The blue whale is a marine mammal and a baleen whale. Reaching a maximum confirmed length of 29.9 meters (98 ft) and weighing up to 199 tonnes, it is the largest animal known ever to have existed. The blue whale's long and slender body can be of various shades of greyish-blue dorsally and somewhat lighter underneath. Four subspecies are recognized: B. m. musculus in the North Atlantic and North Pacific, B. m. intermedia in the Southern Ocean, B. m. brevicauda in the Indian Ocean and South Pacific Ocean, and B. m. indica in the Northern Indian Ocean. There is also a population in the waters off Chile that may constitute a fifth subspecies.

Elephants are the largest living land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae and the order Proboscidea; extinct relatives include mammoths and mastodons. Distinctive features of elephants include a long proboscis called a trunk, tusks, large ear flaps, pillar-like legs, and tough but sensitive grey skin. The trunk is prehensile, bringing food and water to the mouth and grasping objects. Tusks, which are derived from the incisor teeth, serve both as weapons and as tools for moving objects and digging. The large ear flaps assist in maintaining a constant body temperature as well as in communication. African elephants have larger ears and concave backs, whereas Asian elephants have smaller ears and convex or level backs.

Entropy is a scientific concept that is most commonly associated with a state of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynamics, where it was first recognized, to the microscopic description of nature in statistical physics, and to the principles of information theory. It has found far-ranging applications in chemistry and physics, in biological systems and their relation to life, in cosmology, economics, sociology, weather science, climate change, and information systems including the transmission of information in telecommunication.
In mathematics, the Laplace transform, named after its discoverer Pierre-Simon Laplace, is an integral transform that converts a function of a real variable to a function of a complex variable . The transform has many applications in science and engineering, mostly as a tool for solving linear differential equations. In particular, it transforms ordinary differential equations into algebraic equations and convolution into multiplication. For suitable functions f, the Laplace transform is defined by the integral
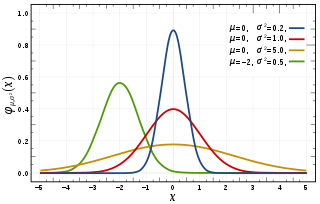
In statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is

The red panda, also known as the lesser panda, is a small mammal native to the eastern Himalayas and southwestern China. It has dense reddish-brown fur with a black belly and legs, white-lined ears, a mostly white muzzle and a ringed tail. Its head-to-body length is 51–63.5 cm (20.1–25.0 in) with a 28–48.5 cm (11.0–19.1 in) tail, and it weighs between 3.2 and 15 kg. It is well adapted to climbing due to its flexible joints and curved semi-retractile claws.
S, or s, is the 19th letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ess, plural esses.

In physics, spacetime is any mathematical model that fuses the three dimensions of space and the one dimension of time into a single four-dimensional continuum. Spacetime diagrams are useful in visualizing and understanding relativistic effects such as how different observers perceive where and when events occur.

The tiger is the largest living cat species and a member of the genus Panthera. It is most recognisable for its dark vertical stripes on orange fur with a white underside. An apex predator, it primarily preys on ungulates, such as deer and wild boar. It is territorial and generally a solitary but social predator, requiring large contiguous areas of habitat to support its requirements for prey and rearing of its offspring. Tiger cubs stay with their mother for about two years and then become independent, leaving their mother's home range to establish their own.

Thomas Stearns Eliot was a poet, essayist, publisher, playwright, literary critic and editor. He is considered to be one of the 20th century's greatest poets, as well as a central figure in English-language Modernist poetry. His trials in language, writing style, and verse structure reinvigorated English poetry. He is also noted for his critical essays, which often reevaluated long-held cultural beliefs.
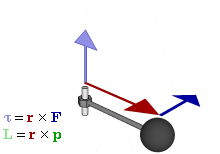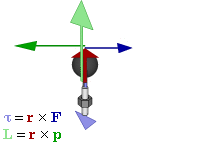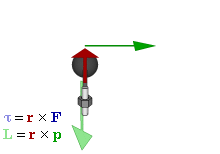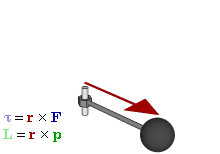
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational analogue of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force. It describes the rate of change of angular momentum that would be imparted to an isolated body.

The lion is a large cat of the genus Panthera native to Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body; short, rounded head; round ears; and a hairy tuft at the end of its tail. It is sexually dimorphic; adult male lions are larger than females and have a prominent mane. It is a social species, forming groups called prides. A lion's pride consists of a few adult males, related females, and cubs. Groups of female lions usually hunt together, preying mostly on large ungulates. The lion is an apex and keystone predator; although some lions scavenge when opportunities occur and have been known to hunt humans, lions typically do not actively seek out and prey on humans.
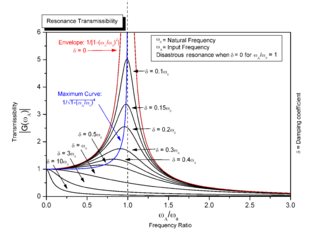
Resonance is a phenomenon that occurs when an object or system is subjected to an external force or vibration that matches its natural frequency. When this happens, the object or system absorbs energy from the external force and starts vibrating with a larger amplitude. Resonance can occur in various systems, such as mechanical, electrical, or acoustic systems, and it is often desirable in certain applications, such as musical instruments or radio receivers. However, resonance can also be detrimental, leading to excessive vibrations or even structural failure in some cases.
Newton's laws of motion are three laws that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it. These laws, which provide the basis for Newtonian mechanics, can be paraphrased as follows:
- A body remains at rest, or in motion at a constant speed in a straight line, unless acted upon by a force.
- The net force on a body is equal to the body's acceleration multiplied by its mass or, equivalently, the rate at which the body's momentum changes with time.
- If two bodies exert forces on each other, these forces have the same magnitude but opposite directions.
Hard rock or heavy rock is a heavier subgenre of rock music typified by aggressive vocals and distorted electric guitars. Hard rock began in the mid-1960s with the garage, psychedelic and blues rock movements. Some of the earliest hard rock music was produced by the Kinks, the Who, the Rolling Stones, Cream, Vanilla Fudge, and the Jimi Hendrix Experience. In the late 1960s, bands such as Blue Cheer, the Jeff Beck Group, Iron Butterfly, Led Zeppelin, Golden Earring, Steppenwolf, Deep Purple and Grand Funk Railroad also produced hard rock.

The speed of sound is the distance travelled per unit of time by a sound wave as it propagates through an elastic medium. At 20 °C (68 °F), the speed of sound in air is about 343 m/s, or one km in 2.91 s or one mile in 4.69 s. It depends strongly on temperature as well as the medium through which a sound wave is propagating. At 0 °C (32 °F), the speed of sound in air is about 331 m/s. More simply, the speed of sound is how fast vibrations travel.

The snow leopard, commonly known as the ounce, is a species of large cat in the genus Panthera of the family Felidae. The species is native to the mountain ranges of Central and South Asia. It is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List because the global population is estimated to number fewer than 10,000 mature individuals and is expected to decline about 10% by 2040. It is mainly threatened by poaching and habitat destruction following infrastructural developments. It inhabits alpine and subalpine zones at elevations of 3,000–4,500 m (9,800–14,800 ft), ranging from eastern Afghanistan, the Himalayas and the Tibetan Plateau to southern Siberia, Mongolia and western China. In the northern part of its range, it also lives at lower elevations.

The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water. Viscosity is defined scientifically as a force multiplied by a time divided by an area. Thus its SI units are newton-seconds per square metre, or pascal-seconds.

In mathematics, the Riemann hypothesis is the conjecture that the Riemann zeta function has its zeros only at the negative even integers and complex numbers with real part 1/2. Many consider it to be the most important unsolved problem in pure mathematics. It is of great interest in number theory because it implies results about the distribution of prime numbers. It was proposed by Bernhard Riemann (1859), after whom it is named.

Dendrocoelidae is a family of freshwater tricladida flatworms that has a holarctic distribution.