This article needs to be updated.(August 2016) |
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 2016 History of Saudi Arabia | ||||

The following lists events that happened in 2016 in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia .
This article needs to be updated.(August 2016) |
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 2016 History of Saudi Arabia | ||||

The following lists events that happened in 2016 in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia .

Human rights in Saudi Arabia are a topic of concern and controversy. Known for its executions of political protesters and opponents, the government of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia has been accused of and denounced by various international organizations and governments for violating human rights within the country. An absolute monarchy under the House of Saud, the government is consistently ranked among the "worst of the worst" in Freedom House's annual survey of political and civil rights and was in 2023 ranked as the world's most authoritarian regime.
Capital punishment in Saudi Arabia is a legal punishment, with most executions in the country being carried out by decapitation (beheading) – Saudi Arabia being the only country in the world to still use the method. In 2022, recorded executions in Saudi Arabia reached 196, the highest number recorded in the country for any year over the last three decades.

Bilateral relations between Iran and Saudi Arabia have been strained over several geopolitical issues, such as aspirations for regional leadership, oil export policy and relations with the United States and other Western countries. Diplomatic relations were suspended from 1987 to 1990, and in 2016 for seven years following certain issues like the intervention in Yemen, Iran embassy bombing in Yemen, incidents in 2015 Hajj, the execution of Nimr al-Nimr, the attack on the Saudi diplomatic missions in Iran. However, in March 2023, after discussions brokered by China and Iraq, Iran and Saudi Arabia agreed to reestablish relations.
The Saudi government does not conduct a census on religion or ethnicity, but some sources estimate the Shia population in Saudi Arabia to make up around 20% of the approximately 34 million natives of Saudi Arabia.
Al-Awamiyah, also spelled Awamia, is a town situated in the Al-Qatif region in the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia. As of 2009, it has a population of about 25,500 people. Al-Awamiyah is bordered by the Al-Ramis farms to the east and some other farms to the west and the south. To the north side, there is a dividing line between Al-Awamiyah and the neighboring Safwa city, so the town cannot expand any more and provide housing land for its growing population. Due to this limited land, the people move out of the town and settle in nearby neighborhoods, notably Al-Nasera which is home to almost 2500 people living in 250 homes.

The protests in Saudi Arabia were part of the Arab Spring that started with the 2011 Tunisian revolution. Protests started with a self-immolation in Samtah and Jeddah street protests in late January 2011. Protests against anti-Shia discrimination followed in February and early March in Qatif, Hofuf, al-Awamiyah, and Riyadh. A Facebook organiser of a planned 11 March "Day of Rage", Faisal Ahmed Abdul-Ahad, was allegedly killed by Saudi security forces on 2 March, with several hundred people protesting in Qatif, Hofuf and al-Amawiyah on the day itself. Khaled al-Johani demonstrated alone in Riyadh, was interviewed by BBC Arabic Television, was detained in ʽUlaysha Prison, and became known online as "the only brave man in Saudi Arabia". Many protests over human rights took place in April 2011 in front of government ministry buildings in Riyadh, Ta'if and Tabuk and in January 2012 in Riyadh. In 2011, Nimr al-Nimr encouraged his supporters in nonviolent resistance.

Ayatollah Sheikh Nimr Baqir al-Nimr, commonly referred to as Sheikh Nimr, was a Shia sheikh from Al-Awamiyah in Saudi Arabia's Eastern Province whose arrest and execution was widely condemned, including by governments and human rights organizations.
Ali Mohammed Baqir al-Nimr is a Saudi Arabian former political prisoner who participated in the Saudi Arabian protests during the Arab Spring as a teenager. He was arrested in February 2012 and sentenced to death in May 2014, having previously awaited ratification of his sentence by King Salman of Saudi Arabia, which was to be carried out by beheading and crucifixion. Ali's trial was considered unfair by Professor of Human Rights Law Christof Heyns, and Amnesty International, as well as French President François Hollande and Prime Minister Manuel Valls, who called for the execution to be stopped.

Iran and Saudi Arabia are engaged in an ongoing struggle for influence in the Middle East and other regions of the Muslim world. The two countries have provided varying degrees of support to opposing sides in nearby conflicts, including the civil wars in Syria and Yemen; and disputes in Bahrain, Lebanon, Qatar, and Iraq. The struggle also extends to disputes or broader competition in other countries globally including in West, North and East Africa, South, Central, Southeast Asia, the Balkans, and the Caucasus.
On January 2, 2016, the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia carried out a mass execution of 47 imprisoned civilians convicted of terrorism in 12 provinces in the country. Forty-three were beheaded and four were executed by firing squads. Among the 47 people killed was Shia Sheikh Nimr al-Nimr. The execution was the largest carried out in the kingdom since 1980. Nimr al-Nimr was sentenced to death by the Specialized Criminal Court on 15 October 2014 for "seeking 'foreign meddling' in Saudi Arabia, 'disobeying' its rulers and taking up arms against the security forces". His execution was condemned by religious and political figures and human rights groups. The Saudi government said the body would not be handed over to the family. Al-Nimr was very critical of the Saudi Arabian government, and called for free elections in Saudi Arabia.
Nimr Baqir al-Nimr Street is a street in Tehran, Iran which connects to Pasdaran Avenue. It is adjacent to the Saudi embassy and some lower-key diplomatic missions. Other buildings include the Rassam Arab-zadeh Carpet (فرش) Museum and Museum of Contemporary Arts and Crafts. In January 2016, some Iranians who protested the execution of Nimr al-Nimr erected street signs bearing the name "Nimr Street" in an effort to encapsulate that name change. Within days Iran Daily reported approval by the Tehran Islamic City Council to rename the street Nimr Baqir al-Nimr Street.
Nimr Baqir al-Nimr was a Shia cleric and critic of the government in Saudi Arabia, who was beheaded on 2 January 2016, one of 47 people executed that day for terrorism offenses. Others executed included Sunnis who had been convicted of involvement in terror attacks linked to al-Qaeda which took place in 2003. News of the killings triggered international demonstrations, and condemnation by nations, supranational organizations, and human rights groups.

The Embassy of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia in Tehran is the diplomatic mission of Saudi Arabia in Iran.

The 2016 attack on the Saudi diplomatic missions in Iran was a mob action on 2 January 2016 by protesters against the execution of a prominent Saudi Arabian Shi'a cleric. Mobs stormed the embassy in Tehran and the Saudi consulate in Mashhad and ransacked them. The embassy building was set on fire with Molotov cocktails and petrol bombs. During the attacks, the police arrived and dispersed protesters from the embassy premises and extinguished the fire.

Bilateral relations exist between the countries of Bahrain and Iran. Since the 1979 Iranian Revolution, relations between the two countries have been strained over various geopolitical issues such as the interpretations of Islam, Awakening of the Islamic world, and relations with the United States, Europe, and other Western countries. In addition, Iran has been severely critical of Bahrain for hosting the United States Fifth Fleet within the Persian Gulf at the Naval Support Activity Bahrain base.
The 2017–2020 Qatif unrest was a phase of conflict in the Qatif region of Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia, between Saudi security forces and the local Shia community, that arose sporadically starting in 1979, including a series of protests and repression during the 2011–12 Saudi Arabian protests.
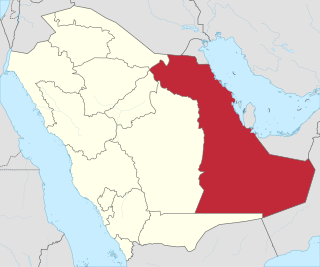
The Qatif conflict is a modern phase of sectarian tensions and violence in Eastern Arabia between Arab Shia Muslims and Arab Sunni majority, which has ruled Saudi Arabia since early 20th century. The conflict encompasses civil unrest which has been sporadically happened since the 1979 uprising, pro-democracy and pro-human rights protests and occasional armed incidents, which increased in 2017 as part of the 2017–20 Qatif unrest.
Israa al-Ghomgham is a Saudi Arabian human rights advocate. She is especially known for her documentation of the 2017–18 Qatif unrest.

Sectarianism in Saudi Arabia refers to the Saudi government's "top-down push towards sectarian polarization" between the Sunni majority, and Shi'ite minority. This encompasses anti-Shi'ite policies by the Saudi regime, as well as tensions between the Sunni majority and the Shi'ite minority. The Saudi government is often viewed to be oppressing the Shi'ite community, who constitute up to 15% of the Saudi population. This occurs against the backdrop of the broader Iran-Saudi Arabia proxy conflict, since Iran is a Shi'ite republic.