
The politics of Malta takes place within a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic republic, whereby the president of Malta is the constitutional head of state. Executive authority is vested in the president of Malta, with the general direction and control of the Government of Malta remaining with the prime minister of Malta, who is the head of government and the cabinet. Legislative power is vested in the Parliament of Malta, which consists of the president of Malta and the unicameral House of Representatives of Malta with the speaker as the presiding officer of the legislative body. Judicial power remains with the chief justice and the judiciary of Malta. Since independence, the party electoral system has been dominated by the Christian democratic Nationalist Party and the social democratic Labour Party.

The Nationalist Party is one of the two major contemporary political parties in Malta, along with the Labour Party.

Edoardo "Eddie" Fenech Adami is a Maltese politician and Nationalist politician who served as the prime minister of Malta from 1987 until 1996, and again from 1998 until 2004. Subsequently, he was the seventh president of Malta from 2004 to 2009. He led his party to win four general elections, in 1987, 1992, 1998 and 2003, as well as the majority of votes in 1981. Staunchly pro-European, Fenech Adami was fundamental for Malta's accession to the European Union.

The Labour Party, formerly known as the Malta Labour Party, is one of the two major political parties in Malta, along with the Nationalist Party. It sits on the centre-left of the political spectrum.

Lawrence Gonzi is a Maltese politician, retired Nationalist politician and lawyer, who served for twenty-five years in various critical roles in Maltese politics. Gonzi was Prime Minister of Malta from 2004 to 2013, and leader of the Nationalist Party. He also served as speaker of the House from 1988 to 1996, and Minister of Social Policy from 1998 to 2004, as well as deputy prime minister from 1999 to 2004. He served in practically all positions in Parliament, being also Leader of the House, an MP and Leader of the Opposition.

The Council of Representatives is the de facto unicameral legislature of the Republic of Iraq. According to the Constitution of Iraq, it is the lower house of the bicameral legislature of the country. As of 2020, it comprises 329 seats and meets in Baghdad inside the Green Zone.

Joseph Muscat is a Maltese politician who served as the 13th prime minister of Malta from 2013 to 2020 and leader of the Labour Party from 2008 to 2020.
Same-sex marriage has been legal in Malta since 1 September 2017 following the passage of legislation in the Parliament on 12 July 2017. The bill was signed into law by President Marie-Louise Coleiro Preca on 1 August 2017. On 25 August 2017, the Minister for Equality, Helena Dalli, issued a legal notice to commence the law on 1 September. Malta was the first European microstate, the 21st country in the world and the thirteenth in Europe to allow same-sex couples to marry nationwide. In 2024, Malta was named one of the best marriage destinations for same-sex couples by a British wedding planning website, and polling suggests that a majority of Maltese people support the legal recognition of same-sex marriage.

George William Vella is a Maltese politician who served as the 10th president of Malta from 2019 to 2024. A member of the Labour Party, he previously served as deputy prime minister of Malta and foreign affairs minister from 1996 to 1998 under prime minister Alfred Sant. In 2013, he returned as foreign affairs minister, an office he held until 2017 under prime minister Joseph Muscat.

Parliamentary elections were held in Sri Lanka on 8 and 20 April 2010, to elect 225 members to Sri Lanka's 14th Parliament. 14,088,500 Sri Lankans were eligible to vote in the election at 11,102 polling stations. It was the first general election to be held in Sri Lanka following the conclusion of the civil war which lasted 26 years.

Presidential elections were held in Moldova on 16 December 2011. The president was elected by the parliament in an indirect election. After the election on 16 December failed, a second attempt was made on 15 January 2012. However, that vote was annulled as being unconstitutional since it had not been held in a secret vote. On 16 March, parliament elected Nicolae Timofti as president by 62 votes out of 101, with the PCRM boycotting the election, putting an end to a political crisis that had lasted since April 2009.

Indirect presidential elections were held in Kosovo on 22 February 2011 and 7 April 2011.

Parliamentary elections were held in Chad on 29 December 2024, along with elections for regional and local offices. These are the first legislative elections to be held in Chad since 2011, and the first since the death of long-time ruler Idriss Déby in 2021, and the accession to leadership of his son, Mahamat Déby, first as leader of a military junta then as president in his own right, laying the groundwork for a hereditary dictatorship.
The Democratic Party was a centrist to centre-left political party in Malta. It was founded in 2016 after a split from the Labour Party. It elected Malta's first two third party MPs for the first time since the country's Independence. In August 2020 the party announced an agreement to merge with the green Democratic Alternative party to form a new party called AD+PD. The merger was conducted on 17 October 2020.

An indirect presidential election was held in Hungary on 13 March 2017. János Áder was elected President of Hungary for a second term.
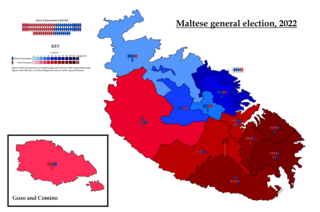
General elections were held in Malta on 26 March 2022 to elect all members of the House of Representatives.

Since the independence of Bangladesh, the presidential election process has been changed several times due to both the presidential and parliamentary arrangements. According to the Second Schedule to the Constitution of 1972, the president of the parliament used to be elected by a secret vote. Later, according to the fourth amendment to the constitution, the provision of the direct election system of presidential election was introduced. But soon after 12th Amendment to the Constitution, the provision of presidential elections through an indirect election was introduced after the parliamentary system was installed. At present, the president is elected by an indirect election by the members of parliament as per Article 48 of the Constitution.

United National Movement – United Opposition "Strength is in Unity" Faction was a politician coalition and a parliamentary faction in Georgia. It was led by United National Movement, the largest party within the bloc, and additionally included Progress and Freedom and Victorious Georgia parties. It was one of the two factions in the 10th Parliament of Georgia, serving in the opposition to the Georgian Dream government.

Presidential elections were held in North Macedonia in 2019. Three candidates were on the ballot in the first round, held on 21 April: Stevo Pendarovski, supported by the ruling coalition led by the Social Democratic Union of Macedonia, including the Democratic Union for Integration; Gordana Siljanovska-Davkova of the leading opposition party VMRO-DPMNE, and Blerim Reka, an independent supported by Albanian opposition parties Alliance for Albanians and Besa Movement. The first round did not result in an absolute majority for any candidate, with Pendarovski receiving the most votes. In the second round held on 5 May, Pendarovski defeated Siljanovska-Davkova with 54% of the vote.

Parliamentary elections were held in the Comoros on 19 January 2020; in constituencies where no candidate received a majority, a second round was held alongside local elections on 23 February. The elections were boycotted by the main opposition parties, including the two largest parties in the outgoing Assembly, the Union for the Development of the Comoros and Juwa Party, in protest at constitutional reform and political repression, The result was a landslide victory for President Azali Assoumani's Convention for the Renewal of the Comoros, which won 20 of the 24 elected seats.



















