
Mauritania is a presidential democracy, but has suffered from repeated military coups since its Independence in November 1960. For 18 years after independence, Mauritania was a one-party state under Moktar Ould Daddah. This was followed by decades of military rule. The first fully democratic presidential election in Mauritania occurred on 11 March 2007, which marked a transfer from military to civilian rule following the military coup in 2005. The election was won by Sidi Ould Cheikh Abdallahi, who was ousted by another military coup in 2008 and replaced by general Mohamed Ould Abdel Aziz. Mauretania underwent its first peaceful transition of power after the 2019 presidential election, although this was between two presidents of the ruling UPR party and former army generals.

Elections in Mauritania encompass four different types: presidential elections, parliamentary elections, regional elections and local elections.

The Mauritanian Parliament is composed of a single chamber, the National Assembly. Composed of 176 members, representatives are elected for a five-year term in single-seat constituencies.

Presidential elections were held in Mauritania on 11 March 2007. As no candidate received a majority of the votes, a second round was held on 25 March between the top two candidates, Sidi Ould Cheikh Abdallahi and Ahmed Ould Daddah. Abdallahi won the second round with about 53% of the vote and took office in April.
The People's Progressive Alliance is a small political party in Mauritania.

The period from the mid-nineteenth to mid-twentieth centuries is the colonial period in Mauritania.

The 2008 Mauritanian coup d'état was a military coup that took place in Mauritania on August 6, 2008, when President Sidi Ould Cheikh Abdallahi was ousted from power by the Armed Forces of Mauritania, led by a group of high-ranking generals he had dismissed from office earlier that day.

Mohamed Ould Abdel Aziz is a retired Mauritanian military officer and politician who served as the 8th President of Mauritania from 2009 to 2019.

Mauritania, formally the Islamic Republic of Mauritania, is a sovereign country in Northwest Africa. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Western Sahara to the north and northwest, Algeria to the northeast, Mali to the east and southeast, and Senegal to the southwest. By land area Mauritania is the 11th-largest country in Africa and 28th-largest in the world; 90% of its territory is in the Sahara. Most of its population of some 4.3 million lives in the temperate south of the country, with roughly a third concentrated in the capital and largest city, Nouakchott, on the Atlantic coast.

Presidential elections were held in Mauritania on 18 July 2009. Mohamed Ould Abdel Aziz, who led the 2008 coup d'état, won a narrow first-round majority in the election, according to official results. A second round, if necessary, would have been held on 1 August 2009.

Parliamentary elections were held in Mauritania on 17 May 1959. The result was a victory for the Mauritanian Regroupment Party, which was the only party to contest the elections, thereby winning all 40 seats in the National Assembly. Voter turnout was 90.3%.

Presidential elections were held for the first time in Mauritania on 20 August 1961 to elect the president for the next five years. Moktar Ould Daddah, who had been acting head of state since independence from France in 1960 was the only candidate, and was elected unopposed. Although he was a member of the ruling Mauritanian Regroupment Party, his candidacy was also supported by the Mauritanian National Union. Voter turnout was 94%.

Parliamentary elections were held in Mauritania on 9 May 1965. Following the merger of all the country's political parties into the Mauritanian People's Party (PPM), the country had become a one-party state in December 1961. As such, the PPM was the only party to contest the election, and won all 40 seats in the National Assembly. Voter turnout was 93%.

Presidential elections were held in Mauritania on 7 August 1966. Following the merger of all the country's political parties into the Mauritanian People's Party (PPM), the country had become a one-party state in December 1961. Its leader, incumbent President Moktar Ould Daddah, was the only candidate, and was re-elected unopposed. Voter turnout was 96%.

General elections were held in Mauritania on 8 August 1971 to elect a President and National Assembly, the first time the two elections had been held together. At the time, the country was a one-party state with the Mauritanian People's Party (PPM) as the sole legal party. Its leader, incumbent President Moktar Ould Daddah, was the only candidate in the presidential election, and was re-elected unopposed to a third term in office, whilst the PPM won all 50 seats in the National Assembly election. Voter turnout for the parliamentary election was reported to be 95.6%.

Presidential elections were held in Mauritania on 8 August 1976, alongside a parliamentary by-election for the new seven seats representing Tiris El Gharbiya, the Mauritanian-occupied area of Western Sahara. At the time, the country was a one-party state with the Mauritanian People's Party (PPM) as the sole legal party. Its leader, incumbent President Moktar Ould Daddah, was the only candidate and was re-elected unopposed. Voter turnout was 97.9%. They were the last elections held until the restoration of multi-party democracy in 1992.

Parliamentary elections were held in Mauritania on 23 November. The opposition has vowed to boycott the election unless the president steps down beforehand. A total of 1,096 candidates have registered to compete for the leadership of 218 local councils across Mauritania, whilst 438 candidates are contesting for the 146 parliamentary seats. Some 1.2 million Mauritanians were eligible to vote in the election. The first round results yielded a landslide victory for the ruling UPR winning 56 seats and their 14 coalition partners winning 34 seats. The Islamist Tewassoul party won 12 seats. The remaining seats were contested in a runoff on 21 December 2013. The UPR won the majority with 75 seats in the Assembly.
Elections to the French National Assembly were held in the constituency of Mauritania–Senegal on 21 October 1945 as part of the wider parliamentary elections. Two members were elected from the seat, with the winners being French Section of the Workers' International (SFIO) candidates Lamine Guèye and Léopold Sédar Senghor.
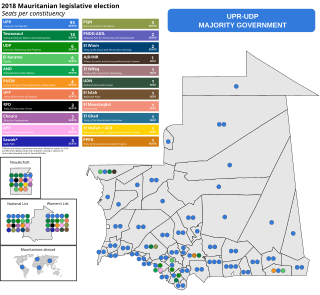
Parliamentary elections were held in Mauritania in September 2018; the first round took place on 1 September, with a second round held on 15 September. At the national level, elections were held in 157 constituencies, each electing one member to the National Assembly. Elections were also held in 13 regional councils and 219 municipalities.

Parliamentary elections were held in Mauritania on 13 and 27 May 2023, alongside regional and local elections.










