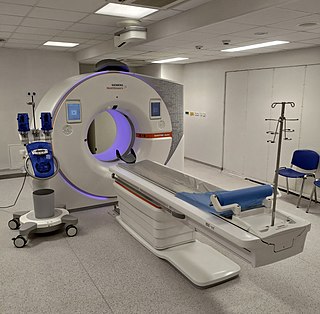
A computed tomography scan is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists.

Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to reveal internal structures hidden by the skin and bones, as well as to diagnose and treat disease. Medical imaging also establishes a database of normal anatomy and physiology to make it possible to identify abnormalities. Although imaging of removed organs and tissues can be performed for medical reasons, such procedures are usually considered part of pathology instead of medical imaging.

Mechanical ventilation or assisted ventilation is the medical term for using a machine called a ventilator to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move air into and out of the lungs, with the main goal of helping the delivery of oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide. Mechanical ventilation is used for many reasons, including to protect the airway due to mechanical or neurologic cause, to ensure adequate oxygenation, or to remove excess carbon dioxide from the lungs. Various healthcare providers are involved with the use of mechanical ventilation and people who require ventilators are typically monitored in an intensive care unit.

Pulmonology, pneumology or pneumonology is a medical specialty that deals with diseases involving the respiratory tract. It is also known as respirology, respiratory medicine, or chest medicine in some countries and areas.

Liquid breathing is a form of respiration in which a normally air-breathing organism breathes an oxygen-rich liquid (such as a perfluorocarbon), rather than breathing air, by selecting a liquid that can hold a large amount of oxygen and is capable of CO2 gas exchange.

Electrical impedance tomography (EIT) is a noninvasive type of medical imaging in which the electrical conductivity, permittivity, and impedance of a part of the body is inferred from surface electrode measurements and used to form a tomographic image of that part. Electrical conductivity varies considerably among various biological tissues or the movement of fluids and gases within tissues. The majority of EIT systems apply small alternating currents at a single frequency, however, some EIT systems use multiple frequencies to better differentiate between normal and suspected abnormal tissue within the same organ.
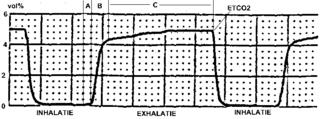
Capnography is the monitoring of the concentration or partial pressure of carbon dioxide (CO
2) in the respiratory gases. Its main development has been as a monitoring tool for use during anesthesia and intensive care. It is usually presented as a graph of CO
2 (measured in kilopascals, "kPa" or millimeters of mercury, "mmHg") plotted against time, or, less commonly, but more usefully, expired volume (known as volumetric capnography). The plot may also show the inspired CO
2, which is of interest when rebreathing systems are being used. When the measurement is taken at the end of a breath (exhaling), it is called "end tidal" CO
2 (PETCO2).

Velocimetry is the measurement of the velocity of fluids. This is a task often taken for granted, and involves far more complex processes than one might expect. It is often used to solve fluid dynamics problems, study fluid networks, in industrial and process control applications, as well as in the creation of new kinds of fluid flow sensors. Methods of velocimetry include particle image velocimetry and particle tracking velocimetry, Molecular tagging velocimetry, laser-based interferometry, ultrasonic Doppler methods, Doppler sensors, and new signal processing methodologies.

Flail chest is a life-threatening medical condition that occurs when a segment of the rib cage breaks due to trauma and becomes detached from the rest of the chest wall. Two of the symptoms of flail chest are chest pain and shortness of breath.

Microtek International Inc. is a Taiwan-based multinational manufacturer of digital imaging products and other consumer electronics. It produces imaging equipment for medical, biological and industrial fields. It occupies 20 percent of the global imaging market and holds 450 patents worldwide.

A CT pulmonary angiogram (CTPA) is a medical diagnostic test that employs computed tomography (CT) angiography to obtain an image of the pulmonary arteries. Its main use is to diagnose pulmonary embolism (PE). It is a preferred choice of imaging in the diagnosis of PE due to its minimally invasive nature for the patient, whose only requirement for the scan is an intravenous line.

Positron emission tomography–computed tomography is a nuclear medicine technique which combines, in a single gantry, a positron emission tomography (PET) scanner and an x-ray computed tomography (CT) scanner, to acquire sequential images from both devices in the same session, which are combined into a single superposed (co-registered) image. Thus, functional imaging obtained by PET, which depicts the spatial distribution of metabolic or biochemical activity in the body can be more precisely aligned or correlated with anatomic imaging obtained by CT scanning. Two- and three-dimensional image reconstruction may be rendered as a function of a common software and control system.
Perfusion is the passage of fluid through the lymphatic system or blood vessels to an organ or a tissue. The practice of perfusion scanning is the process by which this perfusion can be observed, recorded and quantified. The term perfusion scanning encompasses a wide range of medical imaging modalities.
In medicine Imaging Lung Sound Behavior with Vibration Response Imaging (VRI), is a novelty computer-based technology that takes the concept of the stethoscope to a more progressive level. Since the invention of the stethoscope by René-Théophile-Hyacinthe Laennec France in 1816, physicians have been utilizing lung sounds to diagnose various chest conditions. Today auscultation provides physicians with extensive information on the examination of the patient. The skills of the examiner however, vary, as seen in a clinical study that was conducted on the diagnosis of pneumonia in 2004.

Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by long-term respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. GOLD 2024 defined COPD as a heterogeneous lung condition characterized by chronic respiratory symptoms due to abnormalities of the airways and/or alveoli (emphysema) that cause persistent, often progressive, airflow obstruction.
Modes of mechanical ventilation are one of the most important aspects of the usage of mechanical ventilation. The mode refers to the method of inspiratory support. In general, mode selection is based on clinician familiarity and institutional preferences, since there is a paucity of evidence indicating that the mode affects clinical outcome. The most frequently used forms of volume-limited mechanical ventilation are intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV) and continuous mandatory ventilation (CMV). There have been substantial changes in the nomenclature of mechanical ventilation over the years, but more recently it has become standardized by many respirology and pulmonology groups. Writing a mode is most proper in all capital letters with a dash between the control variable and the strategy.

The history of X-ray computed tomography dates back to at least 1917 with the mathematical theory of the Radon transform In the early 1900s an Italian radiologist named Alessandro Vallebona invented tomography which used radiographic film to see a single slice of the body. It was not widely used until the 1930s, when Dr Bernard George Ziedses des Plantes developed a practical method for implementing the technique.
Hyperpolarized 129Xe gas magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used to visualize the anatomy and physiology of body regions that are difficult to image with standard proton MRI. In particular, the lung, which lacks substantial density of protons, is particularly useful to be visualized with 129Xe gas MRI. This technique has promise as an early-detection technology for chronic lung diseases and imaging technique for processes and structures reliant on dissolved gases. 129Xe is a stable, naturally occurring isotope of xenon with 26.44% isotope abundance. It is one of two Xe isotopes, along with 131Xe, that has non-zero spin, which allows for magnetic resonance. 129Xe is used for MRI because its large electron cloud permits hyperpolarization and a wide range of chemical shifts. The hyperpolarization creates a large signal intensity, and the wide range of chemical shifts allows for identifying when the 129Xe associates with molecules like hemoglobin. 129Xe is preferred over 131Xe for MRI because 129Xe has spin 1/2, a longer T1, and 3.4 times larger gyromagnetic ratio (11.78 MHz/T).

Ventilation-perfusion coupling is the relationship between ventilation and perfusion processes, which take place in the respiratory system and the cardiovascular system. Ventilation is the movement of gas during breathing, and perfusion is the process of pulmonary blood circulation, which delivers oxygen to body tissues. Anatomically, the lung structure, alveolar organization, and alveolar capillaries contribute to the physiological mechanism of ventilation and perfusion. Ventilation-perfusion coupling maintains a constant ventilation/perfusion ratio near 0.8 on average, while the regional variation exists within the lungs due to gravity. When the ratio gets above or below 0.8, it is considered abnormal ventilation-perfusion coupling, also known as a ventilation–perfusion mismatch. Lung diseases, cardiac shunts, and smoking can cause a ventilation-perfusion mismatch that results in significant symptoms and diseases, which can be treated through treatments like bronchodilators and oxygen therapy.
Hyperpolarized gas MRI, also known as hyperpolarized helium-3 MRI or HPHe-3 MRI, is a medical imaging technique that uses hyperpolarized gases to improve the sensitivity and spatial resolution of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This technique has many potential applications in medicine, including the imaging of the lungs and other areas of the body with low tissue density.














