Related Research Articles
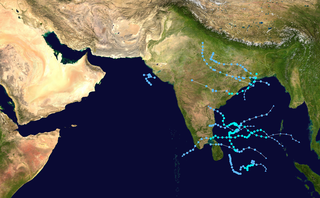
The 2005 North Indian Ocean cyclone season caused much devastation and many deaths in Southern India despite the storms’ weakness. The basin covers the Indian Ocean north of the equator as well as inland areas, sub-divided by the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal. Although the season began early with two systems in January, the bulk of activity was confined from September to December. The official India Meteorological Department tracked 12 depressions in the basin, and the unofficial Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) monitored two additional storms. Three systems intensified into a cyclonic storm, which have sustained winds of at least 63 km/h (39 mph), at which point the IMD named them.

In October 1999, severe flooding affected portions of eastern Mexico and Central America. Rainfall in September preceded the primary event in Mexico, which moistened soils. On October 4, Tropical Depression Eleven developed in the Gulf of Mexico, which drew humidity from the gulf and the Pacific Ocean to produce torrential rainfall in mountainous regions of eastern Mexico, reaching 43.23 in (1,098 mm) in Jalacingo, Veracruz. This was the third-highest tropical cyclone-related rainfall total in Mexico from 1980–2006, and the event caused the highest rainfall related to tropical cyclones in Veracruz, Hidalgo, and Puebla. In some locations, the daily rainfall represented over 10% of the annual precipitation total. The heaviest rainfall occurred in mountainous regions that were the mouths of several rivers. A broad trough absorbed the depression on October 6, and rainfall continued for the next few days. Additional rainfall occurred in Tabasco state on October 18. The floods were estimated as a 1 in 67 year event in one location, although such floods are expected to affect eastern Mexico twice per century, the last time being 1944.

Cyclonic Storm Nilam was a weak, but deadly tropical cyclone that became the deadliest tropical cyclone to directly affect South India since Cyclone Jal in 2010. The second named Cyclonic Storm of the rather quiet 2012 North Indian Ocean cyclone season, Nilam originated from an area of low pressure over the Bay of Bengal on October 28, 2012. The system began as a weak depression 550 km (340 mi) northeast of Trincomalee, Sri Lanka. Over the following few days, the depression gradually intensified into a deep depression, and subsequently a cyclonic storm by October 30. It made landfall near Mahabalipuram on October 31 as a strong cyclonic storm with peak winds of 85 km/h (55 mph). In Chennai's Marina Beach, strong winds pushed piles of sand ashore and seawater reached nearly a 100 m (330 ft) inland. Schools and colleges in the city remained closed for more than three days.

The 2003 Sri Lanka cyclone was a moderately powerful tropical cyclone that produced the worst flooding in Sri Lanka in 56 years. The first storm of the 2003 North Indian Ocean cyclone season, it developed over the Bay of Bengal on May 10. Favorable environmental conditions allowed the system to intensify steadily while moving northwestward. The storm reached peak maximum sustained winds of 140 km/h (85 mph) on May 13, making it a very severe cyclonic storm according to the India Meteorological Department (IMD), which is the official Regional Specialized Meteorological Center for the basin. The cyclone drifted north over the central Bay of Bengal, gradually weakening due to heightened wind shear. Turning eastward, the storm deteriorated to a deep depression on May 16 before it curved northeastward and re-intensified into a cyclonic storm. It came ashore in western Myanmar and dissipated over land the following day.
Beginning on 14 December 2014, a series of floods from the northeast monsoon hit Indonesia, West Malaysia, Southern Thailand, and later Sri Lanka in South Asia. More than 100,000 people were evacuated in Indonesia, 200,000 in Malaysia, and several thousand in Thailand. Floods also affected 1,100,000 in Sri Lanka.
This is a list of notable recorded floods that have occurred in India. Floods are the most common natural disaster in India. The heaviest southwest, the Brahmaputra, and other rivers to distend their banks, often flooding surrounding areas.

Beginning on 14 May 2016, a low pressure area over the Bay of Bengal caused torrential rain to fall across Sri Lanka, causing floods and landslides which affected half a million people. As of 25 May 2016 the death toll was 101 with 100 missing.
The 2017 Sri Lanka floods resulted from a heavy southwest monsoon, beginning around 18 to 19 May 2017. Flooding was worsened by the arrival of the precursor system to Cyclone Mora, causing flooding and landslides throughout Sri Lanka during the final week of May 2017. The floods affected 15 districts, killed at least 208 people and left a further 78 people missing. As of 3 June, 698,289 people were affected, while 11,056 houses were partially damaged and another 2,093 houses completely destroyed. According to Al Jazeera, about 600,000 people have been displaced due to the floods.
2018 Sri Lanka floods and landslides caused from an annual heavy southwest monsoon beginning around 19 May. As of 26 May 2018; the monsoon floods affected in about 19 districts, killed at least 21 people, about 150, 000 people were affected and further left approximately 23 people missing. The death casualties were reported from 22 May onwards in the provinces including South, Northwest, North and East. About 4 people were reported dead due to lightning, 5 people were killed due to floods and lightning, 8 people died due to drowning and further left 4 people dead resulting from fallen trees. The DMC report claimed about 400, 000 people have been displaced to safer locations. About 105 houses were reported to have fully damaged and over 4832 houses have been partially damaged.
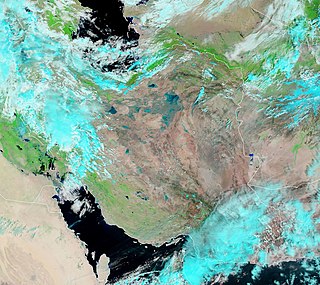
From mid-March to April 2019 widespread flash flooding affected large parts of Iran, most severely in Golestan, Fars, Khuzestan, Lorestan, and other provinces. Iran has been hit by three major waves of rain and flooding over the course of two weeks which led to flooding in at least 26 of Iran's 31 provinces and at least 70 people died nationwide as of 6 April, according to the officials. The first wave of rain began on 17 March, leading to flooding in two northern provinces, Golestan and Mazandaran with the former province receiving as much as 70 percent of its average annual rainfall in single day. Several large dams have been overflowed, particularly in Khuzestan and Golestan, therefore many villages and several cities have been evacuated. About 1,900 cities and villages across country have been damaged by severe floods as well as hundreds of millions of dollars of damage to water and agriculture infrastructure. 78 roads were blocked and the reliability of 84 bridges was questioned.
In mid-March 2019, monsoonal downpours caused widespread flooding and landslides across South Asia.
The 2019 Indian floods were a series of floods that affected over thirteen states in late July and early August 2019, due to excessive rains. At least 200 people died and about a million people were displaced. Karnataka and Maharashtra were the most severely affected states. People died but many were rescued with the help of the Indian Navy.
The 2019 floods and landslides in Sri Lanka were the floods which were caused from heavy torrential rainfalls during September 2019. As of 26 September 2019; the monsoon floods affected in about 13 districts, killing at least 2 persons, injuring 6 people and about 116, 000 people are affected. One casualty was reported in the Galle District and the other one was reported in Kolonnawa, where a teenager drowned in the flood water. About 282 houses were reported to have been damaged mainly in Galle and Matara while 22 houses out of 150 houses were completely destroyed in the two districts.
The 2020 East Africa floods were a natural disaster in Rwanda, Kenya, Somalia, Burundi, Ethiopia, Uganda, Democratic Republic of Congo, Djibouti and Tanzania, affecting at least 700,000 people. They began when excessive rains began falling in March, leading to massive flooding and landslides. They caused more than 430 deaths, notably in Kenya and Rwanda. In the fall another round of floods hit the African Sahel.

2020 Assam floods refers to the significant flood event of the Brahmaputra River in the Indian north-eastern state of Assam and coincided with the COVID-19 pandemic. Initial flooding started in May 2020 due to heavy rainfall affecting 30,000 and destroying crops across 5 districts. As of October 2020 the floods affected over five million people, claiming the lives of 123 people, with an additional 26 deaths due to landslides, 5474 villages were affected and over one hundred and fifty thousand people found refuge in relief camps.

Cyclonic Storm Burevi was a weak tropical cyclone which made landfall in Sri Lanka, becoming the first to do so since a depression in 2014, and brought minimal impact to Southern India in December 2020. The ninth depression and fifth named storm of the 2020 North Indian Ocean cyclone season, Burevi originated from a low-pressure area which formed on November 28. The system gradually became a depression on November 30, with the JTWC issuing a TCFA soon after. The depression then was upgraded into Cyclone Burevi the following day. Burevi slowly intensified reaching its peak intensity on December 2, just before making landfall in Sri Lanka. Burevi then weakened, entering the Gulf of Mannar the next day. Burevi proceeded to dissipate after stalling on December 5.

Tropical Cyclone Eloise was the strongest tropical cyclone to impact the country of Mozambique since Cyclone Kenneth in 2019 and the second of three consecutive tropical cyclones to impact Mozambique in the 2020–21 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season. The seventh tropical depression, fifth named storm and the second tropical cyclone of the season, Eloise's origins can be traced to a disturbance over the central portion of the South-West Indian Ocean basin which developed into a tropical depression on 16 January, and strengthened into a tropical storm on 17 January, though the storm had limited strength and organization. On the next day, the storm entered a more favorable environment, and it soon intensified to a severe tropical storm on 18 January. Late on 19 January, Eloise made landfall in northern Madagascar as a moderate tropical storm, bringing with it heavy rainfall and flooding. The storm traversed Madagascar and entered the Mozambique Channel in the early hours of 21 January. After moving southwestward across the Mozambique Channel for an additional 2 days, Eloise strengthened into a Category 1-equivalent cyclone, due to low wind shear and high sea surface temperatures. Early on 23 January, Eloise peaked as a Category 2-equivalent tropical cyclone on the Saffir–Simpson scale as the center of the storm began to move ashore in Mozambique. Shortly afterward, Eloise made landfall just north of Beira, Mozambique, before rapidly weakening. Subsequently, Eloise weakened into a remnant low over land on 25 January, dissipating soon afterward.
The 2021 floods and landslides in Sri Lanka are flash floods and mudslides which were caused from heavy torrential rainfalls during May and June 2021. As of 7 June 2021; the monsoon floods affected in about 10 districts, killing at least 17 persons including about 10 because of floods and 4 people because of mudslides. About 245,000 people were affected living in Colombo, Puttalam, Kandy, Kalutara, Kurunegala, Gampaha, Nuwara Eliya, Ratnapura and Galle. More than 800 houses were reported to have been damaged.
From January to October 2022, excessive rainfall and widespread monsoon flooding occurred in the South Asian countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, India, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka. It has become the region's deadliest floods since 2020, with over 4,700 people dead.
References
- ↑ "Sri Lanka : Heavy floods in Northern districts of Sri Lanka displace thousands, reservoirs overflow". colombopage.com. Retrieved 26 December 2018.
- ↑ "Over 45,000 affected in North due to rains, floods – Sri Lanka". ReliefWeb. Retrieved 26 December 2018.
- ↑ "Over 75,000 people affected by floods – Sri Lanka". ReliefWeb. Retrieved 26 December 2018.
- ↑ "Sri Lanka – Flash Floods (DG ECHO, Sri Lanka Disaster Management Center, Media)(ECHO Daily Flash of 26 December 2018) – Sri Lanka". ReliefWeb. Retrieved 27 December 2018.
- ↑ "More facilities for flood affected people in Kilinochchi under the guidance of the President - Sri Lanka". ReliefWeb. Retrieved 1 January 2019.
- ↑ "Over 60,000 People Affected By Sri Lanka Flash Floods". NDTV.com. Retrieved 26 December 2018.
- ↑ "Sri Lanka: Floods – Dec 2018". ReliefWeb. Retrieved 26 December 2018.
- ↑ "Over 45,000 affected in North due to rains, floods". dailymirror.lk. Retrieved 26 December 2018.