
Acenaphthene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) consisting of naphthalene with an ethylene bridge connecting positions 1 and 8. It is a colourless solid. Coal tar consists of about 0.3% of this compound.

Carbazole is an aromatic heterocyclic organic compound. It has a tricyclic structure, consisting of two six-membered benzene rings fused on either side of a five-membered nitrogen-containing ring. The compound's structure is based on the indole structure, but in which a second benzene ring is fused onto the five-membered ring at the 2–3 position of indole.

3,3'-Dichlorobenzidine is an organic compound with the formula (C6H3Cl(NH2))2. The pure compound is pale yellow, but commercial samples are often colored. It is barely soluble in water and is often supplied as a wet paste. It is widely used in the production of diarylide yellow pigments used in the production of printing inks. Its use in the production of dyes has been largely discontinued because of concerns about carcinogenicity.
1,2-Dichloro-4-nitrobenzene is an organic compound with the formula 1,2-Cl2C6H3-4-NO2. This pale yellow solid is related to 1,2-dichlorobenzene by the replacement of one H atom with a nitro functional group. This compound is an intermediate in the synthesis of agrochemicals.

Phthalonitrile is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(CN)2, which is an off-white crystal solid at room temperature. It is a derivative of benzene, containing two adjacent nitrile groups. The compound has low solubility in water but is soluble in common organic solvents. The compound is used as a precursor to phthalocyanine and other pigments, fluorescent brighteners, and photographic sensitizers.
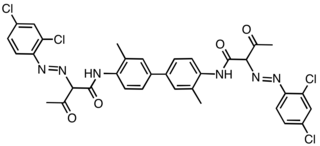
Pigment Yellow 16 is an organic compound that is classified as a diarylide pigment.
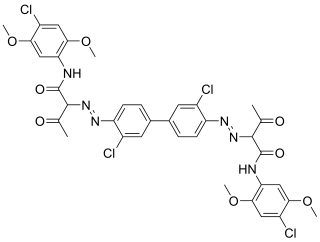
Pigment Yellow 83 is an organic compound that is classified as a diarylide pigment. It is used as a yellow colorant.

Pigment Yellow 81 is an organic compound that is classified as a diarylide pigment. It is used as a yellow colorant.
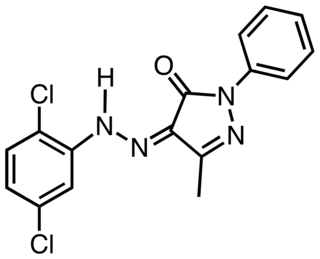
Pigment Yellow 10 is an organic compound that is classified as a monoazopyrazolone pigment. It is used as a yellow colorant, notably as yellow road marking on highways in the US.
Pigment Red 190, also called Vat Red 29, is a synthetic organic compound that is used both as a pigment and as a vat dye. Although structurally a derivative of perylene, it is produced from acenaphthene.
Pigment Red 149 is an organic compound that is used as a pigment. Structurally, it is a derivative of perylene, although it is produced from perylenetetracarboxylic dianhydride by derivatization with 3,5-dimethylaniline.
Pigment Red 178 is an organic compound that is used as a pigment. Structurally, it is a derivative of perylene, although it is produced from perylenetetracarboxylic dianhydride by derivatization with 4-aminoazobenzene.

Pigment Red 179 is an organic compound that is used as a pigment. Structurally, it is a derivative of perylene, although it is produced from perylenetetracarboxylic dianhydride by derivatization with methylamine.

Pigment yellow 139 is an organic compound that is used as a yellow-orange pigment. It is classified as a derivative of isoindoline. This yellow-orange solid is virtually insoluble in most solvents.
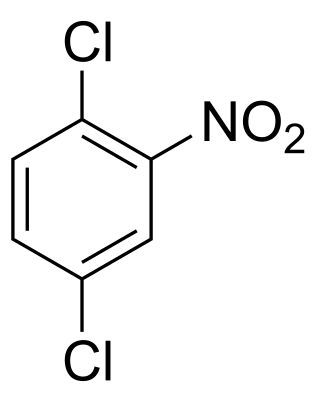
1,4-Dichloro-2-nitrobenzene is an organic compound with the formula C6H3Cl2NO2. One of several isomers of dichloronitrobenzene, it is a yellow solid that is insoluble in water. It is produced by nitration of 1,4-dichlorobenzene. It is a precursor to many derivatives of commercial interest. Hydrogenation gives 1,4-dichloroaniline. Nucleophiles displace the chloride adjacent to the nitro group: ammonia gives the aniline derivative, aqueous base gives the phenol derivative, and methoxide gives the anisole derivative. These compounds are respectively 4-chloro-2-nitroaniline, 4-chloro-2-nitrophenol, and 4-chloro-2-nitroanisole.
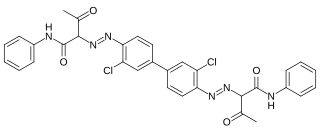
Pigment Yellow 12 is an organic compound and an azo compound. It is a widely used yellow pigment. It is also classified as a diarylide pigment, being derived from 3,3'-dichlorobenzidine. It is closely related to Pigment Yellow 13, wherein the two phenyl groups are replaced by 2,4-xylyl.
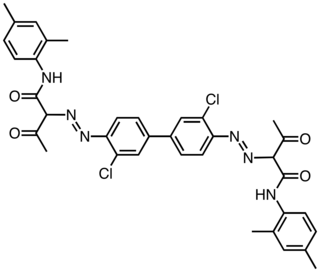
Pigment Yellow 13 is an organic compound and an azo compound. It is a widely used yellow pigment. It is also classified as a diarylide pigment, being derived from 3,3'-dichlorobenzidine. It is closely related to Pigment Yellow 12, wherein the two xylyl groups are replaced by phenyl.

2,6-Dichloroaniline is an organic compound with the formula C6H3Cl2(NH2). It is one of several isomers of dichloroaniline. It is a colorless or white solid. Derivatives include the drugs clonidine and diclofenac.
3,4-Dichloroaniline is an organic compound with the formula C6H3Cl2(NH2). It is one of several isomers of dichloroaniline. It is a white solid although commercial samples often appear gray. It is a precursor to dyes, agricultural chemicals, and drugs including the antimalarial chlorproguanil and the herbicides propanil, linuron, DCMU, and diuron.

2,3-Dichloroaniline is an organic compound with the formula C6H3Cl2(NH2). It is one of several isomers of dichloroaniline. It is a colorless oil although commercial samples often appear colored. It is produced by hydrogenation of 2,3-dichloronitrobenzene.
















