| | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 176 seats in the National Assembly 89 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|---|
|
The next Mauritanian parliamentary election will be held by 2028 to elect the 176 seats of the 11th National Assembly of Mauritania.
| | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 176 seats in the National Assembly 89 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|---|
|
The next Mauritanian parliamentary election will be held by 2028 to elect the 176 seats of the 11th National Assembly of Mauritania.
The 176 members of the National Assembly are elected by two methods (with Mauritanians being able to cast four different votes in a parallel voting system); 125 are elected from single- or multi-member electoral districts based on the departments (or moughataas) that the country is subdivided in (which the exception of Nouakchott, which is divided in three 7-seat constituencies based on the three regions (or wilayas) the city is subdivided into using either the two-round system or proportional representation; in single-member constituencies candidates require a majority of the vote to be elected in the first round and a plurality in the second round. In two-seat constituencies, voters vote for a party list (which must contain one man and one woman); if no list receives more than 50% of the vote in the first round, a second round is held, with the winning party taking both seats. In constituencies with three or more seats, closed list proportional representation is used, with seats allocated using the largest remainder method. For three-seat constituencies, party lists must include a female candidate in first or second on the list; for larger constituencies a zipper system is used, with alternate male and female candidates. The Mauritanian diaspora gets allocated four two-round majoritarian seats.
The remaining 51 seats are elected from three nationwide constituencies, also using closed list proportional representation: a 20-seat national list (which uses a zipper system), a 20-seat women's national list and a new 11-seat youth list (with two reserved for people with special needs), which also uses a zipper system to guarantee the representation of women.
| Polling firm | Fieldwork date | Sample size | El Insaf | RNRD | UDP | Sawab–RAG | El Islah | HATEM | El Karama | AJD/MR | HIWAR | UFP | El Vadila | RFD | PSJN | APP | Ribat | Others | N/A | Excluded |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Afrobarometer [1] | 6 November – 6 December 2023 | 1,200 | 28.5 | 4.3 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 1.6 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 3.6 | 55.2 |
| 2023 election | 13 May 2023 (national list vote) | – | 35.25 | 10.24 | 6.06 | 4.10 | 3.28 | 2.90 | 2.62 | 2.18 | 2.08 | 1.79 | 1.78 | 1.51 | 1.48 | 1.25 | 1.07 | 22.41 | – | – |

Proportional representation (PR) refers to any electoral system under which subgroups of an electorate are reflected proportionately in the elected body. The concept applies mainly to political divisions among voters. The aim of such systems is that all votes cast contribute to the result so that each representative in an assembly is mandated by a roughly equal number of voters, and therefore all votes have equal weight. Under other election systems, a bare plurality or a scant majority are all that are used to elect candidates. PR systems provide balanced representation to different factions, usually defined by parties, reflecting how votes were cast. Where only a choice of parties is allowed, the seats are allocated to parties in proportion to the vote tally or vote share each party receives.

Party-list proportional representation (list-PR) is a system of proportional representation based on preregistered political parties, with each party being allocated a certain number of seats roughly proportional to their share of the vote.

The additional-member system (AMS) is a two-vote seat-linkage-based mixed electoral system used in the United Kingdom in which most representatives are elected in single-member districts (SMDs), and a fixed number of other "additional members" are elected from a closed list to make the seat distribution in the chamber more proportional to the votes cast for party lists. It is distinct from using parallel voting for the list seats in that the "additional member" seats are awarded to parties taking into account seats won in SMDs – these are ignored under parallel voting.

Mixed-member proportional representation is a type of representation provided by some mixed electoral systems which combine local winner-take-all elections with a compensatory tier with party lists, in a way that produces proportional representation overall. Like proportional representation, MMP is not a single system, but a principle and goal of several similar systems. Some systems designed to achieve proportionality are still called mixed-member proportional, even if they generally fall short of full proportionality. In this case, they provide semi-proportional representation.
The D'Hondt method, also called the Jefferson method or the greatest divisors method, is an apportionment method for allocating seats in parliaments among federal states, or in proportional representation among political parties. It belongs to the class of highest-averages methods. Compared to ideal proportional representation, the D'Hondt method reduces somewhat the political fragmentation for smaller electoral district sizes, where it favors larger political parties over small parties.
An electoraldistrict, sometimes called a constituency, riding, or ward, is a geographical portion of a political unit, such as a country, state or province, city, or administrative region, created to provide the voters therein with representation in a legislature or other polity. That legislative body, the state's constitution, or a body established for that purpose determines each district's boundaries and whether each will be represented by a single member or multiple members. Generally, only voters (constituents) who reside within the district are permitted to vote in an election held there. The district representative or representatives may be elected by single-winner first-past-the-post system, a multi-winner proportional representative system, or another voting method.

The Chamber of Deputies is the lower house of the bicameral Italian Parliament, the upper house being the Senate of the Republic. The two houses together form a perfect bicameral system, meaning they perform identical functions, but do so separately. The Chamber of Deputies has 400 seats, of which 392 are elected from Italian constituencies, and 8 from Italian citizens living abroad. Deputies are styled The Honourable and meet at Palazzo Montecitorio.

The National Assembly is the unicameral legislative house of the Parliament of Mauritania. The legislature currently has 176 deputies, elected for five-year terms in electoral districts or nationwide proportional lists.

Parliamentary elections were held in Hungary on 9 April 2006, with a second round of voting in 110 of the 176 single-member constituencies on 23 April. The Hungarian Socialist Party (MSZP) emerged as the largest party in the National Assembly with 186 of the 386 seats, and continued the coalition government with the Alliance of Free Democrats (SZDSZ). It marked the first time a government had been re-elected since the end of Communist rule. To date, this is the most recent national election in Hungary not won by Fidesz-KDNP, and the last in which the victorious party did not win a two-thirds supermajority in parliament.
Elections in Serbia are mandated by the Constitution and legislation. The President of the Republic, National Assembly, provincial (Vojvodina) and local assemblies are all elective offices. Since 1990, twelve presidential, fourteen parliamentary and ten provincial elections were held.
Electoral districts go by different names depending on the country and the office being elected.

An electoral or voting system is a set of rules used to determine the results of an election. Electoral systems are used in politics to elect governments, while non-political elections may take place in business, non-profit organisations and informal organisations. These rules govern all aspects of the voting process: when elections occur, who is allowed to vote, who can stand as a candidate, how ballots are marked and cast, how the ballots are counted, how votes translate into the election outcome, limits on campaign spending, and other factors that can affect the result. Political electoral systems are defined by constitutions and electoral laws, are typically conducted by election commissions, and can use multiple types of elections for different offices.

Parliamentary elections were held in Mauritania on 23 November. The opposition has vowed to boycott the election unless the president steps down beforehand. A total of 1,096 candidates have registered to compete for the leadership of 218 local councils across Mauritania, whilst 438 candidates are contesting for the 146 parliamentary seats. Some 1.2 million Mauritanians were eligible to vote in the election. The first round results yielded a landslide victory for the ruling UPR winning 56 seats and their 14 coalition partners winning 34 seats. The Islamist Tewassoul party won 12 seats. The remaining seats were contested in a runoff on 21 December 2013. The UPR won the majority with 75 seats in the Assembly.

General elections are due to be held in South Sudan on 22 December 2026, the first since independence.

National remnant is an apportionment scheme used in some party-list proportional representation systems that have multi-member electoral districts. The system uses a Largest remainder method to determine some of the seats in each electoral district. However, after the integer part of the seats in each district is allocated to the parties, the seats left unallocated will then be allocated not in each electoral district in isolation, but in a larger division, such as nationwide or in large separate regions that each encompass multiple electoral districts.
The Italian electoral law of 2017, colloquially known by the nickname Rosatellum after Ettore Rosato, the Democratic Party (PD) leader in the Chamber of Deputies who first proposed the new law, is a parallel voting system, which acts as a mixed electoral system, with 37% of seats allocated using a first-past-the-post electoral system and 63% using a proportional method, with one round of voting. The Chamber and Senate of the Republic did not differ in the way they allocated the proportional seats, both using the largest remainder method of allocating seats.
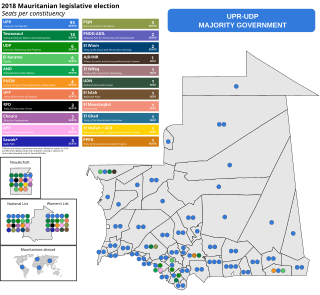
Parliamentary elections were held in Mauritania in September 2018; the first round took place on 1 September, with a second round held on 15 September. At the national level, elections were held in 157 constituencies, each electing one member to the National Assembly. Elections were also held in 13 regional councils and 219 municipalities.

Parliamentary elections were held in Mauritania on 13 and 27 May 2023, alongside regional and local elections.

Mauritania is divided into several electoral districts for the election of deputies to the National Assembly, based on the departments of the country, with the exception of the capital city of Nouakchott, where the electoral districts are based on the three regions the city is divided in.

This is the results breakdown of the parliamentary elections held in Mauritania on 13 and 27 May 2023. The following tables will show detailed results in all of the electoral districts of the country.