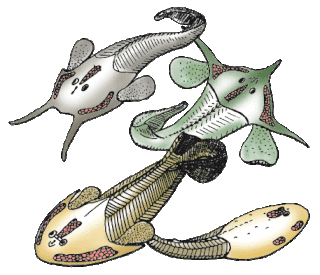
Ostracoderms are the armored jawless fish of the Paleozoic Era. The term does not often appear in classifications today because it is paraphyletic and thus does not correspond to one evolutionary lineage. However, the term is still used as an informal way of loosely grouping together the armored jawless fishes.

Heterostraci is an extinct subclass of pteraspidomorph jawless vertebrate that lived primarily in marine and estuary environments. Heterostraci existed from the mid-Ordovician to the conclusion of the Devonian.

Lepidaspis serrata is an extinct heterostracan jawless fish from Early Devonian Canada. Its scientific name refers to the fact that the armor is composed of hundreds of tiny scales with serrated edges.

Pteraspis is an extinct genus of pteraspidid heterostracan agnathan vertebrate that lived from the Lochkovian to Eifelian epochs of the Devonian period in what is now Brazil, Britain, Ukraine and Belgium.

Drepanaspis is an extinct genus of primitive jawless fish from Early Devonian marine strata of Europe. D. gemuendenensis, of the Hunsrück lagerstätte is the best known, and most thoroughly studied species, as it is known from several articulated specimens.

Astraspida, or astraspids, are a small group of extinct armored jawless vertebrates, which lived in the Middle Ordovician in North America. They are placed among the Pteraspidomorphi because of the large dorsal and ventral shield of their head armor. They are represented by a single genus, Astraspis, including possibly two species, A. desiderata and A. splendens but their remains are fairly abundant in Ordovician sandstones of the USA and Canada (Quebec). The head armor of Astraspis is rather massive, with a series of ten gill openings lining the margin of the dorsal shield, and laterally placed eyes. The dorsal shield is ribbed by strong longitudinal crests, and the tail is covered with large, diamond-shaped scales. They are often grouped together with the Arandaspidida.

Cyathaspis is the type genus of the heterostracan order Cyathaspidiformes. Fossils are found in late Silurian strata in the Cunningham Creek Formation, New Brunswick, Canada and Europe, especially in the Downton Castle Sandstone of Great Britain and Gotland, Sweden. The living animal would have looked superficially like a tadpole, albeit covered in bony plates composed of the tissue aspidine, which is unique to heterostracan armor.

Pteraspidiformes is an extinct order of heterostracan agnathan vertebrates known from extensive fossil remains primarily from Early Devonian strata of Europe and North America, and from Upper Silurian Canada.

Cyathaspidiformes is an extinct order of heterostracan vertebrates known from extensive fossil remains primarily from Silurian to Early Devonian strata of Europe, and North America, and from Early Devonian marine strata of Siberia.

Amphiaspidida is a taxon of extinct cyathaspidid heterostracan agnathans whose fossils are restricted to Lower Devonian marine strata of Siberia near the Taimyr Peninsula. Some authorities treat it as a suborder of Cyathaspidiformes, while others treat it as an order in its own right as "Amphiaspidiformes." In life, they are thought to be benthic animals that lived most of their lives mostly buried in the sediment of a series of hypersaline lagoons. Amphiaspids are easily distinguished from other heterostracans in that all of the plates of the cephalothorax armor are fused into a single, muff-like unit, so that the forebody of the living animal would have looked like a potpie or a hot waterbottle with a pair of small, or degenerated eyes sometimes flanked by preorbital openings, a pair of branchial openings for exhaling, and a simple, slit-like, or tube-like mouth.

Amphiaspidoidei is a taxon of extinct amphiaspidid heterostracan agnathans whose fossils are restricted to Lower Devonian marine strata of Siberia near the Taimyr Peninsula. In life, the amphiaspidids of Amphiaspidoidei are thought to be benthic animals that lived most of their lives mostly buried in the sediment of a series of hypersaline lagoons. Amphiaspids are easily distinguished from other heterostracans in that all of the plates of the cephalothorax armor are fused into a single, muff-like unit, so that the forebody of the living animal would have looked like a potpie or a hot waterbottle with a pair of small, or degenerated eyes flanked by preorbital openings, a pair of branchial openings for exhaling, and a simple, slit-like mouth.

Hibernaspidoidei is a taxon of extinct amphiaspidid heterostracan agnathans whose fossils are restricted to Lower Devonian marine strata of Siberia near the Taimyr Peninsula. In life, hibernaspid amphiaspidids are thought to be benthic animals that lived most of their lives mostly buried in the sediment of a series of hypersaline lagoons. All amphiaspids are easily distinguished from other heterostracans in that all of the plates of the cephalothorax armor are fused into a single, muff-like unit, so that the forebody of the living animal would have looked like a potpie or a hot waterbottle with a pair of small, or degenerated eyes, a pair of branchial openings for exhaling, and, in the case of hibernaspids, a simple, slit-like mouth at the anterior end of a tube-like head.
Siberiaspidoidei is a taxon of extinct amphiaspidid heterostracan agnathans whose fossils are restricted to Lower Devonian marine strata of Siberia near the Taimyr Peninsula. In life, siberiaspids are thought to be benthic animals that lived most of their lives mostly buried in the sediment of a series of hypersaline lagoons. As with all amphiaspids, siberiaspids are easily distinguished from other heterostracans in that all of the plates of the cephalothorax armor are fused into a single, muff-like unit, so that the forebody of the living animal would have looked like a flattened potpie or a hot waterbottle with a pair of small, or degenerated eyes sometimes flanked by preorbital openings, a pair of branchial openings for exhaling, and a simple, slit-like, or tube-like mouth.

Amphiaspis argo is the type species of the cyathaspidid taxon Amphiaspidida, and of the family Amphiaspididae. Its fossils are restricted to early Emsian-aged marine strata of the Taimyr Peninsula, Early Devonian Siberia. A. argo, as with all other amphiaspidids, is thought to have been a benthic filter feeder that lived on top of, or buried just below the surface of the substrate of hypersaline lagoon-bottoms.
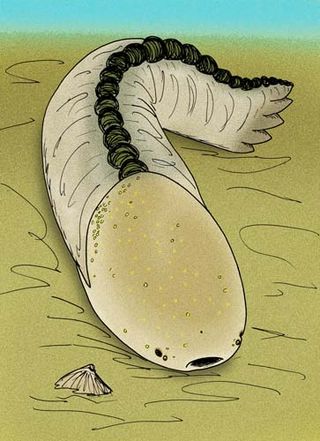
Amphoraspis stellata is an amphiaspidid heterostracan in the family Amphiaspididae. Its fossils are restricted to early Devonian-aged marine strata of the Taimyr Peninsula, Siberia. A. stellata, as with all other amphiaspidids, is thought to have been a benthic filter feeder that lived on top of, or buried just below the surface of the substrate of hypersaline lagoon-bottoms.
Edaphaspis bystrowi is an extinct amphiaspidid cyathaspidid heterostracan. Its fossils are restricted to early Devonian-aged marine strata of the Taimyr Peninsula, Early Devonian Siberia. E. bystrowi, as with all other amphiaspidids, is thought to have been a benthic filter feeder that lived on top of, or buried just below the surface of the substrate of hypersaline lagoon-bottoms. It is the only representative of the family Edaphaspididae.

Gabreyaspididae is a family of extinct amphiaspidid heterostracan agnathans whose fossils are restricted to Lower Devonian marine strata of Siberia near the Taimyr Peninsula. In life, all amphiaspidids are thought to be benthic animals that lived most of their lives mostly buried in the sediment of a series of hypersaline lagoons. Amphiaspids are easily distinguished from other heterostracans in that all of the plates of the cephalothoracic armor are fused into a single, muff-like unit, so that the forebody of the living animal would have looked, in the case of gabreyaspidids, vaguely like a horseshoe crab with a pair of small, or degenerated eyes, with each flanked by a preorbital opening, and a simple, slit-like mouth positioned slightly ventrally.

Olbiaspididae is a family of extinct amphiaspidid heterostracan agnathans whose fossils are restricted to Lower Devonian marine strata of Siberia near the Taimyr Peninsula. In life, all amphiaspidids are thought to be benthic animals that lived most of their lives mostly buried in the sediment of a series of hypersaline lagoons. Amphiaspids are easily distinguished from other heterostracans in that all of the plates of the cephalothoracic armor are fused into a single, muff-like unit, so that the forebody of the living animal would have looked, in the case of olbiaspidids, vaguely like a hot water bottle with a pair of small, or degenerated eyes, with each flanked by a preorbital opening, and a simple, slit-like mouth positioned at the anteriormost portion of the cephalothoracic armor.

Hibernaspis is a genus of extinct amphiaspidid heterostracan agnathans whose fossils are restricted to Lower Devonian marine strata of Siberia near the Taimyr Peninsula. In life, species of Hibernaspis were thought to be benthic animals that lived most of their lives mostly buried in the sediment of a series of hypersaline lagoons. All amphiaspids are easily distinguished from other heterostracans in that all of the plates of the cephalothorax armor are fused into a single, muff-like unit, so that, in the case of Hibernaspis, the forebody of the living animal would have looked like a large guitar pic with serrated edges, with a pair of tiny, degenerated eyes, a pair of branchial openings for exhaling, and a simple, slit-like mouth at the anterior end.

Eglonaspididae is a family of extinct amphiaspidid heterostracan agnathans whose fossils are restricted to Lower Devonian marine strata of Siberia near the Taimyr Peninsula. In life, all of the amphiaspidids are thought to be benthic animals that lived most of their lives mostly buried in the sediment of a series of hypersaline lagoons. Amphiaspids are easily distinguished from other heterostracans in that all of the plates of the cephalothoracic armor are fused into a single, muff-like unit, so that the forebody of the living animal would have looked, in the case of elgonaspidids, very much like a hot water bottle with or without a pair of small, degenerated eyes and a simple, slit-like mouth positioned at the anteriormost portion of the cephalothoracic armor.














