Related Research Articles
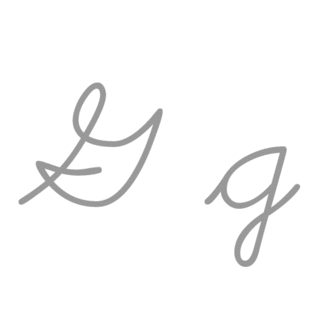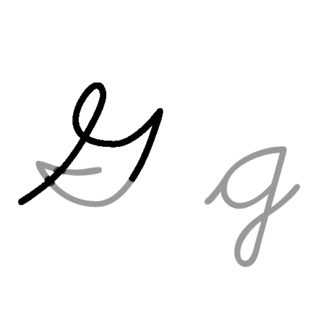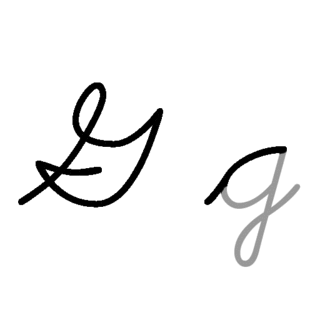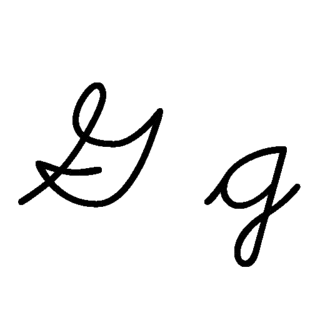
G or g is the seventh letter of the ISO basic Latin alphabet. Its name in English is gee, plural gees.

Herbert George Wells was an English writer. Prolific in many genres, he wrote dozens of novels, short stories, and works of social commentary, history, satire, biography and autobiography. His work also included two books on recreational war games. Wells is now best remembered for his science fiction novels and is often called the "father of science fiction", along with Jules Verne and the publisher Hugo Gernsback.

Christopher George Latore Wallace, better known by his stage names the Notorious B.I.G., Biggie Smalls, or simply Biggie, was an American rapper and songwriter. Rooted in the New York rap scene and gangsta rap traditions, he is considered one of the greatest rappers of all time. The Notorious B.I.G. became known for his distinctive laidback lyrical delivery, offsetting the lyrics' often grim content and his own intimidating appearance. His music was often semi-autobiographical, telling of hardship and criminality, but also of debauchery and celebration.

Cucurbita pepo is a cultivated plant of the genus Cucurbita. It yields varieties of winter squash and pumpkin, but the most widespread varieties belong to the subspecies Cucurbita pepo subsp. pepo, called summer squash.

Among animals, viviparity is development of the embryo inside the body of the parent. This is opposed to oviparity which is a reproductive mode in which females lay developing eggs that complete their development and hatch externally from the mother.
Straightneck squash is a cultivated variety of Cucurbita pepo grown as a type of summer squash that is usually yellow-colored. It is also known as yellow squash, though other squashes, such as crookneck squash, may also be known by that name. It has mildly sweet and watery flesh, and thin tender skins that can be left on the fruit for many types of recipes. It was almost certainly domesticated in the eastern United States, although other variants of the same species were domesticated in Mesoamerica. This squash grows on vined plants reaching 60–90 cm (2.0–3.0 ft) in height that thrive in mild weather. It is well known as an item in American cooking where it is fried, microwaved, steamed, boiled, or baked. It is often used in recipes interchangeably with zucchini. A good yellow summer squash will be small and firm with tender skin free of blemishes and bruising. It is available all year long in some regions, but is at its peak from early through late summer. One similar inedible C. pepo variety is C. pepo var. ovifera.

The G20 is an international forum for the governments and central bank governors from 19 countries and the European Union (EU). Founded in 1999 with the aim to discuss policy pertaining to the promotion of international financial stability, the G20 has expanded its agenda since 2008 and heads of government or heads of state, as well as finance ministers, foreign ministers and think tanks, have periodically conferred at summits ever since. It seeks to address issues that go beyond the responsibilities of any one.

Gastrotheca is a genus of frogs in the family Hemiphractidae. They are found in Central America south of Costa Rica and in South America. Most species occur in the American Cordillera from southern Costa Rica to north-western Argentina. This genus makes up the bulk of marsupial frog diversity; formerly it was placed in the "Leptodactylidae" assemblage.
Agkonia is a genus of moths in the subfamily Arctiinae. The genus was erected by Paul Dognin in 1894.

Halocynthia aurantium, commonly known as the sea peach, is a species of tunicate in the order Stolidobranchia. Sea peaches are commonly found in the northern Pacific ocean, ranging from the Arctic Sea south to Puget Sound, and most common in the Bering Sea at a depth of 40 to 100 metres. The sea peach is typically barrel shaped, growing to a height of 18 centimetres, and its body is attached directly to the substrate. It is usually red or orange with a smooth or wrinkled tunic. There are two siphons at the top. The sea peach is preyed upon by crabs and sea stars.

Comostola is a genus of moths in the family Geometridae erected by Edward Meyrick in 1888. They are found primarily in Asia and Australia.

In telecommunications, 5G is the fifth generation technology standard for broadband cellular networks, which cellular phone companies began deploying worldwide in 2019, and is the planned successor to the 4G networks which provide connectivity to most current cellphones. 5G networks are predicted to have more than 1.7 billion subscribers worldwide by 2025, according to the GSM Association. Like its predecessors, 5G networks are cellular networks, in which the service area is divided into small geographical areas called cells. All 5G wireless devices in a cell are connected to the Internet and telephone network by radio waves through a local antenna in the cell. The main advantage of the new networks is that they will have greater bandwidth, giving higher download speeds, eventually up to 10 gigabits per second (Gbit/s). Due to the increased bandwidth, it is expected the networks will not exclusively serve cellphones like existing cellular networks, but also be used as general internet service providers for laptops and desktop computers, competing with existing ISPs such as cable internet, and also will make possible new applications in internet of things (IoT) and machine to machine areas. 4G cellphones are not able to use the new networks, which require 5G enabled wireless devices.

Alexander Russell was a Scottish physician and naturalist.
Agkonia miranda is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by George Hampson in 1900. It is found in Bolivia.
Agkonia pega is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Paul Dognin in 1894. It is found in Ecuador.

Panara is a genus in the butterfly family Riodinidae present in the Neotropical realm.

Gorgonocephalus arcticus is a species of basket star in the class Ophiuroidea. The genus name comes from the Greek, gorgós meaning "dreaded" and cephalus meaning "head", and refers to the similarity between these echinoids and the Gorgon's head from Greek myth with its coiled serpents for hair. This species is also able to live non parasitically on the exterior of other sessile animals while it continues to grow. G. arcticus have been observed living on the exterior of Boltenia ovifera, a species of tunicates found in a similar range of the Arctic to Cape Cod. This species is found in varying depths in the water column, from as shallow as the sublittoral zone to a maximum depth of 1500 m. Their feeding mechanism has been extensively studied in the wild and in captivity.
Several genera of the Lithosiini tribe of lichen moths are placed as incertae sedis due to the uncertainty of their phylogenetic relationships within the tribe.

Animals make use of a variety of modes of reproduction to produce their young. Traditionally this variety was classified into three modes, oviparity, viviparity, and ovoviviparity.

Boltenia ovifera is a species of ascidian tunicates in the family Pyuridae. It is found in the Arctic to the South of Cape Cod.
References
- ↑ Beccaloni, G.; Scoble, M.; Kitching, I.; Simonsen, T.; Robinson, G.; Pitkin, B.; Hine, A.; Lyal, C., eds. (2003). "Agkonia ovifera". The Global Lepidoptera Names Index . Natural History Museum. Retrieved April 25, 2018.
| This Lithosiini-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |