
Mauritania is a presidential democracy, but has suffered from repeated military coups since its independence in November 1960. For 18 years after independence, Mauritania was a one-party state under Moktar Ould Daddah. This was followed by decades of military rule. The first fully democratic presidential election in Mauritania occurred on 11 March 2007, which marked a transfer from military to civilian rule following the military coup in 2005. The election was won by Sidi Ould Cheikh Abdallahi, who was ousted by another military coup in 2008 and replaced by general Mohamed Ould Abdel Aziz. Mauretania underwent its first peaceful transition of power after the 2019 presidential election, although this was between two presidents of the ruling UPR party.

Politics of The Gambia takes place within the framework of a presidential republic, whereby the President of The Gambia is both head of state and head of government, and of a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and parliaments.

The president of the Arab Republic of Egypt is the executive head of state of Egypt and the de facto appointee of the official head of government under the Egyptian Constitution of 2014. Under the various iterations of the Constitution of Egypt following the Egyptian Revolution of 1952, the president is also the supreme commander of the Armed Forces, and head of the executive branch of the Egyptian government. The current president is Field Marshal Abdel Fattah el-Sisi, who has been in office since 8 June 2014.
A term limit is a legal restriction on the number of terms a person may serve in a particular elected office. When term limits are found in presidential and semi-presidential systems they act as a method of curbing the potential for monopoly, where a leader effectively becomes "president for life". This is intended to protect a republic from becoming a de facto dictatorship. Term limits may be a lifetime limit on the number of terms an officeholder may serve, or a limit on the number of consecutive terms.

The president of Tunisia, officially the president of the Republic of Tunisia, is the head of state of Tunisia. Tunisia is a presidential republic, whereby the president is the head of state and head of government. Under Article 77 of the Constitution of Tunisia, the president is also the commander-in-chief of the Tunisian Armed Forces. The incumbent president is Kais Saied who has held this position since 23 October 2019 following the death of Beji Caid Essebsi on 25 July 2019. The 2022 Tunisian constitutional referendum transformed Tunisia into a presidential republic, giving the president sweeping powers while largely limiting the role of the parliament.

Elections in Mauritania encompass four different types: presidential elections, parliamentary elections, regional elections and local elections.

Elections in Venezuela are held at a national level for the President of Venezuela as head of state and head of government, and for a unicameral legislature. The President of Venezuela is elected for a six-year term by direct election plurality voting, and is eligible for re-election. The National Assembly (Asamblea Nacional) has 165 members (diputados), elected for five-year terms using a mixed-member majoritarian representation system. Elections also take place at state level and local level.

Elections in Benin take place within the framework of a multi-party democracy and a presidential system. Both the President and the National Assembly are directly elected by voters, with elections organised by the Autonomous National Electoral Commission (CENA).

Colonel Ely Ould Mohamed Vall was a Mauritanian political and military figure. Following a coup d'état in August 2005, he served as the transitional military leader of Mauritania until 19 April 2007, when he relinquished power to an elected government.

The National Assembly is the unicameral legislative house of the Parliament of Mauritania. The legislature currently has 176 members, elected for five-year terms in electoral districts or nationwide proportional lists.

The 1992 Constitution of Mali was approved by a referendum on 12 January 1992 after being drawn up by a national conference in August 1991. The constitution provides for multi party democracy within a semi-presidential system. It was briefly suspended after the 2012 military coup.
In December 1984, Haidallah was deposed by Colonel Maaouya Ould Sid'Ahmed Taya, who, while retaining tight military control, relaxed the political climate. Ould Taya moderated Mauritania's previous pro-Algerian stance, and re-established ties with Morocco during the late 1980s. He deepened these ties during the late 1990s and early 2000s as part of Mauritania's drive to attract support from Western states and Western-aligned Arab states. Mauritania has not rescinded its recognition of Polisario's Western Saharan exile government and remains on good terms with Algeria. Its position on the Western Sahara conflict has been, since the 1980s, one of strict neutrality.

The current Constitution of Mauritania was adopted on 12 July 1991. There have been several constitutions since Mauritania's independence in 1960.

Mauritania, officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania, is a sovereign country in Northwest Africa. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Western Sahara to the north and northwest, Algeria to the northeast, Mali to the east and southeast, and Senegal to the southwest. By land area, Mauritania is the 11th-largest country in Africa and the 28th-largest in the world, and 90% of its territory is situated in the Sahara. Most of its population of 4.4 million lives in the temperate south of the country, with roughly one-third concentrated in the capital and largest city, Nouakchott, located on the Atlantic coast.

The Constitution of Liberia is the supreme law of the Republic of Liberia. The current constitution, which came into force on 6 January 1986, replaced the Liberian Constitution of 1847, which had been in force since the independence of Liberia. Much like the 1847 Constitution, the Constitution creates a system of government heavily modeled on the Federal Government of the United States.
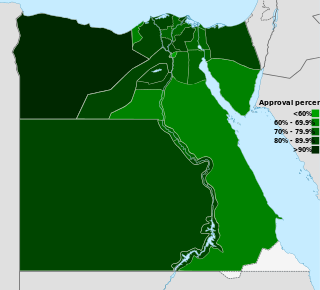
A constitutional referendum was held in Egypt on 19 March 2011, following the 2011 Egyptian revolution. More than 14 million (77%) were in favour, while around 4 million (23%) opposed the changes; 41% of 45 million eligible voters turned out to vote.

A constitutional referendum was held in the Republic of the Congo on 25 October 2015 regarding a proposal to change the constitution, primarily to modify the rules regarding presidential terms.

Presidential elections were held in Guinea on 18 October 2020. Incumbent president Alpha Condé was running for a third term. He was challenged by former prime minister Cellou Dalein Diallo, as well as several other candidates.

A constitutional referendum is planned to be held in Haiti in 2023. It is the first referendum in the country since 1987, and was unilaterally proposed by the administration of Jovenel Moïse. Originally set to be held on 27 June 2021, the referendum was postponed to 26 September 2021, on the same day as the presidential and parliamentary elections. The referendum was again postponed to 7 November. Acting Prime Minister Ariel Henry later postponed it first to February 2022 and then 2023.

This national electoral calendar for 2023 lists the national/federal elections held, and scheduled to be held, in 2023 in all sovereign states and their dependent territories. By-elections are excluded, though national referendums are included. Specific dates are given where these are known.
















