
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar and Indonesia.

India is the second most populated country in the world with nearly a fifth of the world's population. According to the 2019 revision of the World Population Prospects the population stood at 1,352,642,280.

Rajasthan is a state in northern India. It covers 342,239 square kilometres (132,139 sq mi) or 10.4 percent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern side, where it comprises most of the wide and inhospitable Thar Desert and shares a border with the Pakistani provinces of Punjab to the northwest and Sindh to the west, along the Sutlej-Indus River valley. It is bordered by five other Indian states: Punjab to the north; Haryana and Uttar Pradesh to the northeast; Madhya Pradesh to the southeast; and Gujarat to the southwest. Its geographical location is 23.3 to 30.12 North latitude and 69.30 to 78.17 East longitude, with the Tropic of Cancer passing through its southernmost tip

Jammu and Kashmir was a region formerly administered by India as a state from 1954 to 2019, constituting the southern and southeastern portion of the larger Kashmir region, which has been the subject of a dispute between India, Pakistan and China since the mid-20th century. The underlying region of this state were parts of the former princely state of Jammu and Kashmir, whose western districts, now known as Azad Kashmir, and northern territories, now known as Gilgit-Baltistan, are administered by Pakistan. The Aksai Chin region in the east, bordering Tibet, has been under Chinese control since 1962.

Languages spoken in India belong to several language families, the major ones being the Indo-Aryan languages spoken by 78.05% of Indians and the Dravidian languages spoken by 19.64% of Indians, both families together sometimes known as Indic languages. Languages spoken by the remaining 2.31% of the population belong to the Austroasiatic, Sino–Tibetan, Tai–Kadai and a few other minor language families and isolates. India has the world's fourth highest number of languages (447), after Nigeria (524), Indonesia (710) and Papua New Guinea (840). The Indian subcontinent is home to the third most spoken language in the world, Hindi-Urdu; the sixth most spoken language, Bengali; and the twelfth most spoken language, Punjabi.

Nagaland is a state in northeastern India. It is bordered by the state of Arunachal Pradesh to the north, Assam to the west, Manipur to the south and the Sagaing Region of Myanmar to the east. Its capital city is Kohima and its largest city is Dimapur. It has an area of 16,579 square kilometres (6,401 sq mi) with a population of 1,980,602 per the 2011 Census of India, making it one of India's smallest states.
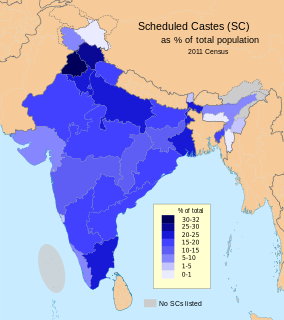
The Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs) are officially designated groups of people in India. The terms are recognised in the Constitution of India and the groups are designated in one or other of the categories. For much of the period of British rule in the Indian subcontinent, they were known as the Depressed Classes.

Torres Novas is a Portuguese municipality in the district of Santarém, in the Médio Tejo of the Centro region. The population of the municipality was approximately 36,717, with the city of Torres Novas has about 15,000 inhabitants in an area that encompasses 270 square kilometres (100 sq mi).

Faizabad district, officially Ayodhya district, is one of the 75 districts of Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. The city of Ayodhya, which is also notable for being the birth place of Hindu deity Rama, is the administrative headquarters of the district. The official name of the district was changed from Faizabad to Ayodhya in November 2018 under Uttar Pradesh chief minister Yogi Adityanath. The district occupies an area of 2,522 square kilometres (974 sq mi), and had a population of 2,470,996 in the 2011 census.

Bathinda district is in Malwa region of Punjab, India. The district encompasses an area of 3,385 square kilometers. By area, Bathinda district is the second-largest in Punjab, after Ludhiana District. It is bounded by Faridkot district and Moga district on the north, Mukatsar district on the west, Barnala and Mansa districts on the east, and the state of Haryana on the south. Bathinda is cotton producing belt of Punjab.
The decennial Census of India has been conducted 15 times, as of 2011. While it has been undertaken every 10 years, beginning in 1872 under British Viceroy Lord Mayo, the first complete census was taken in 1881. Post 1949, it has been conducted by the Registrar General and Census Commissioner of India under the Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India. All the censuses since 1951 were conducted under the 1948 Census of India Act. The last census was held in 2011, whilst the next will be held in 2021. But it is postponed due to the covid-19 pandemic.

The 15th Indian Census was conducted in two phases, house listing and population enumeration. The House listing phase began on 1 April 2010 and involved the collection of information about all buildings. Information for National Population Register (NPR) was also collected in the first phase, which will be used to issue a 12-digit unique identification number to all registered Indian residents by Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI). The second population enumeration phase was conducted between 9 and 28 February 2011. Census has been conducted in India since 1872 and 2011 marks the first time biometric information was collected. According to the provisional reports released on 31 March 2011, the Indian population increased to 1.21 billion with a decadal growth of 17.70%. Adult literacy rate increased to 74.04% with a decadal growth of 9.21%. The motto of the census was 'Our Census, Our future'.
Sankrail is a community development block that forms an administrative division in Howrah Sadar subdivision of Howrah district in the Indian state of West Bengal.

Uluberia II is a community development block that forms an administrative division in Uluberia subdivision of Howrah district in the Indian state of West Bengal.

The Cave of Aroeira is an archaeological and paleoanthropological site in the Portuguese Estremadura Limestone Massif. The cave is located in the village of Almonda, in the civil parish of Zibreira, in the municipality of Torres Novas in the district of Santarém. The cave contained stones from the Paleolithic Acheulean culture, and the skull of Homo heidelbergensis, circa 400,000 years old. The discovery of Aroeira 3 was announced in spring 2017 - the earliest human trace in Portugal.

Jammu and Kashmir is a region administered by India as a union territory and consisting of the southern portion of the larger Kashmir region, which has been the subject of a dispute between India and Pakistan since 1947, and between India and China since 1962. The Line of Control separates Jammu and Kashmir from the Pakistani-administered territories of Azad Kashmir and Gilgit-Baltistan in the west and north. It lies to the north of the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab and to the west of Ladakh, which is also subject to the dispute as a part of Kashmir, and administered by India as a union territory.














