
In mechanics, acceleration is the rate of change of the velocity of an object with respect to time. Accelerations are vector quantities. The orientation of an object's acceleration is given by the orientation of the net force acting on that object. The magnitude of an object's acceleration, as described by Newton's Second Law, is the combined effect of two causes:
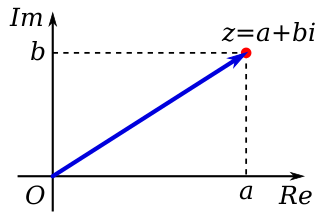
In mathematics, a complex number is an element of a number system that extends the real numbers with a specific element denoted i, called the imaginary unit and satisfying the equation ; every complex number can be expressed in the form , where a and b are real numbers. Because no real number satisfies the above equation, i was called an imaginary number by René Descartes. For the complex number , a is called the real part, and b is called the imaginary part. The set of complex numbers is denoted by either of the symbols or C. Despite the historical nomenclature "imaginary", complex numbers are regarded in the mathematical sciences as just as "real" as the real numbers and are fundamental in many aspects of the scientific description of the natural world.

In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the form of energy that it possesses due to its motion. It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acceleration, the body maintains this kinetic energy unless its speed changes. The same amount of work is done by the body when decelerating from its current speed to a state of rest. Formally, a kinetic energy is any term in a system's Lagrangian which includes a derivative with respect to time and the second term in a Taylor expansion of a particle's relativistic energy.

In Newtonian mechanics, momentum is the product of the mass and velocity of an object. It is a vector quantity, possessing a magnitude and a direction. If m is an object's mass and v is its velocity, then the object's momentum p is :

Nuclear fusion is a reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei, usually deuterium and tritium, are combined to form one or more different atomic nuclei and subatomic particles. The difference in mass between the reactants and products is manifested as either the release or absorption of energy. This difference in mass arises due to the difference in nuclear binding energy between the atomic nuclei before and after the reaction. Nuclear fusion is the process that powers active or main-sequence stars and other high-magnitude stars, where large amounts of energy are released.
In physics, power is the amount of energy transferred or converted per unit time. In the International System of Units, the unit of power is the watt, equal to one joule per second. In older works, power is sometimes called activity. Power is a scalar quantity.

In physics, the special theory of relativity, or special relativity for short, is a scientific theory of the relationship between space and time. In Albert Einstein's 1905 treatment, the theory is based on two postulates:
- The laws of physics are invariant (identical) in all inertial frames of reference.
- The speed of light in vacuum is the same for all observers, regardless of the motion of light source or observer.

In physics, spacetime is any mathematical model that fuses the three dimensions of space and the one dimension of time into a single four dimensional continuum. Spacetime diagrams are useful in visualizing and understanding relativistic effects such as how different observers perceive where and when events occur.

In mathematics, a tensor is an algebraic object that describes a multilinear relationship between sets of algebraic objects related to a vector space. Tensors may map between different objects such as vectors, scalars, and even other tensors. There are many types of tensors, including scalars and vectors, dual vectors, multilinear maps between vector spaces, and even some operations such as the dot product. Tensors are defined independent of any basis, although they are often referred to by their components in a basis related to a particular coordinate system; those components form an array, which can be thought of as a high-dimensional matrix.
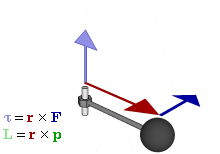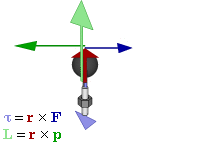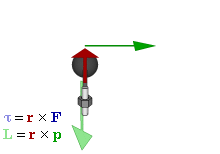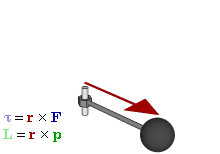
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational analogue of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force. It describes the rate of change of angular momentum that would be imparted to an isolated body.

Voltage, also known as electric pressure, electric tension, or (electric) potential difference, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a static electric field, it corresponds to the work needed per unit of charge to move a test charge between the two points. In the International System of Units (SI), the derived unit for voltage is named volt.

Newton's laws of motion are three basic laws of classical mechanics that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it. These laws can be paraphrased as follows:
- A body remains at rest, or in motion at a constant speed in a straight line, unless acted upon by a force.
- When a body is acted upon by a force, the time rate of change of its momentum equals the force.
- If two bodies exert forces on each other, these forces have the same magnitude but opposite directions.

In physics, work is the energy transferred to or from an object via the application of force along a displacement. In its simplest form, for a constant force aligned with the direction of motion, the work equals the product of the force strength and the distance traveled. A force is said to do positive work if when applied it has a component in the direction of the displacement of the point of application. A force does negative work if it has a component opposite to the direction of the displacement at the point of application of the force.

Time dilation is the difference in elapsed time as measured by two clocks, either due to a relative velocity between them or due to a difference in gravitational potential between their locations. When unspecified, "time dilation" usually refers to the effect due to velocity.
In fluid dynamics, drag is a force acting opposite to the relative motion of any object moving with respect to a surrounding fluid. This can exist between two fluid layers or between a fluid and a solid surface.
In linear algebra, an eigenvector or characteristic vector of a linear transformation is a nonzero vector that changes at most by a constant factor when that linear transformation is applied to it. The corresponding eigenvalue, often represented by , is the multiplying factor.

A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by accumulating electric charges on two closely spaced surfaces that are insulated from each other. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals.

Velocity is the speed and the direction of motion of an object. Velocity is a fundamental concept in kinematics, the branch of classical mechanics that describes the motion of bodies.
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer.

A transformer is a deep learning architecture that relies on the parallel multi-head attention mechanism. The modern transformer was proposed in the 2017 paper titled 'Attention Is All You Need' by Ashish Vaswani et al., Google Brain team. It is notable for requiring less training time than previous recurrent neural architectures, such as long short-term memory (LSTM), and its later variation has been prevalently adopted for training large language models on large (language) datasets, such as the Wikipedia Corpus and Common Crawl, by virtue of the parallelized processing of input sequence. Input text is split into n-grams encoded as tokens and each token is converted into a vector via looking up from a word embedding table. At each layer, each token is then contextualized within the scope of the context window with other (unmasked) tokens via a parallel multi-head attention mechanism allowing the signal for key tokens to be amplified and less important tokens to be diminished. Though the transformer paper came out in 2017, the softmax-based attention mechanism was proposed earlier in 2014 by Bahdanau, Cho, and Bengio for machine translation, and transformers with linearized attention were introduced already in 1992 by Schmidhuber.

















