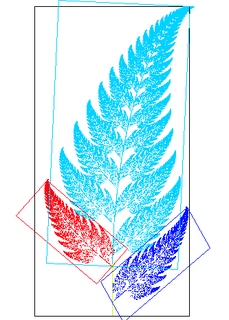
In Euclidean geometry, an affine transformation, or an affinity, is a geometric transformation that preserves lines and parallelism.
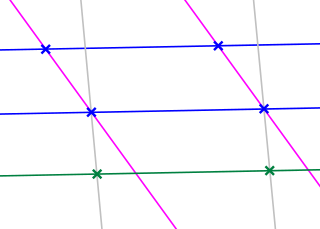
In mathematics, affine geometry is what remains of Euclidean geometry when not using the metric notions of distance and angle.
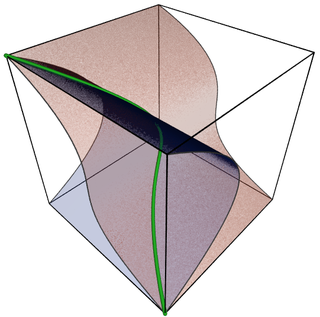
Algebraic varieties are the central objects of study in algebraic geometry, a sub-field of mathematics. Classically, an algebraic variety is defined as the set of solutions of a system of polynomial equations over the real or complex numbers. Modern definitions generalize this concept in several different ways, while attempting to preserve the geometric intuition behind the original definition.

In mathematics, an affine space is a geometric structure that generalizes some of the properties of Euclidean spaces in such a way that these are independent of the concepts of distance and measure of angles, keeping only the properties related to parallelism and ratio of lengths for parallel line segments.
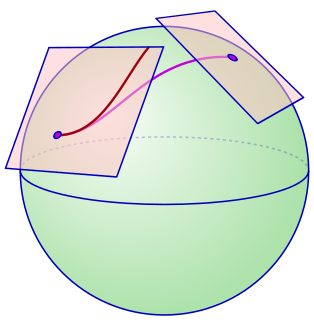
In Differential geometry, an affine connection is a geometric object on a smooth manifold which connects nearby tangent spaces, so it permits tangent vector fields to be differentiated as if they were functions on the manifold with values in a fixed vector space. The notion of an affine connection has its roots in 19th-century geometry and tensor calculus, but was not fully developed until the early 1920s, by Élie Cartan and Hermann Weyl. The terminology is due to Cartan and has its origins in the identification of tangent spaces in Euclidean space Rn by translation: the idea is that a choice of affine connection makes a manifold look infinitesimally like Euclidean space not just smoothly, but as an affine space.

William Kirby was an English entomologist, an original member of the Linnean Society and a Fellow of the Royal Society, as well as a country rector, so that he was an eminent example of the "parson-naturalist". He is considered the "founder of entomology".

Smerinthus cerisyi, the one-eyed sphinx or Cerisy's sphinx, is a moth of the family Sphingidae. The species was first described by William Kirby who named the species in honor of Alexandre Louis Lefèbvre de Cérisy in 1837. It is known from south-eastern Alaska, the southern parts of all Canadian provinces and in the northern border states of the United States south into northern Indiana, Pennsylvania and Ohio and along the west coast to southern California, eastward to the Rocky Mountains and into western New Mexico north to western North Dakota. It has also been recorded from Illinois and as far south as Missouri.

Sericoda is a genus of harpaline ground beetles. They are native to the Holarctic. Their habit resembles some members of the related genus Agonum, but they are generally smaller. The origin of Sericoda is apparently North America, with the Central American genus Elliptoleus the closest living relative.

Agonum is a large genus of ground beetles in the subfamily Harpalinae, tribe Platynini. They are mid-sized to smallish beetles, typically with dark metallic hues – often reddish or bronze, but sometimes black, green etc.

Agonum muelleri is a species of ground beetle native to the Palearctic, the Nearctic and the Near East. In Europe, it is found in Albania, the Azores, Baltic states, Belarus, Benelux, Great Britain including the Isle of Man, Northern Ireland, mainland Portugal, Russia, Sardinia, Sicily (doubtful), mainland Spain, Ukraine, Scandinavia, Slovenia, Croatia, Serbia, Montenegro, Bosnia-Herzegovina, and North Macedonia, and Central Europe.

Nebriinae is a subfamily of beetles in the family Carabidae, containing the following genera:

Platyninae is a subfamily of ground beetles. Occasionally it was treated as a tribe Platynini of subfamily Harpalinae, particularly when this was circumscribed loosely.

The Pericopina is a subtribe of tiger moths in the family Erebidae. The subtribe was described by Francis Walker in 1869.

Platynini is a tribe of ground beetles in the family Carabidae. There are at least 260 described species in Platynini.

Harpalitae is a supertribe of ground beetles in the family Carabidae. There are at least 90 genera and 460 described species in Harpalitae.














