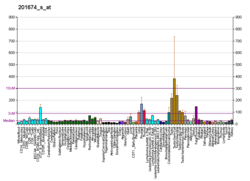
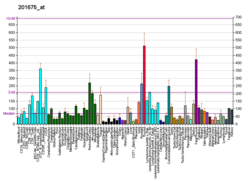
| AKAP1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | AKAP1 , AKAP, AKAP121, AKAP149, AKAP84, D-PPP1R43, PRKA1, SAKAP84, TDRD17, A-kinase anchoring protein 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 602449; MGI: 104729; HomoloGene: 31165; GeneCards: AKAP1; OMA:AKAP1 - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A kinase anchor protein 1, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AKAP1 gene. [5] [6] [7]