than 3.6°F (2°C) warmer on average than during the preindustrial era."

David J. Hayes is an American attorney and legal scholar who serves in the Biden Administration as Special Assistant to the President for Climate Policy. Hayes has led White House work on clean energy deployment issues, climate resilience and greenhouse gas emission reduction and carbon sequestration initiatives. Hayes also has assisted in developing and implementing the climate-related provisions included in the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act and the Inflation Reduction Act.

Power Shift Network is a North American non-profit organization made up of a network of youth-led social and environmental justice organizations working together to build the youth clean energy and climate movement. It runs campaigns in the United States and Canada to build grassroots power and advocate for tangible changes on climate change and social justice at local, state, national and international levels in North America. The organization changed its name from Energy Action Coalition in July 2016 in order to reflect its new leadership and it shift from a coalition to a network structure. The Power Shift Network's members, which include other non-profit organizations and student groups focused on environmental justice, social justice, and climate change, focus their organizing and campaigns on campuses, communities, corporate practices, and politics. The Power Shift Network is part of the Global Youth Climate Movement.

Philip David Radford is an American activist who served as the executive director of Greenpeace USA. He is the founder and President of Progressive Power Lab, an organization that incubates companies and non-profits that build capacity for progressive organizations, including a donor advisory organization Champion.us, the Progressive Multiplier Fund and Membership Drive. Radford is a co-founder of the Democracy Initiative, was founder and executive director of Power Shift, and is a board member of the Mertz Gilmore Foundation. He has a background in grassroots organizing, corporate social responsibility, climate change, and clean energy.

350.org is an international environmental organization addressing the climate crisis. Its stated goal is to end the use of fossil fuels and transition to renewable energy by building a global, grassroots movement.
Post Carbon Institute (PCI) is a think tank which provides information and analysis on climate change, energy scarcity, and other issues related to sustainability and long term community resilience. Its Fellows specialize in various fields related to the organization's mission, such as fossil fuels, renewable energy, food, water, and population. Post Carbon is incorporated as a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization and is based in Corvallis, Oregon, United States.

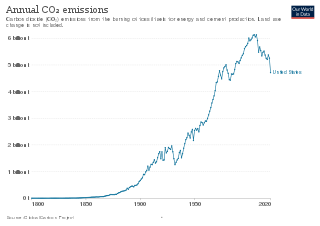
The climate change policy of the United States has major impacts on global climate change and global climate change mitigation. This is because the United States is the second largest emitter of greenhouse gasses in the world after China, and is among the countries with the highest greenhouse gas emissions per person in the world. In total, the United States has emitted over 400 billion metric tons of greenhouse gasses, more than any country in the world.

The energy policy of the Obama administration was defined by an "all-of-the-above" approach which offered federal support for renewable energy deployment, increased domestic oil and gas extraction, and export of crude oil and natural gas. His presidency's first term was shaped by the failure of his signature climate legislation, the American Clean Energy and Security Act, to pass, and then climate and energy disasters including the Deepwater Horizon oil spill in 2010 and then Hurricane Sandy, which took place during the 2012 election. In his second term, Obama lifted the ban on crude oil exports and approved liquified natural gas exports; his planned regulatory approach to reducing greenhouse pollution in the electricity sector, the Clean Power Plan, was blocked by the U.S. Supreme Court.

The environmental policy of the Donald Trump administration represented a shift from the policy priorities and goals of the preceding Barack Obama administration. Where President Obama's environmental agenda prioritized the reduction of carbon emissions through the use of renewable energy with the goal of conserving the environment for future generations, the Trump administration policy was for the US to attain energy independence based on fossil fuel use and to rescind many environmental regulations. By the end of Trump's term, his administration had rolled back 98 environmental rules and regulations, leaving an additional 14 rollbacks still in progress. As of early 2021, the Biden administration was making a public accounting of regulatory decisions under the Trump administration that had been influenced by politics rather than science.

















