The Oligocene is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period and extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present. As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the epoch are slightly uncertain. The name Oligocene was coined in 1854 by the German paleontologist Heinrich Ernst Beyrich; the name comes from the Ancient Greek ὀλίγος and καινός, and refers to the sparsity of extant forms of molluscs. The Oligocene is preceded by the Eocene Epoch and is followed by the Miocene Epoch. The Oligocene is the third and final epoch of the Paleogene Period.

Prineville is a city in and the seat of Crook County, Oregon, United States. It was named for the first merchant located in the present location, Barney Prine. The population was 9,253 at the 2010 census.

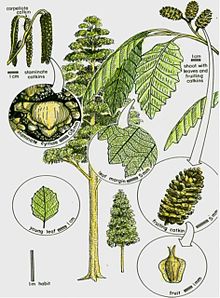
Nothofagus, also known as the southern beeches, is a genus of 43 species of trees and shrubs native to the Southern Hemisphere in southern South America and Australasia. The species are ecological dominants in many temperate forests in these regions. Some species are reportedly naturalised in Germany and Great Britain. The genus has a rich fossil record of leaves, cupules, and pollen, with fossils extending into the late Cretaceous period and occurring in Australia, New Zealand, Antarctica, and South America. In the past, they were included in the family Fagaceae, but genetic tests revealed them to be genetically distinct, and they are now included in their own family, the Nothofagaceae.

Miohippus was a genus of prehistoric horse existing longer than most Equidae. Miohippus lived in what is now North America during the late Eocene to late Oligocene. Miohippus was a horse of the Oligocene. According to the Florida Museum of Natural History, Othniel Charles Marsh first believed Miohippus lived during the Miocene and thus named the genus using this incorrect conclusion. More recent research provides evidence that Miohippus actually lived during the Paleogene period.

Torreya is a genus of conifers comprising six or seven species placed the family Taxaceae, though sometimes formerly placed in Cephalotaxaceae. Four species are native to eastern Asia; the other two are native to North America. They are small to medium-sized evergreen trees reaching 5–20 m, rarely 25 m, tall. Common names include nutmeg yew.

Daphoenus is an extinct genus of bear dogs. Daphoenus inhabited North America from the Middle Eocene to the Middle Miocene, 37.2—16.0 Mya, existing for approximately 21 million years .

The Oregon Coast Range, often called simply the Coast Range and sometimes the Pacific Coast Range, is a mountain range, in the Pacific Coast Ranges physiographic region, in the U.S. state of Oregon along the Pacific Ocean. This north-south running range extends over 200 miles (320 km) from the Columbia River in the north on the border of Oregon and Washington, south to the middle fork of the Coquille River. It is 30 to 60 miles wide and averages around 1,500 feet (460 m) in elevation above sea level. The coast range has three main sections, a Northern, Central, and Southern.
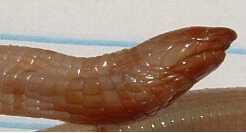
Rhineuridae is a family of amphisbaenians that includes one living genus and species, Rhineura floridana, as well as many extinct species belonging to both Rhineura and several extinct genera. The living R. floridana is found only in Florida no further north than the panhandle, but extinct species ranged across North America, some occurring as far west as Oregon. The family has a fossil record stretching back 60 million years to the Paleocene and was most diverse in the continental interior during the Eocene and Oligocene.
Douglas Ralph Emlong was an amateur fossil collector from the Oregon Coast in the northwestern United States. His collections contributed to the discovery and description of numerous extinct marine mammal species, many of which are ancestral to extant groups. Described as an 'indefatigable' fossil collector with 'Promethian prowess in discovery of unprecedented vertebrate fossils', he contributed substantially to the field from the age of fourteen. The ancestral pinniped Enaliarctos emlongi was named in his honor by Annalisa Berta in 1991.

Water-penny beetles are a family of 272 species of aquatic beetles found on all continents except Antarctica, in both tropical and temperate areas. The young, which live in water, resemble tiny pennies. The larvae feed – usually nocturnally – on algae on rock surfaces. The presence of water-penny larvae in a stream can be used as a test for the quality of the water, as they are pollution-sensitive. They cannot live in habitats where rocks acquire a thick layer of algae, fungi, or inorganic sediment. Therefore, their presence along with other diverse phyla signifies good-quality water. They are around 6 to 10 millimeters in length.
Archaeohippus is an extinct three toed member of the family Equidae known from fossils of early Oligocene to middle Miocene age. The genus is noted for several distinct skeletal features. The skull possesses deeply pocketed fossa in a notably long preorbital region. The genus is considered an example of phyletic dwarfism with adults estimated at being on average 20kg in weight. This is in contrast to the most common equid of the period, Miohippus. Characters of the teeth show a mix of both primitive and advanced traits. The advanced traits are very similar to those shown in the genus Parahippus. The noted similarities of Archaeohippus and Parahippus show them to be descended from a common ancestor and are considered sister species.

Borophagini is a clade or tribe of the subfamily Borophaginae. This is an extinct group of terrestrial canids that were endemic and widespread throughout North America and Central America which lived during the Geringian stage of the Oligocene epoch to the Zanclean age of the Early Pliocene living 30.8—3.6 Mya existing approximately 27.2 million years .
Acer ashwilli is an extinct maple species in the family Sapindaceae described from a group of fossil leaves and samaras. The species is solely known from the Early Oligocene sediments exposed in central Oregon, USA. It is one of several extinct species belonging to the living section Ginnala.
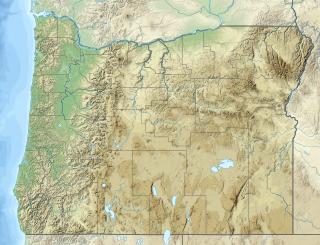
The Crooked River caldera is a large and ancient volcano that straddles three central Oregon counties. The diameter of the caldera is about 41 km x 27 km and is notable for the welded tuff present at Gray Butte, Smith Rock, Powell Buttes, Grizzly Mountain and Barnes Butte. The volcano is considered extinct and last erupted about 29.5 Ma.

Paleontology in Oregon refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Oregon. Oregon's geologic record extends back approximately 400 million years ago to the Devonian period, before which time the state's landmass was likely submerged under water. Sediment records show that Oregon remained mostly submerged until the Paleocene period. The state's earliest fossil record includes plants, corals, and conodonts. Oregon was covered by seaways and volcanic islands during the Mesozoic era. Fossils from this period include marine plants, invertebrates, ichthyosaurs, pterosaurs, and traces such as invertebrate burrows. During the Cenozoic, Oregon's climate gradually cooled and eventually yielded the environments now found in the state. The era's fossils include marine and terrestrial plants, invertebrates, fish, amphibians, turtles, birds, mammals, and traces such as eggs and animal tracks.
Dyticonastis is an extinct genus of amphisbaenians, or worm lizards, that includes a single species, Dyticonastis rensbergeri, that lived during the late Oligocene and early Miocene in what is now Oregon. Fossils of the species come from the John Day Formation. It belongs to Rhineuridae, a family that includes many other extinct North American amphisbaenians but only one living species, Rhineura floridana, from Florida. Dyticonastis rensbergeri occurs the farthest west of all rhineurid species. Like all rhineurids, Dyticonastis has a shovel-like snout adapted for burrowing underground, but it differs from most other members of the group in having a relatively shallow angle to its snout wedge and in having a widened snout tip. The only other rhineurids that share these features are species of the genus Spathorhynchus, which lived from the Middle Eocene to the Early Oligocene in what is now Wyoming. A 2007, phylogenetic analysis of amphisbaenians found that Dyticonastis and Spathorhynchus are each other's closest relatives, suggesting that both taxa may have evolved through vicariant speciation; the growth of the Rocky Mountains during the earliest stages of the Laramide orogeny in the early Paleogene would have separated North American rhineurids into eastern and western populations, with the western population producing Dyticonastis and Spathorhynchus.
Spathorhynchus is an extinct genus of amphisbaenians or worm lizards that existed from the Middle Eocene to the Early Oligocene in what is now Wyoming. It includes two species, the type species S. fossorium, named in 1973 from the Middle Eocene Bridger and Wind River Formations, and the species S. natronicus, named in 1977 from the Lower Oligocene White River Formation. Spathorhynchus belongs to the family Rhineuridae, which includes many other extinct species that ranged across North America at various times in the Cenozoic but only has one surviving member, Rhineura floridana, from Florida. Spathorhynchus differs from all other rhineurids except Dyticonastis from the Late Oligocene-Early Miocene of Oregon in having a slightly widened, spatula-shaped snout tip with a low angle of about 30 degrees. The two taxa may be closely related, having evolved in isolation in western North America after the formation of the Rocky Mountains separated them from rhineurids further east.

The Alsea Formation is a geologic formation in Oregon. It preserves fossils dating back to the Rupelian stage of the Oligocene period.

Meliosma beusekomii is an extinct species of Meliosma from the middle Eocene Clarno Formation of central Oregon