Related Research Articles
The centimetre–gram–second system of units is a variant of the metric system based on the centimetre as the unit of length, the gram as the unit of mass, and the second as the unit of time. All CGS mechanical units are unambiguously derived from these three base units, but there are several different ways in which the CGS system was extended to cover electromagnetism.

A centimetre or centimeter is a unit of length in the International System of Units (SI), equal to one hundredth of a metre, centi being the SI prefix for a factor of 1/100. The centimetre was the base unit of length in the now deprecated centimetre–gram–second (CGS) system of units.
The dyne is a derived unit of force specified in the centimetre–gram–second (CGS) system of units, a predecessor of the modern SI.
The gauss, symbol G, is a unit of measurement of magnetic induction, also known as magnetic flux density. The unit is part of the Gaussian system of units, which inherited it from the older CGS-EMU system. It was named after the German mathematician and physicist Carl Friedrich Gauss in 1936. One gauss is defined as one maxwell per square centimetre.
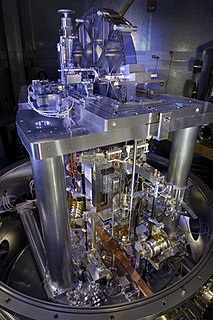
The kilogram is the unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI), having the unit symbol kg. It is a widely used measure in science, engineering and commerce worldwide, and is often simply called a kilo colloquially. It means 'one thousand grams'.
The International System of Units, known by the international abbreviation SI in all languages and sometimes pleonastically as the SI system, is the modern form of the metric system and based on the metre as the unit of length and either the kilogram as the unit of mass or the kilogram-force as the unit of force.</ref> and the world's most widely used system of measurement. Established and maintained by the General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM), it is the only system of measurement with an official status in nearly every country in the world, employed in science, technology, industry, and everyday commerce.

The metric system is a system of measurement that succeeded the decimalised system based on the metre that had been introduced in France in the 1790s. The historical development of these systems culminated in the definition of the International System of Units (SI) in the mid-20th century, under the oversight of an international standards body. Adopting the metric system is known as metrication.
The oersted is the coherent derived unit of the auxiliary magnetic field H in the centimetre–gram–second system of units (CGS). It is equivalent to 1 dyne per maxwell.
The statvolt is a unit of voltage and electrical potential used in the CGS-ESU and gaussian systems of units. In terms of its relation to the SI units, one statvolt corresponds to exactly ccgs 10−8 volt, i.e. to 299.792458 volts.

The gram is a unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one one thousandth of a kilogram.
The maxwell is the CGS (centimetre–gram–second) unit of magnetic flux.

Gaussian units constitute a metric system of physical units. This system is the most common of the several electromagnetic unit systems based on cgs (centimetre–gram–second) units. It is also called the Gaussian unit system, Gaussian-cgs units, or often just cgs units. The term "cgs units" is ambiguous and therefore to be avoided if possible: there are several variants of cgs with conflicting definitions of electromagnetic quantities and units.
The abcoulomb or electromagnetic unit of charge is the derived physical unit of electric charge in the cgs-emu system of units. One abcoulomb is equal to ten coulombs.
The abampere (abA), also called the biot (Bi) after Jean-Baptiste Biot, is the derived electromagnetic unit of electric current in the emu-cgs system of units. One abampere corresponds to ten amperes in the SI system of units. An abampere of current in a circular path of one centimeter radius produces a magnetic field of 2π oersteds at the center of the circle.
The foot–pound–second system or FPS system is a system of units built on three fundamental units: the foot for length, the (avoirdupois) pound for either mass or force, and the second for time.
The abohm is the derived unit of electrical resistance in the emu-cgs (centimeter-gram-second) system of units. One abohm corresponds to 10−9 ohms in the SI system of units, which is a nanoohm.
The electrostatic system of units (CGS-ESU) is a system of units used to measure quantities of electric charge, electric current, and voltage within the centimetre–gram–second system of metric units. In electrostatic units, electrical charge is defined by the force that it exerts on other charges.

The gram per cubic centimetre is a unit of density in the CGS system, commonly used in chemistry, defined as mass in grams divided by volume in cubic centimetres. The official SI symbols are g/cm3, g·cm−3, or g cm−3. It is equivalent to the units gram per millilitre (g/mL) and kilogram per litre (kg/L). The density of water is about 1 g/cm3, since the gram was originally defined as the mass of one cubic centimetre of water at its maximum density at 4 °C.
The statampere (statA) is the derived electromagnetic unit of electric current in the CGS-ESU and Gaussian systems of units.:278 One statampere corresponds to 10/ccgs ampere ≈ 3.33564×10−10 ampere in the SI system of units.
References
- ↑ Graf, Rudolf (1999). Modern Dictionary of Electronics (Seventh ed.). Wobrun, MA: Newness.