Related Research Articles
In music theory, a diatonic scale is any heptatonic scale that includes five whole steps and two half steps (semitones) in each octave, in which the two half steps are separated from each other by either two or three whole steps, depending on their position in the scale. This pattern ensures that, in a diatonic scale spanning more than one octave, all the half steps are maximally separated from each other.

In music, just intonation or pure intonation is the tuning of musical intervals as whole number ratios of frequencies. An interval tuned in this way is said to be pure, and is called a just interval. Just intervals consist of tones from a single harmonic series of an implied fundamental. For example, in the diagram, if the notes G3 and C4 are tuned as members of the harmonic series of the lowest C, their frequencies will be 3 and 4 times the fundamental frequency. The interval ratio between C4 and G3 is therefore 4:3, a just fourth.
In music theory, the term mode or modus is used in a number of distinct senses, depending on context.
In music theory, a scale is any set of musical notes ordered by fundamental frequency or pitch. A scale ordered by increasing pitch is an ascending scale, and a scale ordered by decreasing pitch is a descending scale.

Pythagorean tuning is a system of musical tuning in which the frequency ratios of all intervals are based on the ratio 3:2. This ratio, also known as the "pure" perfect fifth, is chosen because it is one of the most consonant and easiest to tune by ear and because of importance attributed to the integer 3. As Novalis put it, "The musical proportions seem to me to be particularly correct natural proportions." Alternatively, it can be described as the tuning of the syntonic temperament in which the generator is the ratio 3:2, which is ≈ 702 cents wide.
The chromatic scale is a set of twelve pitches used in tonal music, with notes separated by the interval of a semitone. Chromatic instruments, such as the piano, are made to produce the chromatic scale, while other instruments capable of continuously variable pitch, such as the trombone and violin, can also produce microtones, or notes between those available on a piano.
In music theory, the key of a piece is the group of pitches, or scale, that forms the basis of a musical composition in Western classical music, art music, and pop music.
Tonality or key: Music which uses the notes of a particular scale is said to be "in the key of" that scale or in the tonality of that scale.
A pentatonic scale is a musical scale with five notes per octave, in contrast to the heptatonic scale, which has seven notes per octave.
A secondary chord is an analytical label for a specific harmonic device that is prevalent in the tonal idiom of Western music beginning in the common practice period: the use of diatonic functions for tonicization.

A semitone, also called a half step or a half tone, is the smallest musical interval commonly used in Western tonal music, and it is considered the most dissonant when sounded harmonically. It is defined as the interval between two adjacent notes in a 12-tone scale, visually seen on a keyboard as the distance between two keys that are adjacent to each other. For example, C is adjacent to C♯; the interval between them is a semitone.
In music theory, a dominant seventh chord, or major minor seventh chord, is a seventh chord, usually built on the fifth degree of the major scale, and composed of a root, major third, perfect fifth, and minor seventh. Thus it is a major triad together with a minor seventh, denoted by the letter name of the chord root and a superscript "7". An example is the dominant seventh chord built on G, written as G7, having pitches G–B–D–F:
In the musical system of ancient Greece, genus is a term used to describe certain classes of intonations of the two movable notes within a tetrachord. The tetrachordal system was inherited by the Latin medieval theory of scales and by the modal theory of Byzantine music; it may have been one source of the later theory of the jins of Arabic music. In addition, Aristoxenus calls some patterns of rhythm "genera".

The Richter-tuned harmonica, or 10-hole harmonica or blues harp, is the most widely known type of harmonica. It is a variety of diatonic harmonica, with ten holes which offer the player 19 notes in a three-octave range.

A tremolo harmonica is a type of diatonic harmonica, distinct by having two reeds per note. In a tremolo harmonica, the two reeds are tuned slightly off a reference pitch, one slightly sharp and the other slightly flat. This gives a unique wavering or warbling sound created by the two reeds being not exactly in tune with each other and difference in their subsequent waveforms acting against one another. The degree of beating can be varied depending on the desired effect. Instruments where the beating is faster due to the reeds being farther apart from the reference pitch are called "wet", whereas those where the beating is slower and less noticeable due to the reeds being more closely in tune are called "dry".

Diatonic and chromatic are terms in music theory that are most often used to characterize scales, and are also applied to musical instruments, intervals, chords, notes, musical styles, and kinds of harmony. They are very often used as a pair, especially when applied to contrasting features of the common practice music of the period 1600–1900.
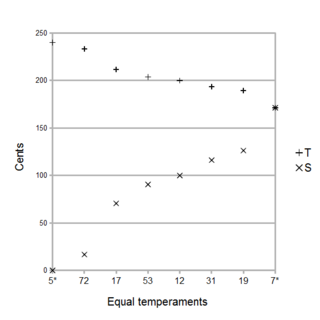
A regular diatonic tuning is any musical scale consisting of "tones" (T) and "semitones" (S) arranged in any rotation of the sequence TTSTTTS which adds up to the octave with all the T's being the same size and all the S's the being the same size, with the 'S's being smaller than the 'T's. In such a tuning, then the notes are connected together in a chain of seven fifths, all the same size which makes it a Linear temperament with the tempered fifth as a generator.
Richter tuning is a system of choosing the reeds for a diatonic wind instrument. It is named after Joseph Richter, a Bohemian instrument maker who adopted the tuning for his harmonicas in the early 19th century and is credited with inventing the blow/draw mechanism that allows the harmonica to play different notes when the air is drawn instead of blown.
Ptolemy's intense diatonic scale, also known as the Ptolemaic sequence, justly tuned major scale, Ptolemy's tense diatonic scale, or the syntonousdiatonic scale, is a tuning for the diatonic scale proposed by Ptolemy, and corresponding with modern 5-limit just intonation. While Ptolemy is famous for this version of just intonation, its important to realize this was only one of several genera of just, diatonic intonations he describes. He also describes 7-limit "soft" diatonics and an 11-limit "even" diatonic.
The jazz minor scale or ascending melodic minor scale is a derivative of the melodic minor scale, except only the ascending form of the scale is used. As the name implies, it is primarily used in jazz, although it may be found in other types of music as well. It may be derived from the major scale with a minor third, making it a synthetic scale, and features a dominant seventh chord on the fifth degree (V) like the harmonic minor scale. It can also be derived from the diatonic Dorian mode with a major seventh.
A variety of musical scales are used in traditional Japanese music. While the Chinese Shí-èr-lǜ has influenced Japanese music since the Heian period, in practice Japanese traditional music is often based on pentatonic or heptatonic scales. In some instances, harmonic minor is used, while the melodic minor is virtually unused.
References
- ↑ Asiatic Society of Japan (1891). Transactions of the Asiatic Society of Japan. Asiatic Society of Japan. pp. 346–. Retrieved 28 September 2012.