
In computing, a printer is a peripheral machine which makes a durable representation of graphics or text, usually on paper. While most output is human-readable, bar code printers are an example of an expanded use for printers. Different types of printers include 3D printers, inkjet printers, laser printers, and thermal printers.
National Rail (NR) is the trading name licensed for use by the Rail Delivery Group, a group representing passenger train operating companies (TOCs) of England, Scotland, and Wales. The TOCs run the passenger services previously provided by the British Railways Board, from 1965 using the brand name British Rail. Northern Ireland, which is bordered by the Republic of Ireland, has a different system. National Rail services share a ticketing structure and inter-availability that generally do not extend to services which were not part of British Rail.
Computer reservation systems, or central reservation systems (CRS), are computerized systems used to store and retrieve information and conduct transactions related to air travel, hotels, car rental, or other activities. Originally designed and operated by airlines, CRSs were later extended for use by travel agencies, and global distribution systems (GDSs) to book and sell tickets for multiple airlines. Most airlines have outsourced their CRSs to GDS companies, which also enable consumer access through Internet gateways.
Sabre Global Distribution System, owned by Sabre Corporation, is a travel reservation system used by travel agents and companies to search, price, book, and ticket travel services provided by airlines, hotels, car rental companies, rail providers and tour operators. Originally developed by American Airlines under CEO C.R. Smith with the assistance of IBM in 1960, the booking service became available for use by external travel agents in 1976 and became independent of the airline in March 2000.
A passenger name record (PNR) is a record in the database of a computer reservation system (CRS) that contains the itinerary for a passenger or a group of passengers travelling together. The concept of a PNR was first introduced by airlines that needed to exchange reservation information in case passengers required flights of multiple airlines to reach their destination ("interlining"). For this purpose, IATA and ATA have defined standards for interline messaging of PNR and other data through the "ATA/IATA Reservations Interline Message Procedures - Passenger" (AIRIMP). There is no general industry standard for the layout and content of a PNR. In practice, each CRS or hosting system has its own proprietary standards, although common industry needs, including the need to map PNR data easily to AIRIMP messages, has resulted in many general similarities in data content and format between all of the major systems.

An electronic ticket is a method of ticket entry, processing, and marketing for companies in the airline, railways and other transport and entertainment industries.

Amadeus IT Group, S.A. is a major Spanish multinational technology company that provides software for the global travel and tourism industry. It is the world's leading provider of travel technology that focus on developing software for airlines, hotels, travel agencies, and other travel-related businesses.

The Shere SMART is a desktop-based railway ticket issuing system, developed by the Guildford-based company Shere Ltd, utilising Newbury Data ND4020 ticket printer, first introduced in Britain in 2003. Since the first trial installation of the system in the ticket office at London Bridge station, approximately 300 terminals have been installed at stations on the Southern and former Thameslink networks.
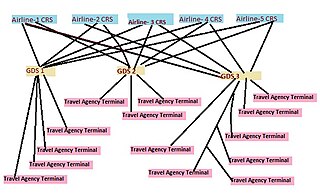
A global distribution system (GDS) is a computerised network system owned or operated by a company that enables transactions between travel industry service providers, mainly airlines, hotels, car rental companies, and travel agencies. The GDS mainly uses real-time inventory from the service providers. Travel agencies traditionally relied on GDS for services, products and rates in order to provide travel-related services to the end consumers. Thus, a GDS can link services, rates and bookings consolidating products and services across all three travel sectors: i.e., airline reservations, hotel reservations, car rentals.

Avantix Mobile ("AVB") is a portable railway ticket issuing system used across the British railway network from 2001 to 2017.
Airline reservation systems (ARS) are systems that allow an airline to sell their inventory (seats). It contains information on schedules and fares and contains a database of reservations and of tickets issued. ARSs are part of passenger service systems (PSS), which are applications supporting the direct contact with the passenger.
ESC/P, short for Epson Standard Code for Printers and sometimes styled Escape/P, is a printer control language developed by Epson to control computer printers. It was mainly used in Epson's dot matrix printers, beginning with the MX-80 in 1980, as well as some of the company's inkjet printers. It is still widely used in many receipt thermal printers. During the era of dot matrix printers, it was also used by other manufacturers, sometimes in modified form. At the time, it was a popular mechanism to add formatting to printed text, and was widely supported in software.
Videcom International Limited is a United Kingdom travel technology company based in Henley-on-Thames. It designs, develops and provides modern computer reservations systems to airlines and the travel industry, specializing in the hosting and distribution of airline sales.
Alternate air ticket purchasing order systems allow for alternative ways of purchasing air tickets and GDS Connectivity not involving Internet or personal TA contact.
Galileo is a computer reservations system (CRS) owned by Travelport. As of 2000, it had a 26.4% share of worldwide CRS airline bookings. In addition to airline reservations, the Galileo CRS is also used to book train travel, cruises, car rental, and hotel rooms.
Corporate travel management is the function of managing a company’s strategic approach to travel, the negotiations with all vendors, day-to-day operation of the corporate travel program, traveler safety and security, credit-card management and travel and expenses ('T&E') data management.

TravelSky Technology Limited is the dominant provider of information technology services to the Chinese air travel and tourism industries. Its clients include airlines, airports, air travel suppliers, travel agencies, individual and corporate travel consumers and cargo services. It is listed on the Hong Kong stock exchange and its majority shareholder or parent group is the China TravelSky Holding Company, a State-owned enterprise (SOE).
Infini is a computer reservations system based in Japan which provides its services in the Japanese market. It was created in 1990 by All Nippon Airways and Abacus (GDS) who currently own 100% of Infini. It utilises technology from Sabre Holdings to provide booking and ticketing capabilities to travel agencies in Japan.
In the aviation industry, a pseudo city code,pseudo-city code, or office ID, is an alpha-numeric identifier for a corporate user of a computer reservation system (CRS) or global distribution system (GDS), typically a travel agency. The codes are typically 3 or 4 characters long,, and are unique to a specific office of a travel agency. They are used to associate each agency's bookings with the agency, and also to identify private fares available to the agency.

In 2014, a new design was introduced for train tickets issued on the National Rail network in Great Britain. The pre-2014 design was similar to the APTIS design introduced in 1986 by British Rail.








