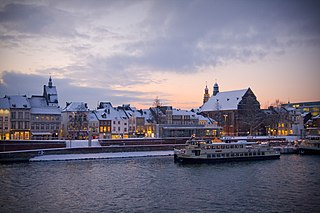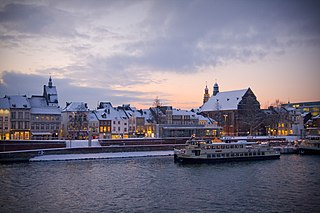
Maastricht is a city and a municipality in the southeastern Netherlands. It is the capital and largest city of the province of Limburg. Maastricht is located on both sides of the Meuse, at the point where the Jeker joins it. Mount Saint Peter (Sint-Pietersberg) is largely situated within the city's municipal borders. Maastricht is adjacent to the border with Belgium and is part of the Meuse-Rhine Euroregion, an international metropolis with a population of about 3.9 million, which includes the nearby German and Belgian cities of Aachen, Liège and Hasselt.

A torc, also spelled torq or torque, is a large rigid or stiff neck ring in metal, made either as a single piece or from strands twisted together. The great majority are open at the front, although some have hook and ring closures and a few have mortice and tenon locking catches to close them. Many seem designed for near-permanent wear and would have been difficult to remove.
Mel Fisher was an American treasure hunter best known for finding the 1622 wreck of the Nuestra Señora de Atocha in Florida waters.

The stater was an ancient coin used in various regions of Greece. The term is also used for similar coins, imitating Greek staters, minted elsewhere in ancient Europe.

A treasure trove is an amount of money or coin, gold, silver, plate, or bullion found hidden underground or in places such as cellars or attics, where the treasure seems old enough for it to be presumed that the true owner is dead and the heirs undiscoverable. An archaeological find of treasure trove is known as a hoard. The legal definition of what constitutes treasure trove and its treatment under law vary considerably from country to country, and from era to era.

The guilder or florin was the currency of the Netherlands from 1434 until 2002, when it was replaced by the euro.
The archaeology of Northern Europe studies the prehistory of Scandinavia and the adjacent North European Plain, roughly corresponding to the territories of modern Sweden, Norway, Denmark, northern Germany, Poland and the Netherlands.


A sycee or yuanbao was a type of gold and silver ingot currency used in imperial China from its founding under the Qin dynasty until the fall of the Qing in the 20th century. Sycee were not made by a central bank or mint but by individual goldsmiths or silversmiths for local exchange; consequently, the shape and amount of extra detail on each ingot were highly variable. Square and oval shapes were common, but boat, flower, tortoise and others are known. Their value—like the value of the various silver coins and little pieces of silver in circulation at the end of the Qing dynasty—was determined by experienced moneyhandlers, who estimated the appropriate discount based on the purity of the silver and evaluated the weight in taels and the progressive decimal subdivisions of the tael.

Tillya tepe, Tillia tepe or Tillā tapa is an archaeological site in the northern Afghanistan province of Jowzjan near Sheberghan, excavated in 1978 by a Soviet-Afghan team led by the Soviet archaeologist Viktor Sarianidi. The hoard found there is often known as the Bactrian gold.
The year 2008 in archaeology

The Hallaton Treasure, the largest hoard of British Iron Age coins, was discovered in 2000 near Hallaton in southeast Leicestershire, England, by volunteers from the Hallaton Fieldwork Group. The initial find was made by Ken Wallace on 19 November 2000, when he found about 130 coins with a metal detector.

The Treasury of the Basilica of Saint Servatius is a museum of religious art and artifacts inside the Basilica of Saint Servatius in Maastricht, Netherlands.

The United World College Maastricht (UWCM) is a United World College located in Maastricht, the Netherlands. The school was established in 2009 and moved to a new campus in the Maastricht neighbourhood of Amby in 2013.

The prehistory of the Netherlands was heavily influenced by the region's constantly changing, low-lying geography. Inhabited by humans for at least 37,000 years, the landscape underwent significant transformations, from the last ice age's tundra climate to the emergence of various Paleolithic groups. The region witnessed the development of the Swifterbant culture, which was closely linked to rivers and open water, while the Mesolithic era saw the creation of the world's oldest recovered canoe, the Pesse canoe. The arrival of agriculture around 5000–4000 BC marked the beginning of the Linear Pottery culture, which gradually transformed prehistoric communities.
The following is a timeline of the history of the municipality of Maastricht, Netherlands.