
The two-round system, also called ballotage, top-two runoff, or two-round plurality, is a single winner voting method. It is sometimes called plurality-runoff, although this term can also be used for other, closely-related systems such as instant-runoff voting or the exhaustive ballot. It falls under the class of plurality-based voting rules, together with instant-runoff and first-past-the-post (FPP). In a two-round system, if no candidate receives a majority of the vote in the first round, the two candidates with the most votes in the first round proceed to a second round where all other candidates are excluded. Both rounds are held under choose-one voting, where the voter marks a single favored candidate.

Eswatini, formally the Kingdom of Eswatini, also known by its former official name Swaziland and formally the Kingdom of Swaziland, is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. It is bordered by Mozambique to its northeast and South Africa to its north, west, south, and southeast. At no more than 200 km (120 mi) north to south and 130 km (81 mi) east to west, Eswatini is one of the smallest countries in Africa; despite this, its climate and topography are diverse, ranging from a cool and mountainous highveld to a hot and dry lowveld.
Norway elects its legislature on a national level. The parliament, the Storting, has 169 members elected for a four-year term by a form of proportional representation in multi-seat constituencies.

Open list describes any variant of party-list proportional representation where voters have at least some influence on the order in which a party's candidates are elected. This is as opposed to closed list, in which party lists are in a predetermined, fixed order by the time of the election and gives the general voter no influence at all on the position of the candidates placed on the party list.

Elections in North Korea are held every four-to-five years for the Supreme People's Assembly (SPA), the country's national legislature, and every four years for Local People's Assemblies. Each candidate is preselected by the North Korean government and there is no option to write in other candidates, meaning that voters may either submit the ballot unaltered as a "yes" vote or request a pen to cross out the name on the ballot. Critics argue that North Korean elections are show elections which lack competition and allow the government to claim a veneer of pseudo-democratic legitimacy. A person's vote is not kept anonymous, and those who cross off the name on a ballot are often subject to legal and professional consequences. According to official reports, turnout is near 100%.

The Parliament of Eswatini is bicameral, consisting of a lower chamber and an upper one. Some of the members of both chambers are elected, while the rest are appointed by the King of Eswatini. Election is by secret ballot in a first-past-the-post system of voting. Members of both chambers serve for five-year terms. All candidates run on a non-partisan basis, as political parties are banned.

The House of Assembly of Eswatini is the lower chamber of the country's bicameral Parliament. The Assembly may debate and pass bills, although as the country is an absolute monarchy, the role of the legislature is mostly advisory.

The Senate of Eswatini is the upper chamber of the country's bicameral Parliament. The Senate may debate or pass a bill, with the exception of a "money bill", which must first be introduced in the lower chamber, the House of Assembly.

The House of Assembly is the legislature of Dominica. It is established by Chapter III of the Constitution of Dominica, and together with the President of Dominica constitutes Dominica's Parliament. The House is unicameral, and consists of twenty-one Representatives, nine senators, and the Attorney General as an ex officio member. The Speaker of the House becomes the thirty-second member if chosen from outside the membership of the House.

The Legislative Assembly, also known as the Parliament of Samoa, is the national legislature of Samoa, seated at Apia, where the country's central administration is situated. Samoan Parliament is composed of two parts: the O le Ao o le Malo and the Legislative Assembly.

The National Assembly is the elected lower house of Bhutan's bicameral Parliament which also comprises the Druk Gyalpo and the National Council.

General elections were held in Swaziland on 19–20 September and 18–19 October 2003. Fifty-five independent candidates were elected to the Parliament. Voter turnout was only 18.4% of the 213,947 registered voters.

General elections were held in Swaziland on 20 September 2013.

The Swazi Democratic Party, also known by its abbreviation SWADEPA, is a political party in Eswatini led by its president Jan Sithole. SWADEPA was established in 2011 and took part in the 2013 parliamentary elections in Swaziland by putting up candidates running as individuals.
Elections in the Republic of India in 2018 included by-elections to the Lok Sabha, elections to the Rajya Sabha, elections to of eight states and numerous other by-elections to state legislative assemblies, councils and local bodies.

General elections were held in Eswatini on 18 August and 21 September 2018.

Government of the Kingdom of Eswatini is the union government created by the constitution of Eswatini where the monarch holds supreme executive, legislative, and judicial powers. The Ngwenyama (lion) is a hereditary leader, rules the country, with the assistance of a council of ministers and a national legislature.

General elections were held in Palau on 3 November 2020 to elect a President and the National Congress.

General elections were held in Seychelles on 22–24 October 2020 to elect the President and members of the National Assembly. The National Assembly elections had been due in 2021, but in July 2020 were brought forward by President Danny Faure in order to hold them together with the presidential elections, a proposal supported by opposition parties.
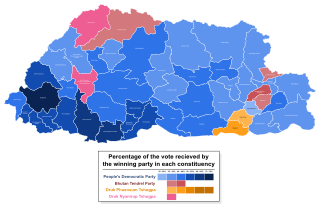
National Assembly elections were held in Bhutan on 30 November 2023 and 9 January 2024.











