
Aporia crataegi, the black-veined white, is a large butterfly of the family Pieridae. A. crataegi is widespread and common. Its range extends from northwest Africa in the west to Transcaucasia and across the Palearctic to Siberia and Japan in the east. In the south, it is found in Turkey, Cyprus, Israel, Lebanon and Syria. It is not present in the British Isles and northern Scandinavia.
The Tagiadini are a tribe in the skipper butterfly subfamily Pyrginae. Many of its genera were of uncertain relationships for long, and delimitation of the Tagiadini versus the Celaenorrhini was quite disputed at times. The species of this tribe are found in mostly tropical regions of Africa, Asia and Australia.

Abantis is an Afrotropical genus of skipper butterflies. They are also known as the paradise skippers. Their imagos are generally attractive with bold or colourful wing and/or body markings. They occur in either forest or savanna, and several species are very localized or thinly distributed. The territorial males are encountered more often than the females. Males engage territorial intruders, and are prone to very rapid and high flight, while females display more relaxed flight habits, closer to the ground. Plants of several families serve as food plants, and only one egg is oviposited per plant. The larva is pale and spotted to varying degrees, and pupates inside a leaf shelter drawn together by silk threads.
Herimosa albovenata, the white-veined skipper, is a butterfly of the family Hesperiidae. It is found in Australia in inland New South Wales, South Australia and Western Australia.
Abantis tettensis, the spotted velvet skipper, is a butterfly of the family Hesperiidae. It is found in South-West Africa, Botswana, Transvaal, northern Cape, from Zimbabwe to Zaire and in Kenya.

Abantis bicolor, the bicoloured skipper, is a butterfly of the family Hesperiidae and the subfamily Pyrginae. Described in 1864 and endemic to South Africa, the bicoloured skipper is restricted to lowland forests from the Eastern Cape to the southern and northern coasts of KwaZulu-Natal.
Abantis paradisea, the paradise skipper, is a butterfly of the family Hesperiidae. It is found in KwaZulu-Natal, Zululand, Transvaal, Swaziland, Zimbabwe and from Botswana to Somalia.

Colotis vesta, the veined tip, veined orange or veined golden Arab, is a butterfly of the family Pieridae. It is found in the Afrotropical realm.

Graphium leonidas, the veined swordtail, veined swallowtail or common graphium, is a species of butterfly in the family Papilionidae, found in Sub-Saharan Africa.

Charaxes achaemenes, the bushveld emperor or bush charaxes, is a butterfly of the family Nymphalidae found across Africa.

Acridocarpus natalitius, the moth fruit, is a species of plant in the Malpighiaceae family. It is found in south-eastern Africa, where it ranges from Pondoland to Limpopo in South Africa, and eastwards to Swaziland and Mozambique. It is critically endangered in eastern Zimbabwe.
Abantis arctomarginata, the tricoloured paradise skipper, is a butterfly in the family Hesperiidae. It is found in Tanzania and Malawi.
Abantis contigua, the contiguous paradise skipper, is a butterfly in the family Hesperiidae. It is found in Cameroon, the Republic of the Congo, Angola, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Uganda, western Kenya and Zambia. The habitat consists of deciduous woodland.

Abantis ja, the Djah paradise skipper, is a butterfly in the family Hesperiidae. The species was first described by Hamilton Herbert Druce in 1909. It is found in Ivory Coast, Ghana, Cameroon, the Republic of the Congo and the Central African Republic. The habitat consists of forests.
Abantis leucogaster, the streaked paradise skipper, is a butterfly in the family Hesperiidae. It is found in Guinea, Sierra Leone, Ivory Coast, Ghana, Nigeria, Cameroon, the Republic of the Congo, the Central African Republic, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Uganda and Tanzania. The habitat consists of primary forests and well-developed secondary forests.

Abantis lucretia, or Lucretia's paradise skipper, is a butterfly in the family Hesperiidae. The species was first described by Hamilton Herbert Druce in 1909. It is found in Guinea, Sierra Leone, Ghana, Nigeria, Cameroon, the Republic of the Congo, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Zambia and Uganda. The habitat consists of forests.
Abantis nigeriana, the Nigerian paradise skipper, is a butterfly in the family Hesperiidae. It is found in Senegal, the Gambia, Burkina Faso, Guinea, Ghana, Nigeria, southern Sudan and Gabon. The habitat consists of Guinea savanna.
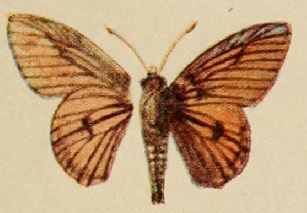
Abantis rubra, the russet paradise skipper, is a butterfly in the family Hesperiidae. It is found in Nigeria, Cameroon, the Republic of the Congo, the Central African Republic and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The habitat consists of forests.

Abantis zambesiaca, the Zambezi paradise skipper, is a butterfly in the family Hesperiidae. It is found in western and southern Tanzania, the Democratic Republic of Congo (Shaba), Zambia, Malawi, Namibia (Caprivi), Mozambique and Zimbabwe. The habitat consists of savanna and Brachystegia woodland.
Venosa may also refer to:









