| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
Events in the year 2013 in Gabon .
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
Events in the year 2013 in Gabon .

A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on 24–25 May 2013, the second of three lunar eclipses in 2013. It was visually imperceptible due to the small entry into the penumbral shadow.

A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on 18–19 October 2013, the last of three lunar eclipses in 2013.

An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit between Thursday, May 9 and Friday, May 10, 2013, with a magnitude of 0.9544. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 3.6 days before apogee, the Moon's apparent diameter was smaller.
A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Sunday, November 3, 2013, with a magnitude of 1.0159. It was a hybrid event, a narrow total eclipse, and beginning as an annular eclipse and concluding as a total eclipse, in this particular case. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 2.9 days before perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was larger.

A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Friday, October 3, 1986, with a magnitude of 1. It was a hybrid event, with only a fraction of its path as total, and longer sections at the start and end as an annular eclipse. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. The Moon's apparent diameter was near the average diameter because it occurred 8.3 days after apogee and 3.7 days before perigee.

A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon’s ascending node of orbit on Thursday, April 20, 2023, with a magnitude of 1.0132. It was a hybrid event, a narrow total eclipse, and beginning and ending as an annular eclipse. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun thereby totally or partly obscuring the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A hybrid solar eclipse is a rare type of solar eclipse that changes its appearance from annular to total and back as the Moon's shadow moves across the Earth's surface. Totality occurs between the annularity paths across the surface of the Earth, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Hybrid solar eclipses are extremely rare, occurring in only 3.1% of solar eclipses in the 21st century. Occurring about 4.1 days after perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was larger.
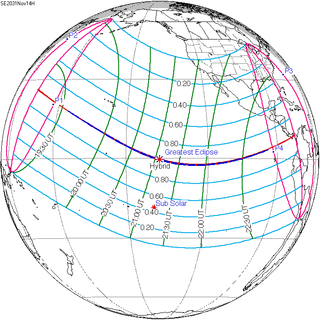
A total solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Friday, November 14, 2031, with a magnitude of 1.0106. It is a hybrid event, with portions of its central path near sunrise and sunset as an annular eclipse. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 3.1 days before perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter will be larger.

An annular solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Wednesday, May 21, 2031, with a magnitude of 0.9589. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 3.8 days before apogee, the Moon's apparent diameter will be smaller.
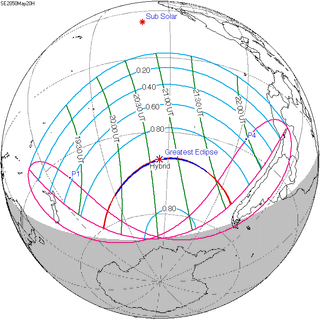
A total solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Friday, May 20, 2050, with a magnitude of 1.0038. It is a hybrid event, with only a fraction of its path as total, and longer sections at the start and end as an annular eclipse. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 5.2 days after perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter will be larger.

A partial solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Monday, November 14, 2050, with a magnitude of 0.8874. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.

A total solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Thursday, November 25, 2049, with a magnitude of 1.0057. It is a hybrid event, with only a fraction of its path as total, and longer sections at the start and end as an annular eclipse. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 3.2 days before perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter will be larger.

A total solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Tuesday, December 6, 2067, with a magnitude of 1.0011. It is a hybrid event, beginning and ending as an annular eclipse. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 3.4 days before perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter will be larger.

Saros cycle series 123 for solar eclipses occurs at the Moon's ascending node, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, containing 70 eclipses, 44 of which are umbral. The first eclipse in the series was on 29 April 1074 and the last will be on 31 May 2318. The most recent eclipse was a partial eclipse on 25 November 2011 and the next will be a partial eclipse on 5 December 2029.

Saros cycle series 133 for solar eclipses occurs at the Moon's ascending node, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, containing 72 eclipses, 53 of which are umbral. The first eclipse in the series was on 13 July 1219 and the last will be on 5 September 2499. The most recent eclipse was a total eclipse on 13 November 2012 and the next will be a total eclipse on 25 November 2030.

Saros cycle series 135 for solar eclipses occurs at the Moon's ascending node, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, containing 71 eclipses, including 53 umbral eclipses. The longest duration of totality will be 2 minutes, 27 seconds on May 12, 2431 while the longest annular was 10 minutes 14 seconds on 24 December 1601.
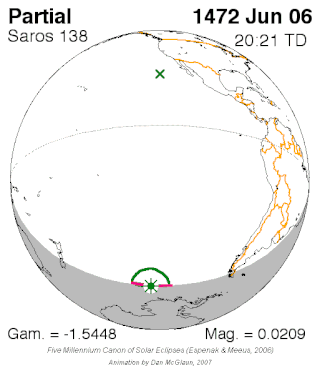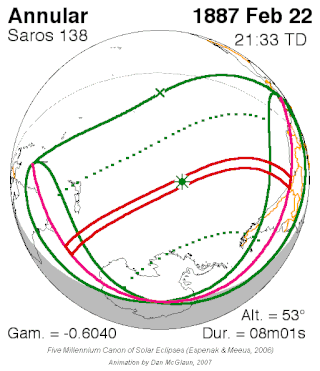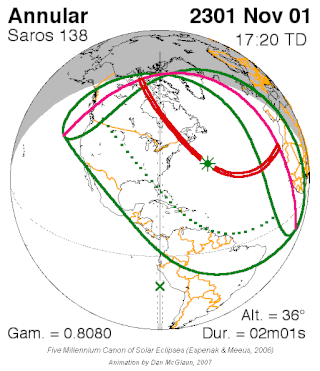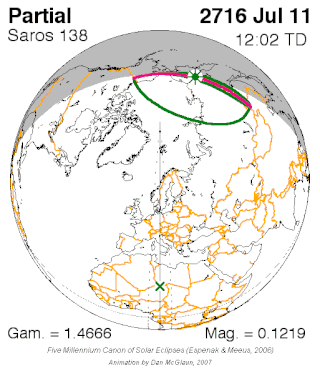
Saros cycle series 138 for solar eclipses occurs at the Moon's descending node, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, containing 70 eclipses, 54 of which are umbral. The first eclipse of the series was on 6 June 1472 and the last will be on 11 July 2716. The most recent eclipse was an annular eclipse on 10 May 2013 and the next will be an annular eclipse on 21 May 2031.
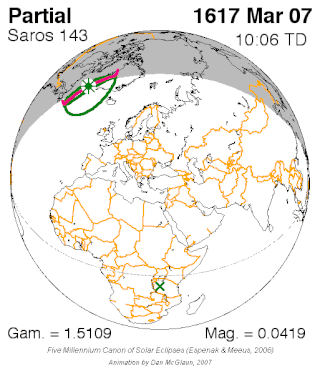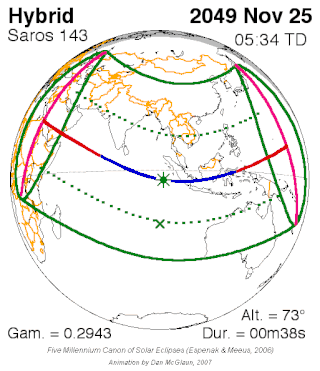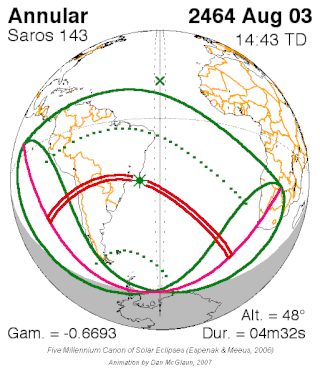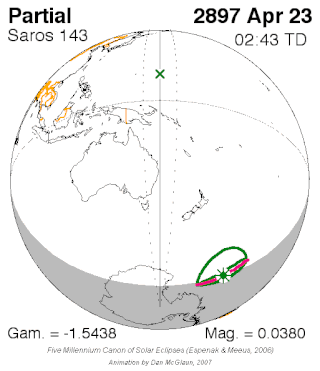
Saros cycle series 143 for solar eclipses occurs at the Moon's ascending node, repeating every 18 years and 11 days, containing 72 eclipses, 42 of which are umbral. The first eclipse in the series was on 7 March 1617 and the last will be on 23 April 2897. The most recent eclipse was a hybrid eclipse on 3 November 2013 and the next will be a hybrid eclipse on 14 November 2031.

A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Wednesday, December 23, 1908, with a magnitude of 1.0024. It was a hybrid event, with only a fraction of its path as total, and longer sections at the start and end as an annular eclipse. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 3.1 days before perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was larger.

A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit between Thursday, June 17 and Friday, June 18, 1909, with a magnitude of 1.0065. It was a hybrid event, with only a fraction of its path as total, and longer sections at the start and end as an annular eclipse. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. The Moon's apparent diameter was near the average diameter because it occurred 5.4 days after perigee and 7.5 days before apogee.

A total solar eclipse occurred on June 24, 1778. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.