
Acridine is an organic compound and a nitrogen heterocycle with the formula C13H9N. Acridines are substituted derivatives of the parent ring. It is a planar molecule that is structurally related to anthracene with one of the central CH groups replaced by nitrogen. Like the related molecules pyridine and quinoline, acridine is mildly basic. It is an almost colorless solid, which crystallizes in needles. There are few commercial applications of acridines, at one time acridine dyes were popular but they are now relegated to niche applications, such as with acridine orange. The name is a reference to the acrid odour and acrid skin-irritating effect of the compound.
Glycomics is the comprehensive study of glycomes, including genetic, physiologic, pathologic, and other aspects. Glycomics "is the systematic study of all glycan structures of a given cell type or organism" and is a subset of glycobiology. The term glycomics is derived from the chemical prefix for sweetness or a sugar, "glyco-", and was formed to follow the omics naming convention established by genomics and proteomics.
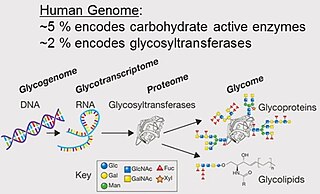
The glycome is the entire complement of sugars, whether free or present in more complex molecules, of an organism. An alternative definition is the entirety of carbohydrates in a cell. The glycome may in fact be one of the most complex entities in nature. "Glycomics, analogous to genomics and proteomics, is the systematic study of all glycan structures of a given cell type or organism" and is a subset of glycobiology.
Aminoacridine may refer to any of several chemical compounds:

9-Aminoacridine is a highly fluorescent dye used clinically as a topical antiseptic and experimentally as a mutagen, an intracellular pH indicator and a small molecule MALDI matrix.

4-Aminoacridine is an aminoacridine.
In mass spectrometry, a matrix is a compound that promotes the formation of ions. Matrix compounds are used in matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI), matrix-assisted ionization (MAI), and fast atom bombardment (FAB).
Nerida Fay Ellerton is an Australian mathematics educator and historian of mathematics, who works at Illinois State University as professor of mathematics education. As well as studying the present state of mathematics education, she and her husband McKenzie A. (Ken) Clements have researched the history of mathematics education, in the process discovering school worksheets in the Harvard Library that are among the oldest known writings of Abraham Lincoln.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.




