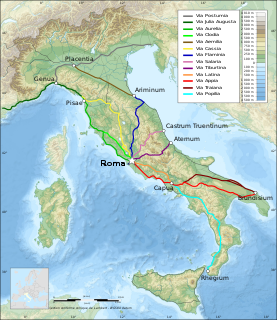
The Via Aemilia was a trunk Roman road in the north Italian plain, running from Ariminum (Rimini), on the Adriatic coast, to Placentia (Piacenza) on the river Padus (Po). It was completed in 187 BC. The Via Aemilia connected at Rimini with the Via Flaminia to Rome, which had been completed 33 years earlier.
Aemilia is a large main-belt asteroid. Aemilia was discovered by the French brothers Paul Henry and Prosper Henry on January 26, 1876. The credit for this discovery was given to Paul. It is probably named after the Via Aemilia, a Roman road in Italy that runs from Piacenza to Rimini.

Neurospora crassa is a type of red bread mold of the phylum Ascomycota. The genus name, meaning "nerve spore" in Greek, refers to the characteristic striations on the spores. The first published account of this fungus was from an infestation of French bakeries in 1843.
Aemilia Lepida is the name of several ancient Roman women belonging to the gens Aemilia. The name was given to daughters of men belonging to the Lepidus branch of the Aemilius family. The first Aemilia Lepida to be mentioned by Roman historians was the former fiancée of the younger Cato. Subsequent Aemiliae are known because of their marriages.

The Via Aemilia Scauri was an ancient Roman road built by the consul Marcus Aemilius Scaurus during his term as Censor in 109 BC.
Mating types are molecular mechanisms that regulate compatibility in sexually reproducing eukaryotes. They occur in isogamous and anisogamous species. Depending on the group, different mating types are often referred to by numbers, letters, or simply "+" and "−" instead of "male" and "female", that refer to "sexes" or differences in size between gametes. Syngamy can only take place between gametes carrying different mating types.

Aemilia Tertia, also known as Aemilia Paulla, was the wife of the Roman consul and censor Scipio Africanus. She was the daughter, possibly the third surviving daughter, of the consul Lucius Aemilius Paullus and the sister of the consul Lucius Aemilius Paulus Macedonicus.

Naming conventions for women in ancient Rome differed from nomenclature for men, and practice changed dramatically from the Early Republic to the High Empire and then into Late Antiquity. Females were identified officially by the feminine of the family name (nomen gentile, that is, the gens name), which might be further differentiated by the genitive form of the father's cognomen, or for a married woman her husband's. Numerical adjectives might distinguish among sisters, such as Tertia, "the Third". By the late Republic, women also adopted the feminine of their father's cognomen.
Emilia is a historic region of northern Italy, which approximately corresponds to the western and north-eastern portions of the modern region Emilia-Romagna, with the area of Romagna forming the remainder of the modern region.
Aemilia is a genus of tiger moths in the family Erebidae. It was initially named Ameles, but this name properly refers to a praying mantis genus.

Pseudohemihyalea is a genus of arctiine tussock moths in the Erebidae family. While the caterpillars of most species of Pseudohemihyalea feed on broad-leaved trees, the P. ambigua group has larvae that feed on conifers. Their forewing coloration has accordingly evolved to light-and-dark lengthwise striping, giving better camouflage among the slim needles of the host plants. In this, they seem to be convergent to certain geometer moths, such as Caripeta piniata or Sabulodes niveostriata.
Pseudoliva is a genus of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Pseudolividae. Pseudoliva is the type genus of that family.

Manzonia crassa is a species of minute sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk or micromollusk in the family Rissoidae.

Aemilia ockendeni is a moth of the family Erebidae. It is found in Peru and Bolivia.
Aemilia mincosa is a moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Druce in 1906. It is found in Peru.
Aemilia pagana is a moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Schaus in 1894. It is found in Brazil.
Aemilia peropaca is a moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Seitz in 1920. It is found in Colombia.
Aemilia rubriplaga is a moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Francis Walker in 1855. It is found in Venezuela.

Porticus Aemilia was a portico in ancient Rome. It was one of the largest commercial structures of its time and functioned as a storehouse and distribution center for goods entering the city via the Tiber river.









