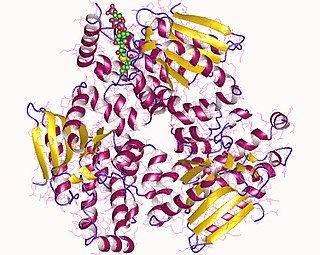
Enoyl-CoA-(∆) isomerase (EC 5.3.3.8, also known as dodecenoyl-CoA- isomerase, 3,2-trans-enoyl-CoA isomerase, ∆3 ,∆2 -enoyl-CoA isomerase, or acetylene-allene isomerase, is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of cis- or trans-double bonds of coenzyme A bound fatty acids at gamma-carbon to trans double bonds at beta-carbon as below:
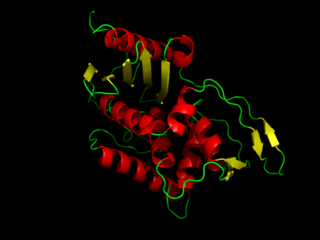
DD-transpeptidase is a bacterial enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of the R-L-αα-D-alanyl moiety of R-L-αα-D-alanyl-D-alanine carbonyl donors to the γ-OH of their active-site serine and from this to a final acceptor. It is involved in bacterial cell wall biosynthesis, namely, the transpeptidation that crosslinks the peptide side chains of peptidoglycan strands.
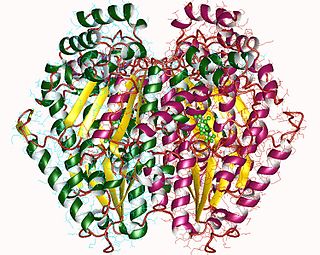
Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase (GPI), alternatively known as phosphoglucose isomerase/phosphoglucoisomerase (PGI) or phosphohexose isomerase (PHI), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GPI gene on chromosome 19. This gene encodes a member of the glucose phosphate isomerase protein family. The encoded protein has been identified as a moonlighting protein based on its ability to perform mechanistically distinct functions. In the cytoplasm, the gene product functions as a glycolytic enzyme that interconverts glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) and fructose-6-phosphate (F6P). Extracellularly, the encoded protein functions as a neurotrophic factor that promotes survival of skeletal motor neurons and sensory neurons, and as a lymphokine that induces immunoglobulin secretion. The encoded protein is also referred to as autocrine motility factor (AMF) based on an additional function as a tumor-secreted cytokine and angiogenic factor. Defects in this gene are the cause of nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia, and a severe enzyme deficiency can be associated with hydrops fetalis, immediate neonatal death and neurological impairment. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2014]
In molecular biology, initiation factors are proteins that bind to the small subunit of the ribosome during the initiation of translation, a part of protein biosynthesis.

EF-Tu is a prokaryotic elongation factor responsible for catalyzing the binding of an aminoacyl-tRNA (aa-tRNA) to the ribosome. It is a G-protein, and facilitates the selection and binding of an aa-tRNA to the A-site of the ribosome. As a reflection of its crucial role in translation, EF-Tu is one of the most abundant and highly conserved proteins in prokaryotes. It is found in eukaryotic mitochondria as TUFM.
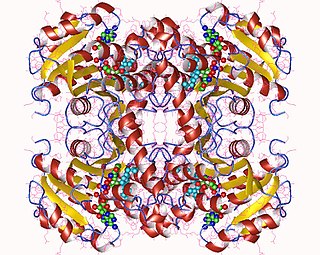
Enoyl-acyl carrier protein reductase, is a key enzyme of the type II fatty acid synthesis (FAS) system. ENR is an attractive target for narrow-spectrum antibacterial drug discovery because of its essential role in metabolism and its sequence conservation across many bacterial species. In addition, the bacterial ENR sequence and structural organization are distinctly different from those of mammalian fatty acid biosynthesis enzymes.
The long chain fatty acyl-CoA ligase is an enzyme of the ligase family that activates the oxidation of complex fatty acids. Long chain fatty acyl-CoA synthetase catalyzes the formation of fatty acyl-CoA by a two-step process proceeding through an adenylated intermediate. The enzyme catalyzes the following reaction,

Protein disulfide-isomerase A3 (PDIA3), also known as glucose-regulated protein, 58-kD (GRP58), is an isomerase enzyme encoded by the autosomal gene PDIA3 in humans. This protein localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and interacts with lectin chaperones calreticulin and calnexin (CNX) to modulate folding of newly synthesized glycoproteins. It is thought that complexes of lectins and this protein mediate protein folding by promoting formation of disulfide bonds in their glycoprotein substrates.

In molecular biology, Beta-ketoacyl-ACP synthase EC 2.3.1.41, is an enzyme involved in fatty acid synthesis. It typically uses malonyl-CoA as a carbon source to elongate ACP-bound acyl species, resulting in the formation of ACP-bound β-ketoacyl species such as acetoacetyl-ACP.
D-Bifunctional protein deficiency is an autosomal recessive peroxisomal fatty acid oxidation disorder. Peroxisomal disorders are usually caused by a combination of peroxisomal assembly defects or by deficiencies of specific peroxisomal enzymes. The peroxisome is an organelle in the cell similar to the lysosome that functions to detoxify the cell. Peroxisomes contain many different enzymes, such as catalase, and their main function is to neutralize free radicals and detoxify drugs. For this reason peroxisomes are ubiquitous in the liver and kidney. D-BP deficiency is the most severe peroxisomal disorder, often resembling Zellweger syndrome.
The crotonase family comprises mechanistically diverse proteins that share a conserved trimeric quaternary structure, the core of which consists of 4 turns of a (beta/beta/alpha)n superhelix.
In enzymology, a trans-2-decenoyl-[acyl-carrier protein] isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Acyl-CoA-binding protein in humans belongs to the family of Acyl-CoA-binding proteins.

Protein disulfide-isomerase, also known as the beta-subunit of prolyl 4-hydroxylase (P4HB), is an enzyme that in humans encoded by the P4HB gene. The human P4HB gene is localized in chromosome 17q25. Unlike other prolyl 4-hydroxylase family proteins, this protein is multifunctional and acts as an oxidoreductase for disulfide formation, breakage, and isomerization. The activity of P4HB is tightly regulated. Both dimer dissociation and substrate binding are likely to enhance its enzymatic activity during the catalysis process.

Peroxisomal 3,2-trans-enoyl-CoA isomerase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PECI gene.

Enoyl Coenzyme A hydratase, short chain, 1, mitochondrial, also known as ECHS1, is a human gene.
Endozepines are endogenous compounds that bind to the benzodiazepine binding site on the GABAA receptor complex. That is to say, endozepines are the natural ligands of the benzodiazepine receptor. Endozepines may have sedative effects similar to benzodiazepine medications such as diazepam, or they may have opposite effects, depending on whether they are agonists, antagonists, or inverse agonists.

In molecular biology, chaperone DnaJ, also known as Hsp40, is a molecular chaperone protein. It is expressed in a wide variety of organisms from bacteria to humans.

Ketoacyl synthases (KSs) catalyze the condensation reaction of acyl-CoA or acyl-acyl ACP with malonyl-CoA to form 3-ketoacyl-CoA or with malonyl-ACP to form 3-ketoacyl-ACP. This reaction is a key step in the fatty acid synthesis cycle, as the resulting acyl chain is two carbon atoms longer than before. KSs exist as individual enzymes, as they do in type II fatty acid synthesis and type II polyketide synthesis, or as domains in large multidomain enzymes, such as type I fatty acid synthases (FASs) and polyketide synthases (PKSs). KSs are divided into five families: KS1, KS2, KS3, KS4, and KS5.
Protein methylation is a type of post-translational modification featuring the addition of methyl groups to proteins. It can occur on the nitrogen-containing side-chains of arginine and lysine, but also at the amino- and carboxy-termini of a number of different proteins. In biology, methyltransferases catalyze the methylation process, activated primarily by S-adenosylmethionine. Protein methylation has been most studied in histones, where the transfer of methyl groups from S-adenosyl methionine is catalyzed by histone methyltransferases. Histones that are methylated on certain residues can act epigenetically to repress or activate gene expression.














