
The history of the Maldives is intertwined with the history of the broader Indian subcontinent and the surrounding regions, comprising the areas of South Asia and the Indian Ocean. The modern nation is formed of 26 natural atolls, comprising 1194 islands. Historically, the Maldives has held strategic importance due to its location on the major marine routes of the Indian Ocean. The Maldives's nearest neighbors are the British Indian Ocean Territory, Sri Lanka and India. The United Kingdom, Sri Lanka, and some Indian kingdoms have had cultural and economic ties with the Maldives for centuries. In addition to these countries, Maldivians also traded with Aceh and many other kingdoms in what is today Indonesia and Malaysia. The Maldives provided the primary source of cowrie shells, which were then used as currency throughout Asia and parts of the East African coast. Most likely, the Maldives were influenced by the Kalingas of ancient India. The Kalingas were the earliest region of India to trade with Sri Lanka and the Maldives and were responsible for the spread of Buddhism. Stashes of Chinese crockery found buried in various locations in the Maldives also show that there was direct or indirect trade contact between China and the Maldives. In 1411 and 1430, the Chinese admiral Zheng He (鄭和) visited the Maldives. The Chinese also became the first country to establish a diplomatic office in the Maldives when the Chinese nationalist government based in Taipei opened an embassy in Malé in 1966. The Embassy of the People's Republic of China has since replaced this office.

The Maldivian Democratic Party is the first political party formed in the Republic of Maldives with a total membership of 50,980 individuals as of July 28, 2024.

Elections in Benin take place within the framework of a multi-party democracy and a presidential system. Both the President and the National Assembly are directly elected by voters, with elections organised by the Autonomous National Electoral Commission (CENA).

General elections were held in the Central African Republic on March 13, 2005 to elect the President and National Assembly. A second round was held for both elections on May 8, marking the end of the transitional process that began with the seizure of power by François Bozizé in a March 2003 coup, overthrowing President Ange-Félix Patassé. A new constitution was approved in a referendum in December 2004 and took effect the same month.

General elections were held in Uganda on 23 February 2006. They were the first multi-party elections since President Yoweri Museveni took over power in 1986, and followed a referendum the previous year on scrapping the ban on party politics.

Guatemalan Christian Democracy was a Christian democratic political party in Guatemala. The DCG was a member of Christian Democrat International.

The Party for Social Renewal is a political party in Guinea-Bissau. It is one of the country's leading parties and is currently the main opposition party.

The Nigerien Party for Democracy and Socialism is a political party in Niger. It is a broadly left-leaning party, part of the Socialist International; it came to power in 2011 following the election of the former long-time leader Mahamadou Issoufou. Mohamed Bazoum is the former president of the party and the former Secretary-General is Foumakoye Gado.
The Orange Democratic Movement (ODM) is a centre-left political party in Kenya. It is the successor of a grassroots people's movement that was formed during the 2005 Kenyan constitutional referendum campaign. This movement separated in August 2007 into the Orange Democratic Movement Party of Kenya and the Wiper Democratic Movement – Kenya.
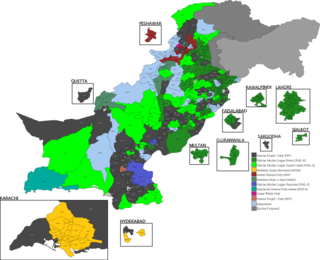
General elections were held in Pakistan on 18 February 2008 to elect members of the 13th National Assembly and the four Provincial Assemblies.

Mohamed Waheed Hassan Manik is a Maldivian politician who served as president of the Maldives from 7 February 2012 to 17 November 2013, having succeeded to the office following the resignation of President Mohamed Nasheed, under whom he served as Vice President. He had previously worked as a news anchor, a teacher, a principle, a United Nations international civil servant with UNICEF, UNDP and UNESCO, and as member of the Maldivian Parliament.

Parliamentary elections were held in Iran on 8 March 1996, with a second round on 19 April. The Combatant Clergy Association and its allies emerged as the largest bloc in the Majlis, winning 110 of the 270 seats.
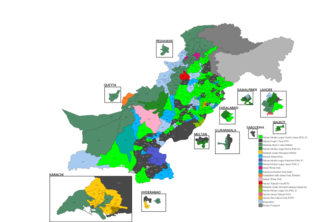
General elections were held in Pakistan on 10 October 2002 to elect the 12th National Assembly and four Provincial Assemblies. The elections were held under the military government of Pervez Musharraf. The two mainstream parties, Pakistan Peoples Party (PPP) and Pakistan Muslim League (N) (PML-N) had several restrictions imposed on them and their leaders Benazir Bhutto and Nawaz Sharif were in exile. In order to address the restrictions, PPP created the Pakistan Peoples Party Parliamentarians (PPPP) under the leadership of Ameen Faheem, to contest the elections on its behalf. The PML-N meanwhile, suffering from the party's division into two factions: one that remained loyal to Sharif and were contesting the elections under the leadership of Javed Hashmi, and the other which had broken away to form the pro-Musharraf Pakistan Muslim League (Q) (PML-Q) under the leadership of Mian Muhammad Azhar. The emergence of the PML-Q marked the beginning of multi-party politics in the country, bringing an end to the decade-long two-party system between the PPP and PML-N.
Elections were held in the state of Western Australia on 24 April 1901 to elect 50 members to the Western Australian Legislative Assembly. It was the first election to take place since responsible government without the towering presence of Premier Sir John Forrest, who had left state politics two months earlier to enter the first Federal parliament representing the Division of Swan, and the first state parliamentary election to follow the enactment of women's suffrage in 1899.

Ibrahim Ismail, popularly known as ‘Ibra’, is a Maldivian politician and former member of the People’s Majlis and the Special Majlis. Prior to his career in politics, he was also an administrator in the education sector.

The parliamentary election for the 9th Islamic Consultative Assembly, or Majlis, were held in Iran on Friday, 2 March 2012 with a second round on 4 May 2012 in those 65 districts where no candidate received 25% or more of the votes cast. More than 5,000 candidates registered but more than a third were disqualified by the Guardian Council leaving about 3,400 candidates to run for the 290 seat representing the 31 provinces.

General elections were held in Libya on 19 February 1952 to elect the members of the House of Representatives, the lower house of Parliament, except in three constituencies in Tripolitania, where the elections were delayed until March after rioters destroyed the electoral register on election day. They were the first elections in the country's history.
Presidential elections were held in the Maldives on 7, 9 and 16 November 2013. The first round was held on 7 September. As no candidate received a majority, a second round was planned to be held in 28 September between the candidates who received the most votes in the first round, former President Mohamed Nasheed and Abdulla Yameen, paternal half-brother of former president Maumoon Abdul Gayoom. Incumbent President Mohammed Waheed Hassan was eliminated in the first round after receiving less votes than three other candidates.
The 2011–2013 Maldives political crisis began as a series of peaceful protests that broke out in the Maldives on 1 May 2011. They would continue, eventually escalating into the resignation of President Mohamed Nasheed in disputed circumstances in February 2012. Demonstrators were protesting what they considered the government's mismanagement of the economy and were calling for the ouster of President Nasheed. The main political opposition party in the country, the Dhivehi Rayyithunge Party led by the former president of the country Maumoon Abdul Gayoom accused President Nasheed of "talking about democracy but not putting it into practice." The protests occurred during the Arab Spring.
Parliamentary elections were held in the Maldives on 6 April 2019. The result was a landslide victory for the Maldivian Democratic Party, which won 65 of the 87 seats in the People's Majlis. This was the first time in Maldivian history that one party was able to secure a supermajority in parliament.
















