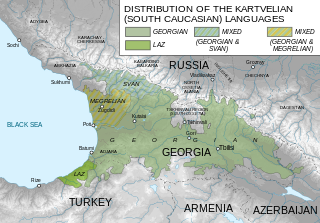
The Laz language or Lazuri is a Kartvelian language spoken by the Laz people on the southeastern shore of the Black Sea. In 2007, it was estimated that there were around 20,000 native speakers in Turkey, in a strip of land extending from Melyat to the Georgian border, and around 1,000 native speakers around Adjara in Georgia. There are also around 1,000 native speakers of Laz in Germany.

The adjective hygrophanous refers to the color change of mushroom tissue as it loses or absorbs water, which causes the pileipellis to become more transparent when wet and opaque when dry.

A germ pore is a small pore in the outer wall of a fungal spore through which the germ tube exits upon germination. It can be apical or eccentric in its location, and, on light microscopy, may be visualized as a lighter coloured area on the cell wall.

Agrocybe is a genus of mushrooms in the family Strophariaceae. The genus has a widespread distribution, and contains about 100 species.

The Zydretae were an ancient people of Colchis recorded by the Classical accounts as dwelling on the coast of the Pontus Euxinus, on the southern side of the Apsarus river, and between the Machelonoi and the Lazi tribes. The early 2nd century Roman author Arrian lists several neighboring and probably ethnically related tribes on a west to east orientation: the Sannoi (Sanigs), Drilae, Machelonoi, Heniochoi, Zudreitai, and Lazoi. The anonymous Periplus Ponti Euxini places them further south between the Akamosis and Archabis rivers. Little is known about the Zydretae's social and political life, but at that time when Arrian described them, they seem to have been subjected to the king of Iberia in eastern Georgia.

Alexander Hanchett Smith was an American mycologist known for his extensive contributions to the taxonomy and phylogeny of the higher fungi, especially the agarics.

Agrocybe pediades, commonly known as the common fieldcap or common agrocybe, is a typically lawn and other types of grassland mushroom, but can also grow on mulch containing horse manure. It was first described as Agaricus pediades by Swedish mycologist Elias Magnus Fries in 1821, and moved to its current genus Agrocybe by Victor Fayod in 1889. A synonym for this mushroom is Agrocybe semiorbicularis, though some guides list these separately. Technically it is edible, but it could be confused with poisonous species, including one of the genus Hebeloma.
Agrocybe farinacea is a species of mushroom in the family Strophariaceae. It has been reported to contain the hallucinogen psilocybin, however there has been no recent chemical analysis carried out on this mushroom, nor any modern reports of psychoactivity.

Agrocybe praecox, commonly known as the spring fieldcap, spring agrocybe or early agrocybe, is a species of brown-spored mushroom which appears early in the year in woods, gardens and fields. According to modern taxonomic analysis, it is just one of a cluster of closely similar species which are often referred to as the Agrocybe praecox complex. It is found in Europe, North Africa and North America.

Agrocybe putaminum, commonly known as the mulch fieldcap, is a species of agaric fungus in the family Strophariaceae in the Agrocybe sororia complex. Described as new to science in 1913, it is found in Asia, Australia, Europe, and western North America, where it grows in parks, gardens, and roadsides in woodchip mulch. Fruitbodies of the fungus have a dull brownish-orange cap with a matte texture, a grooved stipe, and a bitter, mealy taste.

Cyclocybe aegerita, also calledAgrocybe cylindracea, Agrocybe aegerita or Pholiota aegerita, is a mushroom in the genus Cyclocybe which is commonly known as the poplar fieldcap or poplar mushroom, or velvet pioppini. In Japan, it is called Yanagi-matsutake (柳松茸).
Unspecific peroxygenase (EC 1.11.2.1, aromatic peroxygenase, mushroom peroxygenase, haloperoxidase-peroxygenase, Agrocybe aegerita peroxidase) is an enzyme with systematic name substrate:hydrogen peroxide oxidoreductase (RH-hydroxylating or -epoxidising). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Agrocybe allocystis is a species of agaric fungus in the family Strophariaceae. Found in Argentina, it was described as new to science by mycologist Rolf Singer in 1969.
Agrocybe procera is a species of agaric fungus in the family Strophariaceae. Found in Chile, it was described as new to science by mycologist Rolf Singer in 1969.
Agrocybe viscosa is a species of agaric fungus in the family Strophariaceae. Found in Chile, it was described as new to science by mycologist Rolf Singer in 1969.

Agrocybe rivulosa is a species of mushroom in the genus Agrocybe. The first recorded sighting of the mushroom was in 2003. The species was first found in Britain in the year 2004. It is a relatively large mushroom, with a stem of 5 to 10 centimeters, and a cap which reaches 4 to 10 centimeters across. The colour of the cap ranges from yellow to pale orange-brown. It has been eaten, and is reasonably tasty with no obvious toxicity.

Agrocybe retigera is a species of mushroom in the genus Agrocybe. The first known sighting of the species was in the early 1950s. It was first described by author Speggazini Singer in 1950. The mushroom has since been found in common areas, especially grassy ones, such as gardens, meadows and parks. Agrocybe retigera is most commonly found in tropical and sub-tropical areas around the globe. The size of the cap is usually between 17 and 44 millimetres, and it is generally pale in colour. The colour of the mushroom itself ranges from cream to pale-brown.

Agrocybe sororia is a species of Basidiomycota mushroom in the genus Agrocybe.

Cyclocybe parasitica, also known as tawaka in Māori language or poplar mushroom, is a species of gilled mushroom in the genus Cyclocybe found mostly in New Zealand and Australia. It grows on native and introduced trees where it can cause heart rot, and does not seem to be associated with conifers.













