
Zingiberaceae or the ginger family is a family of flowering plants made up of about 50 genera with a total of about 1600 known species of aromatic perennial herbs with creeping horizontal or tuberous rhizomes distributed throughout tropical Africa, Asia, and the Americas. Members of the family Zingiberaceae including turmeric, ginger, Javanese ginger, and galangal have been used for centuries in traditional medicine. Preclinical studies of Zingiberaceae extracts have shown analgesic properties.

Galangal is a common name for several tropical rhizomatous spices.

Alpinia is a genus of flowering plants in the ginger family, Zingiberaceae. It is named for Prospero Alpini, a 17th-century Italian botanist who specialized in exotic plants. Species are native to Asia, Australia, and the Pacific Islands, where they occur in tropical and subtropical climates. Several species are cultivated as ornamental plants. Species of the genus are known generally as shell ginger.

Alpinia purpurata, red ginger, also called ostrich plume and pink cone ginger, are native Malaysian plants with showy flowers on long brightly colored red bracts. They look like the bloom, but the true flower is the small white flower on top.

Amomum is a genus of plants native to China, the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia, New Guinea, and Queensland. It includes several species of cardamom, especially black cardamom. Plants of this genus are remarkable for their pungency and aromatic properties.

Alpinia nutans, the shellflower, or dwarf cardamom, is a Southeast Asian plant of the ginger family (Zingiberaceae), and is a medicinal plant used to control hypertension, as diuretic, antifungal, and antiulcer. In Japan it is used as food preservative.

Alpinia zerumbet, commonly known as shell ginger, is a perennial species of ginger native to East Asia. They can grow up to 8 to 10 ft tall and bear colorful funnel-shaped flowers. They are grown as ornamentals and their leaves are used in cuisine and traditional medicine. They are also sometimes known as the pink porcelain lily, variegated ginger or butterfly ginger.

Etlingera elatior is a species of herbaceous perennial plant. Botanical synonyms include Nicolaia elatior, Phaeomeria magnifica, Nicolaia speciosa, Phaeomeria speciosa, Alpinia elatior, and Alpinia magnifica.

Alpinia galanga, a plant in the ginger family, bears a rhizome used largely as an herb in Unani medicine and as a spice in Arab cuisine and Southeast Asian cookery. It is one of four plants known as "galangal", and is differentiated from the others with the common names lengkuas, greater galangal, and blue ginger.
Shellflower may refer to:

Alpinia officinarum, known as lesser galangal, is a plant in the ginger family, cultivated in Southeast Asia. It originated in China, where its name ultimately derives. It can grow 1.5 to 2 m high, with long leaves and reddish-white flowers. The rhizomes, known as galangal, are valued for their sweet spicy flavor and aromatic scent. These are used throughout Asia in curries and perfumes, and were previously used widely in Europe. They are also used as an herbal remedy.

Kaempferia galanga, commonly known as kencur, aromatic ginger, sand ginger, cutcherry, or resurrection lily, is a monocotyledonous plant in the ginger family, and one of four plants called galangal. It is found primarily in open areas in Indonesia, southern China, Taiwan, Cambodia, and India, but is also widely cultivated throughout Southeast Asia.

Alpinia caerulea, commonly known as native ginger or in the case of the subspecies from the Atherton Tableland red back ginger, is an understorey perennial herb to 3 m, growing under rainforest, gallery forest and wet sclerophyll forest canopy in eastern Australia.
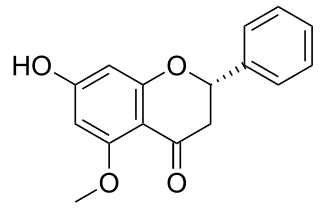
Alpinetin is a phytochemical isolated from a variety of plants including those of the genus Alpinia. It is going through tests to see if it is a vasorelaxant.
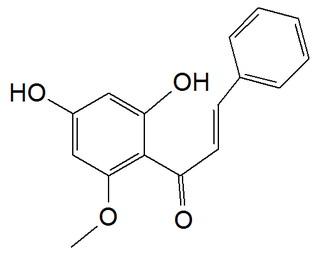
Cardamomin is a chalconoid that has been isolated from several plants including Alpinia katsumadai and Alpinia conchigera. It has received growing attention from the scientific community due to the expectations toward its benefits to human health.
Alpinia conchigera, the lesser alpinia, is a plant species in the genus Alpinia.
Alpinia nigra is a medium-sized herb belonging to the ginger family. The rhizome is well known in many Asian cultures as a medicinal and culinary item. In many Asian tribal communities it is a part of the diet along with rice.

Hellenia is a genus of plants in the Costaceae described as a genus with this name in 1791. It is native to Southeast Asia, southern China, the Indian Subcontinent, New Guinea, and Queensland. The type species was "H. grandiflora" Retz., which is a synonym of Hellenia speciosa.
Alpinia rafflesiana, commonly known in Malaysia as Tepus Telor, is a perennial herb belonging to the family Zingiberaceae. It is native to peninsular Malaysia.
Rosemary Margaret Smith (1933–2004) was a Scottish botanist and illustrator who specialized in the taxonomy of the Zingiberaceae, or ginger family. Many of the species she classified and identified as being placed into improper genera were found in Asian countries, especially in the isolated island of Borneo.













