
Petrochemicals are the chemical products obtained from petroleum by refining. Some chemical compounds made from petroleum are also obtained from other fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas, or renewable sources such as maize, palm fruit or sugar cane.
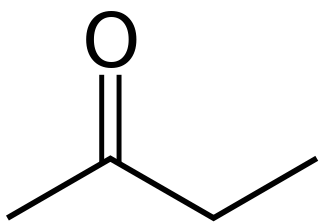
Butanone, also known as methyl ethyl ketone (MEK) or ethyl methyl ketone, is an organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)CH2CH3. This colorless liquid ketone has a sharp, sweet odor reminiscent of acetone. It is produced industrially on a large scale, but occurs in nature only in trace amounts. It is partially soluble in water, and is commonly used as an industrial solvent. It is an isomer of another solvent, tetrahydrofuran.

Terpenes are a class of natural products consisting of compounds with the formula (C5H8)n for n ≥ 2. Terpenes are major biosynthetic building blocks. Comprising more than 30,000 compounds, these unsaturated hydrocarbons are produced predominantly by plants, particularly conifers. In plants, terpenes and terpenoids are important mediators of ecological interactions, while some insects use some terpenes as a form of defense. Other functions of terpenoids include cell growth modulation and plant elongation, light harvesting and photoprotection, and membrane permeability and fluidity control.

Tetrahydrofuran (THF), or oxolane, is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4O. The compound is classified as heterocyclic compound, specifically a cyclic ether. It is a colorless, water-miscible organic liquid with low viscosity. It is mainly used as a precursor to polymers. Being polar and having a wide liquid range, THF is a versatile solvent. It is an isomer of another solvent, butanone.

Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is an organosulfur compound with the formula (CH3)2SO. This colorless liquid is the sulfoxide most widely used commercially. It is an important polar aprotic solvent that dissolves both polar and nonpolar compounds and is miscible in a wide range of organic solvents as well as water. It has a relatively high boiling point. DMSO is metabolised to compounds that leave a garlic-like taste in the mouth after DMSO is absorbed by skin.

Polyvinyl alcohol (PVOH, PVA, or PVAl) is a water-soluble synthetic polymer. It has the idealized formula [CH2CH(OH)]n. It is used in papermaking, textile warp sizing, as a thickener and emulsion stabilizer in polyvinyl acetate (PVAc) adhesive formulations, in a variety of coatings, and 3D printing. It is colourless (white) and odorless. It is commonly supplied as beads or as solutions in water. Without an externally added crosslinking agent, PVA solution can be gelled through repeated freezing-thawing, yielding highly strong, ultrapure, biocompatible hydrogels which have been used for a variety of applications such as vascular stents, cartilages, contact lenses, etc.
Organochlorine chemistry is concerned with the properties of organochlorine compounds, or organochlorides, organic compounds containing at least one covalently bonded atom of chlorine. The chloroalkane class includes common examples. The wide structural variety and divergent chemical properties of organochlorides lead to a broad range of names, applications, and properties. Organochlorine compounds have wide use in many applications, though some are of profound environmental concern, with TCDD being one of the most notorious.
In materials science, the sol–gel process is a method for producing solid materials from small molecules. The method is used for the fabrication of metal oxides, especially the oxides of silicon (Si) and titanium (Ti). The process involves conversion of monomers in solution into a colloidal solution (sol) that acts as the precursor for an integrated network of either discrete particles or network polymers. Typical precursors are metal alkoxides. Sol–gel process is used to produce ceramic nanoparticles.
Straight-chain terminal alkenes, also called linear alpha olefins (LAO) or normal alpha olefins (NAO), are alkenes (olefins) having a chemical formula CnH2n, distinguished from other alkenes with a similar molecular formula by being terminal alkenes, in which the double bond occurs at the alpha position, and by having a linear (unbranched) hydrocarbon chain.

Hafnium(IV) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula HfCl4. This colourless solid is the precursor to most hafnium organometallic compounds. It has a variety of highly specialized applications, mainly in materials science and as a catalyst.

Thiodiglycol, or bis(2-hydroxyethyl)sulfide (also known as 2,2-thiodiethanol or TDE), is the organosulfur compound with the formula S(CH2CH2OH)2. It is miscible with water and polar organic solvents. It is a colorless liquid. It is structurally similar to diethylene glycol.

2-Ethylhexanol is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3CH2CH2CH2CH(CH2CH3)CH2OH. It is a branched, eight-carbon chiral alcohol. It is a colorless liquid that is poorly soluble in water but soluble in most organic solvents. It is produced on a large scale (>2,000,000,000 kg/y) for use in numerous applications such as solvents, flavors, and fragrances and especially as a precursor for production of other chemicals such as emollients and plasticizers. It is encountered in plants, fruits, and wines. The odor has been reported as "heavy, earthy, and slightly floral" for the R enantiomer and "a light, sweet floral fragrance" for the S enantiomer.

1-Butanol, also known as butan-1-ol or n-butanol, is a primary alcohol with the chemical formula C4H9OH and a linear structure. Isomers of 1-butanol are isobutanol, butan-2-ol and tert-butanol. The unmodified term butanol usually refers to the straight chain isomer.

Cyclic olefin copolymer (COC) is an amorphous polymer made by several polymer manufacturers. COC is a relatively new class of polymers as compared to commodities such as polypropylene and polyethylene. This newer material is used in a wide variety of applications including packaging films, lenses, vials, displays, and medical devices.
Oxo alcohols are alcohols that are prepared by adding carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen to an olefin to obtain an aldehyde using the hydroformylation reaction and then hydrogenating the aldehyde to obtain the alcohol. An intermediate step of adding two aldehydes together to obtain a larger aldehyde can precede the hydrogenation. Long chain oxo-alcohols are often prepared using alpha-olefins from the Shell higher olefin process, to give secondary alcohols such as isodecyl alcohol.
Isopropyl alcohol is a colorless, flammable organic compound with a pungent alcoholic odor.
In organosilicon chemistry, polysilazanes are polymers in which silicon and nitrogen atoms alternate to form the basic backbone. Since each silicon atom is bound to two separate nitrogen atoms and each nitrogen atom to two silicon atoms, both chains and rings of the formula [R2Si−NR]n occur. R can be hydrogen atoms or organic substituents. If all substituents R are hydrogen atoms, the polymer is designated as perhydropolysilazane, polyperhydridosilazane, or inorganic polysilazane ([H2Si−NH]n). If hydrocarbon substituents are bound to the silicon atoms, the polymers are designated as Organopolysilazanes. Molecularly, polysilazanes [R2Si−NH]n are isoelectronic with and close relatives to polysiloxanes [R2Si−O]n (silicones).

Tantalum(V) ethoxide is a metalorganic compound with formula Ta2(OC2H5)10, often abbreviated as Ta2(OEt)10. It is a colorless solid that dissolves in some organic solvents but hydrolyzes readily. It is used to prepare films of tantalum(V) oxide.
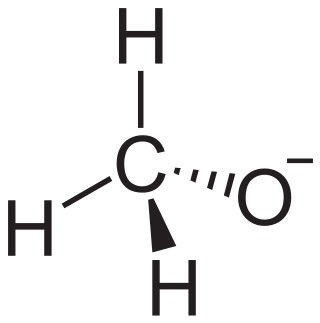
In chemistry, an alkoxide is the conjugate base of an alcohol and therefore consists of an organic group bonded to a negatively charged oxygen atom. They are written as RO−, where R is the organyl substituent. Alkoxides are strong bases and, when R is not bulky, good nucleophiles and good ligands. Alkoxides, although generally not stable in protic solvents such as water, occur widely as intermediates in various reactions, including the Williamson ether synthesis. Transition metal alkoxides are widely used for coatings and as catalysts.















