
Ras homolog gene family, member B, also known as RHOB, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the RHOB gene.

Transforming protein RhoA, also known as Ras homolog family member A (RhoA), is a small GTPase protein in the Rho family of GTPases that in humans is encoded by the RHOA gene. While the effects of RhoA activity are not all well known, it is primarily associated with cytoskeleton regulation, mostly actin stress fibers formation and actomyosin contractility. It acts upon several effectors. Among them, ROCK1 and DIAPH1 are the best described. RhoA, and the other Rho GTPases, are part of a larger family of related proteins known as the Ras superfamily, a family of proteins involved in the regulation and timing of cell division. RhoA is one of the oldest Rho GTPases, with homologues present in the genomes since 1.5 billion years. As a consequence, RhoA is somehow involved in many cellular processes which emerged throughout evolution. RhoA specifically is regarded as a prominent regulatory factor in other functions such as the regulation of cytoskeletal dynamics, transcription, cell cycle progression and cell transformation.

Insulin receptor substrate 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IRS2 gene.

Rab GDP dissociation inhibitor alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GDI1 gene.

Proto-oncogene vav is a protein that in humans is encoded by the VAV1 gene.

RHO protein GDP dissociation inhibitor of Rho proteins regulates GDP/GTP exchange. The protein plays an important role in the activation of the oxygen superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase of phagocytes. This process requires the interaction of membrane-associated cytochrome b559 with 3 cytosolic components: p47-phox, p67-phox and a heterodimer of the small G-protein p21Rac1 and rho GDI. The association of p21rac and GDI inhibits dissociation of GDP from p21rac, thereby maintaining it in an inactive form. The proteins are attached via a lipid tail on p21rac that binds to the hydrophobic region of GDI. Dissociation of these proteins might be mediated by the release of lipids from membranes through the action of phospholipases. The lipids may then compete with the lipid tail on p21rac for the hydrophobic pocket on GDI.
Rac2 is a small signaling G protein, and is a member of the Rac subfamily of the family Rho family of GTPases. It is encoded by the gene RAC2.

Ras-related protein Ral-A (RalA) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RALA gene on chromosome 7. This protein is one of two paralogs of the Ral protein, the other being RalB, and part of the Ras GTPase family. RalA functions as a molecular switch to activate a number of biological processes, majorly cell division and transport, via signaling pathways. Its biological role thus implicates it in many cancers.

Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ARHGDIA gene.

Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ARHGDIB gene. Aliases of this gene include RhoGDI2, GDID4, Rho GDI 2, and others.
Ras-related protein Rab-9A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAB9A gene.

RhoG is a small monomeric GTP-binding protein, and is an important component of many intracellular signalling pathways. It is a member of the Rac subfamily of the Rho family of small G proteins and is encoded by the gene RHOG.

Rab GDP dissociation inhibitor beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GDI2 gene.
Ras-related protein Ral-B (RalB) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RALB gene on chromosome 2. This protein is one of two paralogs of the Ral protein, the other being RalA, and part of the Ras GTPase family. RalA functions as a molecular switch to activate a number of biological processes, majorly cell division and transport, via signaling pathways. Its biological role thus implicates it in many cancers.

Kinesin-associated protein 3 (KAP3) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIFAP3 gene. It is a non-motor, accessory subunit which co-oligomerizes with the motor subunits KIF3A and KIF3B or KIF3C, to form heterotrimeric kinesin-2 motor proteins. Kinesin-2 KAP subunits were initially characterized in echinoderms and mice.
GTP-binding protein GEM is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GEM gene.

Integrin beta-8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ITGB8 gene.

Rap guanine nucleotide exchange factor 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAPGEF2 gene.

Rap1 GTPase-GDP dissociation stimulator 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RAP1GDS1 gene.
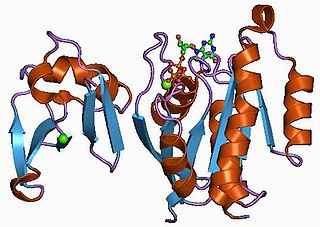
Ras-related protein Rap-1b, also known as GTP-binding protein smg p21B, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAP1B gene.
























