Related Research Articles

The Freedom Front Plus is a right-wing political party in South Africa that was formed in 1994. It is led by Pieter Groenewald. Since 2024, it is a part of the current South African government of national unity together with the African National Congress (ANC), the Democratic Alliance and other parties.

The National Assembly is the directly elected house of the Parliament of South Africa, located in Cape Town, Western Cape. It consists of four hundred members who are elected every five years using a party-list proportional representation system where half of the members are elected proportionally from nine provincial lists and the remaining half from national lists so as to restore proportionality.

Lephalale Municipality is a local municipality within the Waterberg District Municipality, in the Limpopo province of South Africa. The seat is Lephalale.
Like South Africa's eight other provinces, the Northern Cape is governed by a parliamentary system, in which the Premier of the Northern Cape is elected by the Northern Cape Provincial Legislature and in turn selects the Northern Cape Executive Council. As in most other provinces, the African National Congress (ANC) has led the Northern Cape Provincial Government since the end of apartheid. In the most recent provincial election, held in 2019, the ANC won 18 of 30 seats in the provincial legislature and the Democratic Alliance was the official opposition in the legislature. Pursuant to the same election, Zamani Saul was elected Premier of the province.
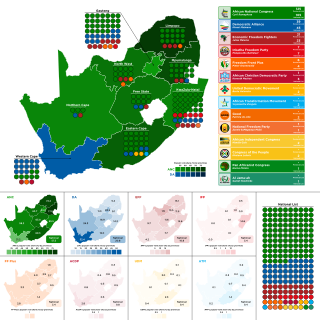
General elections were held in South Africa on 8 May 2019 to elect a new President, National Assembly and provincial legislatures in each province. These were the sixth elections held since the end of apartheid in 1994 and determined who would become the next President of South Africa.
The council of the City of Cape Town in the Western Cape, South Africa is elected every five years by a system of mixed-member proportional representation. Half of the councillors are elected by first-past-the-post voting from individual wards, while the other half are appointed from party lists so that the total number of party representatives is proportional to the number of votes received. By-elections are held to replace the councillors elected by wards if a vacancy occurs.

The 2019 Western Cape provincial election was held on 8 May 2019 to elect the 6th Western Cape Provincial Parliament. It was the sixth provincial election held since the establishment of the provincial legislature in 1994.

The Electoral Commission of South Africa (IEC) announced on 20 March 2019 that a record number of 48 parties had registered candidates for the national parliamentary election. This is 19 more parties that contested the 2014 national elections. In the provincial legislature elections, the total number of parties registering candidates were:

The 2021 South African municipal elections were held on 1 November 2021, to elect councils for all district, metropolitan and local municipalities in each of the country's nine provinces. It is the sixth municipal election held in South Africa since the end of apartheid in 1994, held every five years. The previous municipal elections were held in 2016. On 21 April 2021, President Cyril Ramaphosa announced that the elections will be held on Wednesday, 27 October 2021. It had been recommend by Dikgang Moseneke to delay the municipal elections until 2022. The Electoral Commission of South Africa (IEC) requested the Constitutional Court to support the date postponement. The Economic Freedom Fighters (EFF) supported the date postponement while the Democratic Alliance (DA) was against the postponement of the date. The Constitutional Court dismissed the application to postpone the date until 2022, ruling that they had to take place between 27 October and 1 November. On 9 September 2021, the Minister of Cooperative Governance and Traditional Affairs, Nkosazana Dlamini-Zuma announced that the elections would be held on 1 November.

The 2019 Gauteng provincial election was held on 8 May 2019, concurrently with the 2019 South African general election, to elect the 73 members of the Gauteng Provincial Legislature.

General elections were held in South Africa on 29 May 2024 to elect a new National Assembly as well as the provincial legislature in each of the nine provinces. This was the 7th general election held under the conditions of universal adult suffrage since the end of the apartheid era in 1994. The new National Council of Provinces (NCOP) will be elected at the first sitting of each provincial legislature.
The uMhlathuze Local Municipality council consists of sixty-seven members elected by mixed-member proportional representation. Thirty-four councillors are elected by first-past-the-post voting in thirty-four wards, while the remaining thirty-three are chosen from party lists so that the total number of party representatives is proportional to the number of votes received.
The 2019 Northern Cape provincial election was held on 8 May 2019 to allocate the 30 seats of the Northern Cape Provincial Legislature. Like all the South African provincial elections, it was held on the same day as the South African general election. 21 political parties participated in the election, of which only the African National Congress, Democratic Alliance, Economic Freedom Fighters, and Freedom Front Plus won seats. The ANC lost two seats, but maintained a majority.
The Multi-Party Charter (MPC), officially the Multi-Party Charter For South Africa (MPCSA), formerly known as the Moonshot Pact, is a pre-election agreement in South Africa that presents a united front in the 2024 South African general election against the three-decade rule of the African National Congress (ANC) and the recent rise of the controversial Economic Freedom Fighters (EFF), uMkhonto we Sizwe and Patriotic Alliance (PA).

The 2024 Western Cape provincial election was held on 29 May 2024, concurrently with the 2024 South African general election, to elect the 42 members of the 7th Western Cape Provincial Parliament.

The 2024 Gauteng provincial election was held on 29 May 2024, concurrently with the 2024 South African general election, to elect the 73 members of the Gauteng Provincial Legislature.

The Third Cabinet of Cyril Ramaphosa, also self-described as a "Government of National Unity" (GNU), was formed following the election of Ramaphosa to a second full term as President of South Africa following the 2024 general election. His party, the African National Congress (ANC), lost its absolute majority in the parliamentary election and was reduced to a plurality in the National Assembly. Following the election, the parties engaged in negotiations on forming a coalition government. On 14 June 2024, the ANC, the Democratic Alliance (DA), the Inkatha Freedom Party (IFP), Patriotic Alliance (PA) and Good, agreed to form a landmark national unity government, with Cyril Ramaphosa being re-elected President of South Africa. This marks the first time the ANC has had to govern without an absolute majority since the end of apartheid in 1994.
The Progressive Caucus is a political alliance in South Africa, formed in opposition to the Government of National Unity (GNU). The term 'progressive' is used by the caucus to describe itself, though this designation does not necessarily reflect endorsement of traditionally progressive policies.
References
- ↑ "Sun sets on 2024 elections | SAnews". www.sanews.gov.za. 2024-06-02. Retrieved 2024-06-04.
- ↑ "NORTHERN CAPE - PROVINCIAL LEGISLATURE - 2019". results.elections.org.za. 2019. Archived from the original on 2021-11-06. Retrieved 2021-11-28.
- ↑ Felix, Jason. "COALITION NATION | With love from the FF Plus: ANC looks set to govern Northern Cape yet again". News24. Retrieved 2024-06-13.
